Задание №1.
Read the text and answer the questions.
1. What are sources of on-board DC power?
2. What are sources of AC power?
AC/DC POWER SOUCES
AC Power Sources
The electrical network of the A 320/321 is normally supplied by two engine driven AC generators (IDG 1/2).
The drive unit (for constant speed) and the generator are integrated in one unit (Integrated Drive Generator; IDG).
Technical data:
Nominal power: 90 kVA
Nominal voltage: 115/200 V AC, three-phase
Nominal speed/frequency: 12000 rpm/ 400 Hz
The APU drives a third, auxiliary, generator (APU GEN) which can replace either main generator (GEN 1 and/or GEN 2).
The APU generator also serves as an independent AC power supply on ground.
Technical data:
Nominal power: 90 kVA
Nominal voltage: 115/200 V AC, three-phase
Nominal speed/frequency: 24000 rpm/ 400 Hz
In case of emergency configuration (loss of GEN 1,2 and APU) in flight, an AC generator driven by a hydraulic motor (CSM/G: Constant Speed Motor/Generator) supplies the systems required for aircraft control.
Technical data:
Nominal power: 5 kVA
Nominal voltage: 115/200 V AC, three-phase
Nominal speed/frequency: 12000 rpm/ 400 Hz
An external power receptacle, in front of the nose wheel well, enables to connect a ground power source to the electrical network during ground operation.
DC Power Source
The DC electrical system is normally supplied from the AC electrical system via Transformer Rectifiers.
Technical data:
Nominal current output: 200 A DC
Nominal voltage: In 115/200 V AC, three-phase Out 28 V DC
Two airborne nickel-cadmium batteries are installed.
The main functions of the batteries are:
Technical data:
Nominal capacity: 23 Ah
Nominal voltage: 24 V DC
DC-AC Inverter
One static inverter of 1000 VA nominal power transforms the direct current voltage from battery 1 into a single phase 115 V, 400 Hz, alternating current.
The static inverter is automatically activated in the event of loss of all AC power sources and supplies the AC essential network.
Vocabulary:
1. generator |ˈdʒenəreɪtə| – генератор
2. constant speed drive |ˈkɔnstənt spi:d ˈdraiv| - привод постоянных оборотов
3. DC – direct current |diˈrekt ˈkʌrənt| – постоянный ток
4. AC – alternating current | ˈɔ:ltǝ:neitiŋ ˈkʌrənt|-переменный ток
5. APU - auxiliary power unit |ɔ: gˈziljəri ˈpauə ˈju:nit|– вспомогательная силовая установка (малый газотурбинный двигатель)
6. rectifier |ˈrektifaɪə| – выпрямитель (тока)
7. inverter |inˈvǝ: tə| – инвертор (тока)
8. receptacle |rɪˈseptəkl| - розетка
Power Sources
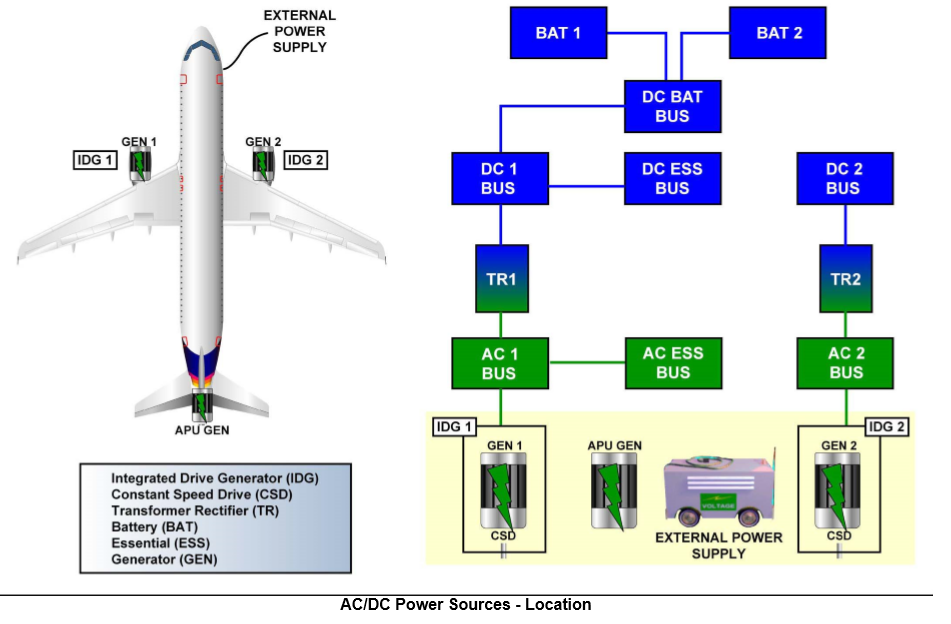
Пояснения к тексту и схеме:
1. Generator- a mechanically driven device for producing alternating current for airplane electrical system.
Генератор – механически проводимое в движение устройство для выработки переменного тока для электрической системы самолета.
2. Axillary power unit - a small turbine engine in the airplane for supplying electrical and pneumatic power for systems operation on the ground or in flight.
Вспомогательная силовая установка, малый газотурбинный двигатель на самолете для снабжения электрической и пневматической мощностями для работы системы на земле и в полете.
3. Battery - an electrical device for changing stored chemical energy into direct electric current.
Батарея (гальванический элемент) – электрическое устройство для превращения накопленной химической энергии в постоянный электрический ток.
4. Bus - a single wire or a group of wires which transfers power, data between several units or modules.
Шина - одиночный провод или группа проводов, которая проводит электрическую мощность, информацию между различными блоками и модулями.
5. Battery bus - an electrical conductor supplied with direct current from the battery or transformer – rectifier for power supply to operating components.
Шина батареи – электрический проводник, на который подается постоянный электрический ток от батареи или трансформатора – выпрямитель для подачи электрической мощности к работающим элементам.
6.Transformer rectifier - an electric device for changing alternating current to direct current to supply airplane electrical systems.
Блок трансформатора – выпрямителя – электрическое устройство для изменения переменного тока в постоянный, чтобы снабжать электрические системы самолета.
Задание 2.
Установите соответствие между английскими и русскими терминами и решите, какие позиции схемы «Power Sources» соответствуют каждому определению.
Английская спецификация:
1. generator
2. auxiliary power unit
3. battery
4. battery bus
5. transformer rectifier
Русская спецификация:
1. шина батареи
2. батарея
3. трансформатор – выпрямитель
4. вспомогательная силовая установка
5. генератор
Conversation.
Задание 3.
Read the text and answer the questions.
Abbreviations:
Kva – kilovott-ampere - киловольт-ампер
Rpm – revolutions per minute – оборотов в минуту
W – watt – ватт
There are two types of electric current. The first type is called direct current (DC). Direct current is the current which always flows in one direction. The second type is alternating current. Alternating current is the current which changes its direction many times per second. The number of changes of direction per second is called frequency of AC. Frequency of AC in is measured in ampers (A), milliampers (mA) or microampers, depending on strength of the current.
1. What is direct current?
2. What is alternating current?
3. What is frequency of alternating current?
4. What is frequency of AC in the mains on board of civil Aviation air planes?
5. What units are used for measuring electric current?
Задание 4.
Read the text and answer the questions.
Transformers and Rectifiers.
Transformer is an electro-mechanical device for changing the ratio between current and voltage. Almost all on-board transformers are of a stepping-down type. All on-board electronic devices and their integrated circuits require + 12 volts DC for their operation. We have to step down the AC voltage from the mains up to this value and then to convert it into DC.
Rectifier is an electronic device for converting alternating current, necessary for computer circuits. All rectifiers operate on the principle of one-way conductivity of a rectifying diode. This means that the rectifying diode conducts current in one direction and does not conduct current in the opposite direction.
1. What do we use transformers for?
2. what are rectifiers for?
3. what is the principle of their operating?
Topics for presentations:
1. Sources of on board DC power.
2. Sources of on board AC power.

















