Contents
page
Introduction ………………………………………………………………. 3
I. Theoretical part…………………………………………………………… 4
1.1 Definitions "teacher" and "pupil"
1.2 The role of teacher and his activity
1.3 Relationships between teachers and pupils. The basic problems and
difficulties
II.Practical part……………………………………………………………….. 6
2.1 Purposes and aims
2.2 Methods of research
2.3 Results of research……………………………………………………………………………
Conclusion …………………………………………………………………….. 12
List of literature ………………………………………………………………… 13
Introduction
Question of forming relationships between teachers and pupils has always been a very interesting and actual question for teachers, psychologists, sociologists and the public. Pupils often say that many teachers don't understand them, don't consider their interests. A lot of children mark bias of teachers.
Teachers think that problems are because of laziness of pupils, their unwillingness to listen and think at the lessons, complexity of separate sections of the curriculum, default of homework, the weak help and a lack of control from parents and many other reasons.
In this work we will try to place all points over «i» in mutual relations between teachers and pupils. And the purpose of our work is to investigate relationships between pedagogical collective and pupils of school №1.
The object of the research work is relationships between teachers and pupils.
The subject of the research work is interpersonal relations between teachers and pupils.
Theoretical part
1.1 Definitions "teacher" and "pupil"
It is possible to find various definitions of "teacher" in references.
• Teacher - the expert who is carrying out training, education and formation at comprehensive schools of the Russian Federation. /The encyclopedic dictionary/
• Teacher - the person who is engaged in teaching of any subject in lowest and high school, the school worker. /The explanatory dictionary by Ushakov/
Definition of the pupil:
• Pupil - the person who is studying at high school, technical training college
• Pupil - the follower of any doctrine
Absence of an active position and desire to study is one of problems in relationships between teachers and pupils.
1.2 The role of teacher and his activity
The teacher is a person pupils imitate or want to be similar. What abilities should have a teacher in order not only to win attention of the pupil, but also to learn them? N.D.Levitov allocates the following basic pedagogical abilities, which are necessary to each teacher. They are:
• Ability to transfer knowledge to children in the short and interesting form;
• Ability to understand pupils, based on observation;
• An independent and creative way of thinking;
• Resource or fast and exact orientation in any situation.
1.3 Relationships between teachers and pupils. The basic problems and difficulties.
The problem of mutual relationships between teachers and pupils at the teenage problematical period rises extraordinary and sharply. According to teachers and pupils, there can be following difficulties:
1) Absence of mutual understanding and human affinity with teachers; Pupils and teachers should be close to each other.
2) Difficulties in finding of "common language";
3) Bias of teachers to pupils;
3) Disrespecting to each other;
4) Falling authority of teacher as a significant person;
5) Low level of teachers’ and students’ communication skills.
Training and developing is one of the central problems of pedagogical psychology. Among statements of pupils there is also an opinion that teachers are too assured of their own infallibility and thy never recognize the errors.
II . Practical part
2.1 Purposes and aims:
1. To reveal the basic problem zones in relationships in a «teacher-pupil» system
2. To make questions for two different questionnaires
3. To interrogate teachers and pupils of school number 1
4. To analyze results and draw conclusions
2.2 Methods of research
Within the limits of research “Problems in relationships between teachers and pupils” we have interrogated 18 ninth-graders and the same number of teachers of our school. As a main method we have chosen questioning. The pupils were asked the following questions:
What qualities should teachers have?
Can you represent yourself in a role of a teacher?
What do you think about teacher who overstates marks to other students? What about you?
Are you a favorite one at any teacher?
Which part of the lesson is the most pleasant for you best of all?
What lessons do you like best of all?
The questionnaire for teachers includes such questions, as:
Is it pedagogically correct to choose «favorites» from pupils?
Is it admissible to show hostility to pupils?
Do you think to put the two is an extreme measure or a usual business?
What do you think about school uniform? What kind of clothes pupil should come to school in?
Do you think a subject you teach is the major for pupils?
Do you think you are a good teacher?
Describe an "ideal" pupil. Name some personalities.
How do you see school in future?
2.3 Results
From the point of view of pupils, the main qualities of the teacher are professionalism (78 % of pupils have noted this quality), the sense of humour (22 %) and kindness (28 %).
The most part of interrogated 9th-formers (61 %) cannot imagine themselves as a teacher, and only 39 % are ready to try to imagine themselves in their places.
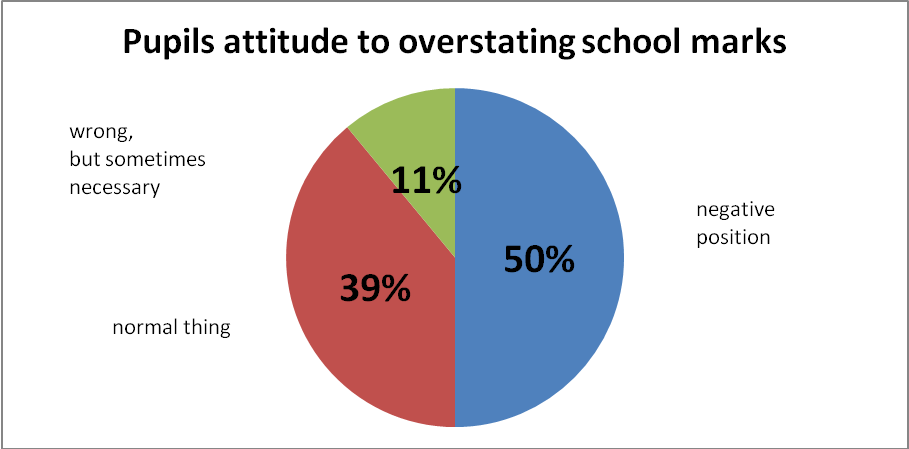
On the Diagram №1 the position of ninth-graders to overstating marks by teachers are presented. 50 % of pupils have negative position to this question, 39 % are indifferent to the given phenomenon. At the same time, as 11 % consider it is wrong, but sometimes it is necessary.
Diagram № 1
62 % of interrogated students believe that they are not favorite ones at any teacher, 33 % do not know, 5 % (only one person) supposes that he/she is the favorite pupil the class.
Also we have suggested pupils to choose and specify a part of a lesson which is pleasant to them most of all. Following answers have been received:
* an explanation of a new material,
* the end of a lesson,
* the period before the beginning of tasks (especially controlled and checked tasks ),
* differently, it depends on the lesson / teacher and the theme.
The given answers testify that pupils are pleasant to learn something new when there is an explanation of a new unfamiliar material. Many answers say that ninth-graders prefer such activities as the beginning or end of a lesson when the lesson is getting out and pupils have a possibility to have a rest.
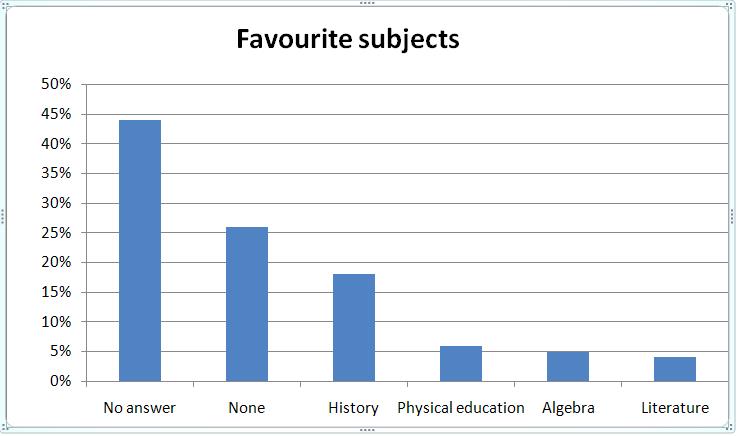
Frequently, the relation to the teacher is connected with the relation to a subject, therefore the particular interest has presented in the rating of school subjects, which you can see on Diagram №2. It is necessary to notice that 44 % did not give the answer to this question at all. And 26 % of pupils have not got a favorite subject. It testifies that interests of ninth-graders are not generated. According to a rating, English is on top. Maybe, high interest to the subject or to a teacher can dominate. Unfortunately, but their educational interests are not formed yet. Diagram № 2
In the second part of practical work we are going to tell you about those results which have been received at questioning of teachers.
All teachers don’t consider correct to allocate any pupils on the basis of personal liking, and only some of them in the questionnaires wrote that they’ve got some pupils they love best of all. But they try not to show their sympathy to public.
100% of the interrogated teachers believe it is inadmissible to show hostility to pupils.
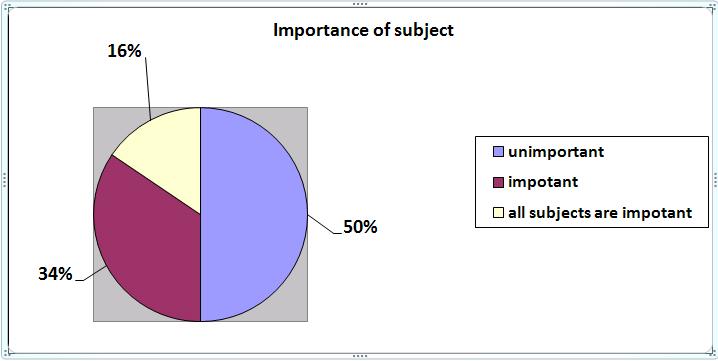
Apparently, on the Diagram №3, half of teachers think putting bad marks is a usual process at school. 34 % regard marks «2» as an extreme measure, 16 % suppose also that it depends on a situation at the lesson and could be very individual.
Diagram № 3

School uniform, its necessity for educational institution, is one of a very sharp and discussed question at school. It is necessary to notice that all teachers at our school positively concern a school uniform. At the same time pupils don’t share teachers’ opinions. Each of them wants to safe their individuality and don’t want to be the same as others. So they prefer to put on different clothes to school.
It is often possible to face opinion that each teacher considers the subject he / she as the main one among all the school subjects. We suggest looking variants of teachers’ answers on the next Diagram.
Diagram № 4
On a question, whether teachers consider they are good teachers, following results have been received: 50 % were at a loss with the answer, 34 % - do not think so, 16 % agree to be good teachers.
Within the limits of research work it was important to make "an ideal" portrait of the pupil which, according to teachers, includes following characteristics:
- Non- indifferent to people and school,
- Should carry out teacher’s demands and other duties,
- Responsible, intelligent, cultured, self-sufficient.
Nowadays when the education system worries a considerable quantity of reforms and transformations, it is very important to present future school. According to teachers, the future school is:
- A school with a new modern infrastructure,
- A convenient school with an atmosphere of comfort for teachers, pupils and parents,
- A school which is loved by people, who go there,
- School where pupils have such subjects as a management or business.
Conclusion
The object of the research work is relationships between teachers and pupils.
The subject of the research work is interpersonal relations between teachers and pupils.
In our work we used the following method: the method of questioning.
Having finished our survey we can note this work was difficult but very useful and interesting for us. We could ask and answer the questions about actual problem as relationships between teachers and pupils. This activity is quite new for us and has a very definite practical meaning.
It’s very interesting to think and understand people who play a great role in the life of each generation, especially in our lives. First in our life we have a chance to make a real statistics and, may be, to have a close and frank conversation with some teachers from our school.
In conclusion, we can say there are different reasons of problems between people who teach and study at school. The most famous are:
Misunderstanding ‘cause of different opinion and point of view,
The conflict of the generations (between children and adults),
The protest again the teachers and their requirements,
Subjective estimation.
When we face the problems we should find a constructive decision and try to solve the problems. We have to make tolerant and friendly relationships between teachers, pupils and their parents.
School is a place where teachers work and pupils study, so it must be a place of childhood which stays in our memory for all our live!
List of Literature
1. Pedagogicheskaya psikhologiya. Zimnyaya I.A. M.: Logos, 2004 - 384 s.
2. Mandel' B. R. Pedagogicheskaya psikhologiya: Uchebnoe posobie / B.R. Mandel'. - M.: KURS: NITs Infra-M, 2012. - 368 s
3. Mandel' B. R. Pedagogicheskaja psihologija: otvety na trudnye voprosy. Izdatel'stvo: Feniks, 2007 g.,469 s.
4. Harlamov I. F. Pedagogika. – M.: Gardariki, 1999. – 520 s.
5. Ozhegov S.I. Tolkovyj slovar' ., OOO «Beta Frejm». 2012 g, 678 s.
6. Obshhaja psihologija : slovar' / pod red. A. V. Petrovskogo. — M. : PER SJe, 2005. — 251 s.
7. Tolkovyj slovar' russkogo jazyka. Tom I. Pod redakciej D.N. Ushakova. – M.: OOO «Izdatel'stvo Astrel'», OOO «Izdatel'stvo AST», 2000., 528s.
8. http://student.km.ru/
9. http://sociosphera.ucoz.ru/
10. http://family.concepcia.ru/
12




























