МИНИСТЕРСТВО ЛЕСНОГО ХОЗЯЙСТВА
И ОХРАНЫ ОБЪЕКТОВ ЖИВОТНОГО МИРА НИЖЕГОРОДСКОЙ ОБЛАСТИ
Государственное бюджетное профессиональное
образовательное учреждение Нижегородской области
«КРАСНОБАКОВСКИЙ ЛЕСНОЙ КОЛЛЕДЖ»
(ГБПОУ НО «КБЛК»)
МЕТОДИЧЕСКИЕ УКАЗАНИЯ
по дисциплине «Иностранный язык (Английский язык)»
для студентов I курса
Тема 17 Научно-технический прогресс
Тема 18 Известные ученые
Тема 19 Профессиональные требования
для специальности 43.02.14 «Гостиничное дело»
Составили:
преподаватели
иностранного языка
Воронина М.В.,
Булкина Т.А.
Красные Баки
2023
Lesson 1
Достижения и инновации
№1. Translate the following words:
Science, cover, broad, deal with, relationship, wide, variety, search for, clue, universe, origin, cell, research, solve, complicated, unity, attempt, happen, consider, prove, divide, major, grow (grew), boundary, clear, numerous, overlap, interconnect, influence, provide, discovery, invention, shape, Universe, tool.
№2. Read the text and translate it:
The word “science” comes from the Latin word “scientia”, which means “knowledge”. Science covers the broad field of knowledge that deals with facts and the relationship among these facts. Scientists study a wide variety of subjects. Some scientists search for clues to the origin of the Universe and examine the structure of the cells of living plants and animals. Other researches investigate why we act the way we do, or try to solve complicated mathematical problems.
Scientists use systematic methods of study to make observations and collect facts. They develop theories that help them order and unity facts. Scientific theories consist of general principals or laws that attempt to explain how and why something happens or happened. A theory is considered to become a part of scientific knowledge if it has been tested experimentally and proved to be true.
Scientific study can be divided into three major groups: the natural, social and technical sciences. As science, knowledge grew and became more complicated. Many new fields of science appeared. At the same time, the boundaries between scientific fields became less clear. Numerous areas of science overlap each other and it is often hard to tell where one science ends and another begins. All sciences are closely interconnected. Science has great influence on our life. It provides the basis of modern technology – the tools and machines that make our life and work easier. The discoveries and inventions of scientists also help shape our view about ourselves and our place in the Universe.
№3. Find in the text the synonyms for:
learn, a large number of, look for, decide, difficult problems, try, scientific research, major groups, various.
№4. Ask questions to the following sentences.
1. The word “science” comes from the Latin word “scientia”.
2. Scientists use systematic methods of study to make observations and collect facts.
3. Scientific study can be divided into three major groups: the natural.
4. Scientists use systematic methods of study to make observations and collect facts
5. Science has great influence on our life.
№5. Write the achievements and innovations in Russia by your specialty (8-10):
| Achievement or innovation | Inventor | Date |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
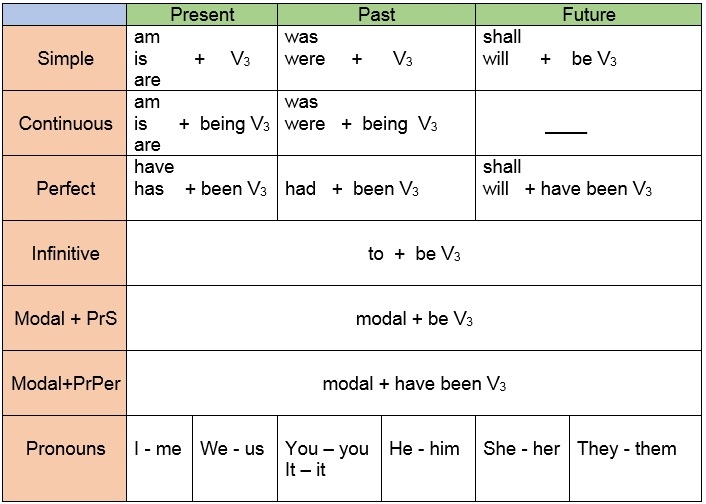
№6. Study the material “Passive Voice:
№7. Make passive sentences in the present simple
1. the room/sweep/twice a day
2. I/give/ presents every birthday
3. nice cars/produce/in Germany
4. more trees/cut down/day by day
5. I/ring/my friends/every evening
№8. Make passive sentences in the past simple
1. this song/sing/everywhere/in 1970
2. flowers/plant/in this area
3. strawberry/grow/in this town
4. telephone/invent/in England
5. my car/produce/in 2008
№9. Make passive sentences:
Claire knits nice jumpers for the kids.
The pirates had found the treasure.
Terry bought a new house in London.
Lesson 2
Отраслевые выставки
№1. Read, translate the text and make up 8 your own questions. Answer the questions:
There are two types of fairs and exhibitions: specialized, showing of one or several industries, and general, covering many different fields. A fair or an exhibition is always an event which attract serious businessman and the general public. At many exhibitions there are stands and stalls selling all kinds of goods. The businessman can get acquainted of the new goods, establish business contacts, sign a contract for the purchase. The themes and mottoes of the exhibitions are different but the keynote remains: it is peace and progress all over the world through trade and cooperation.
Very many national and international specialized exhibitions are held every year in different countries of our world. From year to year the number of companies and countries participating in such exhibitions is growing. The scope of exhibitions is also getting larger. The present exhibitions include a wide range of showpieces showing the important achievements in different fields of science, industry and agriculture of different countries.
What role do the specialized exhibitions play?
What can you see on the specialized exhibitions?
№2. Read the dialogue and answer the questions
- The exhibition will open in three months. It’s time to start a pre-exhibition publicity campaign, isn’t it?
- Placing advertisement in the press?
- Not only that. We want to advertise on the radio, television and hoardings.
- That may be very expensive.
- We are sure the expense will be worth it.
- I’ll do all arrangements, buy space in business publications and time on radio and television. We can begin distributing advertising literature.
- We’ve prepared colourful advertising literature for the exhibition.
- Good. I hope we haven’t forgotten anything?
- Oh, yes, another thing. Would you arrange for photographers and journalists to take pictures and give a good write-up of the exhibition?
- OK. Good-bye.
1. In what way did the Organizing Committee want pre-exhibition publicity campaign to be arranged?
2. Do businessmen object spending money on advertising?
3. What kind of proposals did the Organizing Committee come up with?
4. Why did the representatives of the Organizing Committee decide to invite photographers and journalists?
№3. Поставьте глагол в нужную форму, образуйте отрицательную и вопросительную формы:
I … (to go) to school at 8 o’clock every day.
Nick … (to play) football in the gym on Sundays.
They … (to read) books every evening.
№4. Поставьте глагол в нужную форму, образуйте отрицательную и вопросительную формы:
Vlad … (to go) to college last year.
She … (to swim) very well a year ago.
They … (to speak) English last lesson.
№5. Поставьте глагол в нужную форму, образуйте отрицательную и вопросительную формы:
I … (to invite) my friends tomorrow.
They … (to go) to the theatre in a week.
Alex … (to watch) a new film next Tuesday.
№6. Употребите глагол в форме сослагательного наклонения:
If I hadn’t been rude to him yesterday we … (not, to quarrel).
If Barbara … (to come) to my birthday party I would be so pleased.
If Jack were a polite man, he … (not, to behave) in such a way.
№7. Повторите материал «Указатели времени»
|
| Simple | Progressive | Perfect | Perfect Progressive |
| Present | always, usually, often, seldom, rarely, sometimes, every week, regularly | now, at present, at the moment, nowadays, this week, Look! Listen! | since, already, just, yet, recently, today, ever, never | for …, all day long, lately, when |
| Past | yesterday, last week, two days ago | at 2 o’clock yesterday, while…, when…, the whole day | since, by, after, before | for, all day/night, by, when
|
| Future | tomorrow, next week, in a week, in 2039 | at 10 o’clock tomorrow, all day long tomorrow | by the time tomorrow, by, before | for, all day/night, by, when |
Lesson 3
Inventors and their inventions
№1. Match the following English nouns with their Russian equivalents
| 1) discovery 2) achievement 3) invention 4) explanation 5) observation 6) research 7) knowledge 8) science 9) progress 10) experiment | a) исследование b) наблюдение c) опыт d) открытие e) развитие f) наука g) объяснение h) достижение i) знания j) изобретение |
№2. Match the following English verbs with their Russian equivalents
| 1) to improve 2) to discover 3) to research 4) to invent 5) to involve 6) to identify 7) to design 8) to achieve 9) to promote 10) to encourage | a) изобретать b) способствовать c) улучшать d) достигать e) поощрять f) проектировать g) распознавать h) вовлекать i) открывать j) исследовать |
№3. Read and translate the text “Inventors and their inventions”:
Samuel Colt was an American. He lived in the 19th century. In 1836 he designed and patented a pistol. It was a pistol with a revolving barrel that could fire six bullets one after another. It was the first pistol of its kind. Later there came many other pistols with six
bullets.
Rudolf Diesel was a German engineer. He was born in 1858 and died in 1913. In 1897 he invented a new internal combustion engine. This engine is known as a diesel. And it began a transport revolution in cars, lorries, trains and ships.
Samuel Finley Morse was born in 1791. He died in 1872. He was a portrait painter. Then he became an inventor. For twelve years he tried to perfect the telegraph and he was a success. Later he invented the telegraphic dot-and-dash alphabet. Now it is known as Morse code. Morse code was not only one in America of that time. There were some others. But now we use Morse code all over the world.
Charles Makintosh lived from 1766 to 1843. He lived in Scotland and was a chemist by profession. He worked in a textile industry. In 1823 he developed a rubber solution. This rubber solution was used for raincoat production. Raincoats with this rubber solution didn’t allow water to penetrate. These raincoats were called makintoshes. Now people all over the world use them in spring and in autumn.
Charles Rolls was born in 1881 in Great Britain. He died in 1910. He was an aristocrat and businessman. He was especially interested in cars. Once he met another enthusiast of cars Henry Royce. Henry Royce was a famous car engineer. They decided to design the most comfortable and reliable car. At the beginning of the 20th century it seemed to be a fantasy. But they worked hard and at last in 1907 they created the famous Rolls-Royce car. It was so comfortable and reliable that one of the models of Rolls-Royce cars «Silver Ghost» hadn’t changed greatly for 20 years since 1907.
Gottlieb Daimler and Charles Benz were two inventors. They lived in Germany. They were both interested in car production. At the end of the 19th century, each of them designed a car. At the same time, they organized two independent firms to produce them.
All the cars produced by the firm of Daimler were called «Mercedes». Mercedes was a daughter’s name of one of the stockholders of the firm. This man saved the firm of Daimler from financial crisis at the beginning of the 20th century. But after the World War I the firm of Daimler met with financial difficulties again.
№4. Give a brief summary of the text. Complete the table.
|
| Name | Country | Invention | Advantage |
| 1. | Samuel Colt | America | A pistol with a revolving barrel | It could fire six bullets one after another |
| 2. |
|
|
|
|
| 3. |
|
|
|
|
| 4. |
|
|
|
|
| 5. |
|
|
|
|
| 6. |
|
|
|
|
№5. Match the names with their discoveries and inventions.
| 1. Gallileo Gallilei | a) paper |
| 2. Isaak Newton | b) thermometer and microscope |
| 3. Alexander Bell | c) low of universal gravity |
| 4. Alexander Popov | d) diesel engine |
| 5. John Logie Baird | e) telephone |
| 6. Rudolf Diesel | f) table of chemical elements |
| 7. Dmitry Mendeleev | g) radio |
| 8. Tsai Lun | h) television |
| 9. Nicolas Cugnot | i) automobile |
| 10. Thomas Edison | j) light bulb |
№6. Study the information Gerund
Герундий — это неличная форма глагола, обладающая признаками как глагола, так и существительного. Подобной формы в русском языке нет.
Как и глагол, герундий имеет формы времени и залога, может определяться наречием.
| Форма | Действительный залог | Страдательный залог |
| Indefinite | reading | being read |
| Perfect | having read | having been read |
На русский язык герундий переводится существительным, неопределенной формой глагола, деепричастием, глаголом в личной форме или придаточным предложением.
В предложении герундий может употребляться в следующих функциях:
1. Подлежащего:
Your coming now and saying "I'm her father" doesn't change my feellings. - To, что вы пришли сейчас и говорите: «Я - ее отец»,- не меняет моих чувств.
2. Именной части сказуемого:
Seeing is believing. - Увидеть - значит поверить.
3. Дополнения (прямого, предложного):
The teacher has aimed at teaching students to speak in correct English. - Учитель поставил цель научить учащихся правильно говорить на английском языке.
4. Определения:
The difficulties of rebuilding the plant were successfully overcome. - Трудности, связанные с перестройкой завода, были успешно преодолены.
5. Обстоятельств:
You can help him by supporting him. - Вы можете помочь ему тем, что поддержите его.
Глаголы с предлогами, после которых употребляется только герундий:
to give up, to be afraid of, to be famous for, to be fond of, to be interested in, to be worth of, to be proud of, to depend on, to insist on (upon), to know of, to object to, to prevent from, to think of, to go on. После составных предлогов употребляется только герундий: because of, on account of, thanks to, due to, owing to, instead of, in spite of, for the purpose of, with a view of, of (no) use
№7. Translate into Russian
He always suggested staying here.
The job involves travelling to Germany once a month.
I proposed having party at the beach.
I promised to care for the cat but I’m not much good at babysitting.
He is capable of standing on his head and playing the saxophone.
You’d better start digging the garden.
Writing letters is more boring than phoning.
It is not worth helping him do this job.
My wife apologized for being late.
I’m very excited about attending tomorrow’s game.
№8. Translate into English
Мой дядя бросил курить и сейчас предпочитает есть.
Пожалуйста, прекратите шептаться.
Мне нравится быть одному. Я никогда не чувствую себя одиноко.
Я перешел дорогу, не посмотрев.
Подумай хорошо (carefully), прежде чем принять решение.
Lesson 4
Famous Inventors and their inventions
№1. Choose and write the right answer in Passive Voice:
1. Who invented the first telephone in 1876?
a) Alexander Popov b) Alexander Bell c) Albert Einstein
2. Who invented the first incandescent lamp?
а) Alexander Bell b) Alexander Popov с) Thomas Edison
3. Who invented the first multiple telegraph?
a) Alexander Bell b) Alexander Popov c) Albert Einstein
4. Who built the first vacuum cleaner?
a) James M. Spangler b) Akito Morita c) Alexander Bell
5. Who invented the first mechanical programmable computer?
a) Charles Babbage b) Alexander Popov c) Bill Gates
6. Who invented the first electronic programmable computer?
a) H.L.Hazen b) John William Mauchly c) Nikolai Lobachevsky
7. Who developed the first personal stereo – Sony Walkman?
a) Karl Benz b) Orville Wright c) Akito Morita
8. Who invented the first radio?
a) Alexander Bell b) Alexander Popov с) Thomas Edison
9. Who created the world’s first car assembly line?
a) Henry Ford b) Akito Morita c) Bill Gates
10. Who made the table of chemical elements?
a) Alexander Popov b) Dmitry Mendeleev c) Ivan Pavlov
11. Who made the vaccines against cholera?
a) Louis Pasteur b) John Logie Baird c) Marie Curie
12. Who invented the diesel engine?
a) Alexander Bell b) Rudolf Engine c) Michael Faraday
13. Who created Microsoft-DOS?
a) Thomas Edison b) John Logie Baird c) Bill Gates
14. Who invented the first paper?
a) Ivan Pavlov b) Isaac Newton c) Ts’ai Lun
15. Who discovered gravity?
a) Isaac Newton b) Dmitry Mendeleev c) Ivan Pavlov
16. Who invented electricity?
a) Michael Faraday b) Alexander Bell c) Isaac Newton
17. Who invented theory of relativity?
a) Ivan Pavlov b) Albert Einstein c) Karl Benz
18. Who produced the first petrol-driven motor car?
a) Karl Benz b) Akito Morita c) Bill Gates
19. Who was Albert Einstein?
a) chemist b) physicist c) biologist
20. Who invented the vaccines against cholera?
a) Louis Pasteur b) John Logie Baird c) Marie Curie
21. What country did Nicolas Copernic come from?
a) Italy b) Poland c) Greece
№2. Fill the table
| Invention | Inventor | Country | Date |
| hairbrush |
|
|
|
| copier |
|
|
|
| camera |
|
|
|
| umbrella |
|
|
|
| clock |
|
|
|
| coat hangers |
|
|
|
| electric flat iron |
|
|
|
№3. Choose the right form:
1. I want (to see/seeing) Paris.
2. We enjoy (to swim/swimming).
3. I would like (to live/living) in a small town.
4. I hope (to visit/visiting) you next week.
5. My brother hates (to help/helping) me with my homework.
6. We stayed in the house until it stopped (to rain/raining).
7. I don’t really mind (to cook/cooking).
8. We would prefer (to buy/buying) a new house.
9. I love (to travel/travelling) by train.
10. We like (to learn/learning) English.
№4. Choose gerund or infinitive
I am planning (to visit/visiting) my granny next week.
When they finish (to eat/eating) their lunch, they’ll go to the office.
He suggested (to buy/buying) some food.
Does Sally enjoy (to go/going) to the gym?
Don’t put off (to write/writing) a report till the end of the month.
John refused (to answer/answering) my question.
My brother intends (to get/getting) married soon.
I think she didn’t mean (to hurt/hurting) you.
Keep (to beat/beating) the eggs.
Fred can’t afford (to travel/travelling) this year.
№5. Write numbers:
8, 13, 2nd, ½, 74, 21st, 6 ¼, 12.6, 43rd, 8 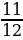
№6. Insert the pronoun, name the type of it:
John is late. We won't wait ..., because movie is beginning.
My textbook is at home today. Will you, please, give me ......?
This is a black pencil, … are green pencils.
Lesson 5
Famous Inventors and their inventions
№1. Read and translate the text:
The Pencil. In 1564, a graphite mine was found in Cumbria. The graphite was cut into sticks, the sticks were put into wooden holders – and the pencil was born. One pencil can draw a line 56 kilometres long. It can write about 45,000 words. Today, pencils are used by people all over the world.
The Fizzy Drink. Do you enjoy drinking fizzy drinks? You’re not alone. In the UK, the average person drinks 96.5 litres of fizzy drinks a year. The fizzy drink was invented by British chemist Joseph Priestly (1733-1804). Priestly found a way to put gases in liquids. He made the first glass of man-made soda water in 1767. Priestly didn’t know it, but he was changing the drinking habits of the world forever.
The Match. Today, matches are found in every kitchen. They are used to light cookers, candles and campfires. The match was invented in 1826 by British chemist John Walker (1781-1859). Unfortunately, Walker did not patent his matches, so he didn’t get much money for this important invention.
The Christmas Card. Sir Henry Cole (1808-1882) was bored with writing letters to people at Christmas. In 1843, Cole paid an artist to draw a Christmas picture. Then he printed the picture on cards and sent them to all his friends and relatives. Cole realised he could make money from the cards. He made another 1,000 cards and sold them, and the Christmas card was born.
The Electric Toaster. Have you ever thought about the word “toast”? It comes from the Latin word “tostum” which means “to burn.” People have made toast for hundreds of years as a way of prolonging the life of bread. At first, it was made by toasting bread over an open fire. Then, in 1893, Englishman Rookes Evelyn Bell Crompton invented the first electric toaster. Unfortunately, his toaster wasn’t efficient. It only toasted one side of the bread.
№2. Write out the verbs in Past Simple Passive Voice from the text and translate them (5 verbs).
№3. Write out the plural nouns from the text and translate them (15 nouns).
№4. Continue the sentences:
1) People use it to take photos …
a) camera
b) videophone
c) computer
d) mower
2) People use it to cook, defrost, reheat pre-prepared food …
a) vacuum cleaner
b) TV set
c) microwave oven
d) camera
3) People use it to cut and collect the grass …
a) microwave over
b) mower
c) mobile telephone
d) computer
4) People use it to wake up …
a) alarm clock
b) cordles phone
c) roller blades
d) fax machine
5) People use it to wash the dishes …
a) electronic game
b) camera
c) dishwasher
d) mower
6) People use it to write programs, play games, find and use information …
a) camera
b) mower
c) computer
d) fax machine
7) People use it to operate the TV set from distance …
a) TV remote-control unit
b) computer
c) camera
d) TV set
8) People use it to do calculations in sunlight or daylight …
a) computer
b) vacuum cleaner
c) solar powered calculator
d) videophone
9) People use it to send and receive urgent messages …
a) mower
b) computer
c) fax machine
d) mobile telephone
10) People use it to receive or make calls around the home …
a) mower
b) cordless phone
c) fax machine
d) videophone
№5. Write plural nouns:
book, photo, box, activity, leaf, bacterium, sheep, information, tomato, man
№6. Вставьте глагол to have в нужной форме и составьте отрицательное и вопросительное предложения из данных предложений:
Jane … a birthday party every year.
Carol and Mike … a dog next week.
They … the interesting travelling last month.
№7. Вставьте глагол to be в нужной форме и составьте отрицательное и вопросительное предложения из данных предложений:
He … a hardworking student last year.
The students … at the English lesson now.
I … a good specialist in 2026.
№8. Составьте отрицательное и вопросительное предложения из данных предложений. Переведите предложения:
There are some English books on the table.
There were very many mistakes in your dictation.
There will be a conference next week.
Lesson 6
Дресс-код. Правила поведения
№1. Read and translate the text “Dress code at the workplace”
A dress code indicates conformity, a sense of belonging and to a degree a sense of discipline. It creates an atmosphere of uniformity. It gives you a method to identify yourself with a larger group through the way you dress. Above all, it clears confusion for most people as to what is expected of them – no one wants to be that person who is underdressed or worse, overdressed. When there are set rules, it is easy to follow them.
dress code indicates conformity, a sense of belonging and to a degree a sense of discipline. It creates an atmosphere of uniformity. It gives you a method to identify yourself with a larger group through the way you dress. Above all, it clears confusion for most people as to what is expected of them – no one wants to be that person who is underdressed or worse, overdressed. When there are set rules, it is easy to follow them.
In the corporate world, it is very common for men to “wear a suit” to work – a collared long sleeve shirt, a tie and smart pants with a jacket, along with smart shoes. Wearing a suit to work shows your respect and attitude towards your job. If you’re dressed smartly, and you’re neat and tidy it implies that you’re a hardworking person who is dedicated to their work.
Women wear something similar to what men wear. It is more common and acceptable for women to wear pants now, so either smart pants with a shirt and a jacket. There is also the option of wearing a skirt – which should never be shorter than a hand above the knee. Anything higher will be seen as inappropriate and unacceptable. Each company has their own dress code. Some companies are more relaxed than others.
№2. Answer the questions:
1. What is dress code?
2. What does it show “wearing a suit” to work?
3. What does it imply if you’re dressed smartly, and you’re neat and tidy?
4. What do women wear in the corporate world?
5. How long should the skirt be?
6. Is there one single standard of dress code for all people and companies?
7. What atmosphere does a dress code create?
№3. What is deemed acceptable and unacceptable in dress code at the workplace? Fill in the lines of the table:
1. Casual trousers, smart pants or smart jeans.
2. Collared shirts, turtlenecks or sweaters.
3. A skirt 10 cm below the knee
4. T-shirts or sweatshirts with logos.
5. Low cut or strapless tops.
6. Showing any underwear.
7. A short sleeve shirt with open sandals.
8. A strict dress in a business style.
№4. Choose the adjective for the type of clothing and translate them:
| open, smart, casual, nice tailored, strict, formal dark, strapless, collared long sleeve, business, comfortable, white |
a … … … shirt, … trousers, … shoes, … attire, a … … suit, a … dress, … … skirts, … blouses, … tops, … sandals, … footwear
№5. Answer the questions:
1. Are the clothes important for you?
2. What clothes do you prefer to wear?
3. What style of clothes do you wear?
4. Do you like to wear bright or dark clothes?
5. Do you wear formal clothes when you are in college?
6. Do you prefer to wear elegant or casual clothes?
7. Can clothes change your feelings?
№6. Study the material “Infinitive”:
Инфинитив – это неличная или неопределенная форма глагола, которая отвечает на вопрос «что делать?», «что сделать?». Инфинитив называет только действие, не указывая лица, числа и наклонения.
Инфинитив в английском языке может принимать шесть временных форм.
|
| Активный залог | Пассивный залог |
| Simple (Indefinite) | to ask | to be asked |
| Progressive (Continuous) | to be asking | – |
| Perfect | to have asked | to have been asked |
| Perfect Progressive (Continuous) | to have been asking | – |
| Verbs which are usually followed by an infinitive: afford, agree, appear, arrange, ask, attempt, care, choose, claim, come, consent, dare, decide, demand, deserve, determine, elect, expect, fail, get, hate, help, hesitate, hope, hurry, intend, learn, manage, mean, need, offer, plan, prepare, pretend, promise, refuse, resolve, say, seem, tend, threaten, want, wish. | Verbs which are usually followed by a gerund: acknowledge, admit, adore, anticipate, appreciate, avoid, celebrate, confess, contemplate, delay, deny, describe, detest, discuss, dislike, dread, endure, enjoy, fancy, finish, imagine, involve, keep, justify, mention, mind, miss, omit, postpone, practise, quit, recall, recommend, regret, report, resume, risk, suggest, tolerate, understand. |
№7. Complete with a gerund or an infinitive and translate the sentences:
1. She agreed … (pay) the electricity bill the following week.
2. Hector dislikes … (go) to the opera.
3. Martin admitted … (steal) the money from the safe.
4. Elizabeth didn’t need … (do) the final exams.
5. I regretted … (forget) to call my grandfather for his birthday.
6. Your aunt wished … (visit) Australia in Summer.
7. Please, avoid … (touch) the wires with wet hands.
8. Your friend seems … (be) very busy today.
9. We suggested … (sell) our apartment at the seaside.
10. I’m amazed because you didn’t hesitate … (accept) that job.
№8. Поставьте глагол в форме инфинитива или герундия:
I am planning … (to visit/visiting) London next week.
When they finish … (to eat/eating) their breakfast, they’ll go to the college.
He suggested … (to buy/buying) some fruits.
Keep … (to beat/beating) the eggs.
Fred can’t afford … (to travel/travelling) this year.
John refused … (to answer/answering) my question.
№9. Составьте к предложениям все типы вопросов:
Family is very important for every person.
She works at college.
They spoke English last lesson.
Lesson 7
Professions in Hospitality
№1. Read and translate the text:
There are various professions in hospitality business. One of the most important is the profession of the receptionist who works in the front office of a hotel.
The receptionist is in charge of the check-in. She meets and greets guests, registers them and assigns rooms to them. Her main duty is to provide the brief and convenient check-in procedure. The receptionist must help guests do the hotel formalities. She asks the guest to fill in a registration card and to sign it. She also answers the phone and takes messages for the hotel guests. The receptionist also provides the check-out formalities.
The concierge must help the guests with the information about the hotel, the city and make travel arrangements. She must be knowledgeable, fluent in many foreign languages and have an outgoing personality. Fluency in English, French and German is a must for her. Besides, she must be computer literate, have a pleasant telephone manner and a positive helpful attitude. She actually acts as a travel agent: she books flights, tours and visits. The concierge must help guests in all ways.
The hotel manager is just a professional hotelier. For the hotel guests the hotel manager is the host who must offer hospitality to the guests. For the hotel staff he is the person who must establish the policy of the hotel and its operations. There may be different management positions in a hotel: the assistant manager, the resident manager, the night manager. The assistant manager helps the manager and manages the hotel when the manager is not present. The resident manager permanently lives in the hotel. The night manager is on duty during the night.
№2. Answer the following questions:
Which is the most important profession in the hotel business?
What are the duties of the receptionist?
What must a concierge do?
What kind of person is the concierge?
Who is the hotel manager for the guests?
What is he for the hotel staff?
Who establishes the policy of the hotel?
Which are the major management positions in hospitality?
What do these managers do?
№3. Translate in to English:
1.Кассир должен быть грамотным, честным, аккуратным.
2. Менеджер должен быть лидером, владеть организаторскими навыками, уметь работать в команде.
3. Администратор должен иметь презентабельный внешний вид, быть общительным, дружелюбным.
4. Консьерж должен быть знающим, внимательным, владеть иностранными языками
5. Портье должен быть дружелюбным, тактичным, исполнительным.
№4. Поставьте глагол в нужную форму, образуйте отрицательную и вопросительную формы:
Mary … (to eat) dinner in the kitchen at that moment.
The children … (to brush) their teeth now.
I … (to do) my homework right now.
№5. Поставьте глагол в нужную форму, образуйте отрицательную и вопросительную формы:
I … (to read) a text the whole day yesterday.
He … (not/to play) football from 6 till 7 last week.
The children … (to look after) by a granny the whole holidays last summer.
№6. Вставьте необходимый предлог в предложение, назовите его вид:
The guests are sitting … the table.
Are you usually at home … 7 o'clock … the evenings?
The boys ran … the road.
№7. Прочитайте предложения, образуйте отрицательную и вопросительную формы. Объясните значение модальных глаголов:
They can understand French.
Everybody must соmе to college on time.
She should read aloud.
№8. Вставьте much или many:
There are … students in our college.
I don’t have … time. I have to leave now.
How … girls were present in English lesson today?
How … water is there in the glass?
Lesson 8
Lexical-grammar exercises
№1. Read the texts and match them with the most suitable heading (example: 1-A). One heading is odd.
A. Science
B. College
C. Hobby
D. Family
E. Sport
F. Travelling
1. We all need to exercise. Regular exercises give you more energy. That is why many people who suffer from general tiredness should take more exercise than more rest. Exercise makes you feel and look better. The best exercise is one, which involves in repeated movements, those are walking, jogging or swimming. Bending and stretching will add flexibility and feeling of lightness.
2. On the ground floor there are the classrooms for the first-year students, workshop and a library. There are all kinds of tools and machines in the workshops. In the library two librarians help students to find the books they need. In the reading room there are laptops which we can use dining the breaks and after classes. Our canteen is spacious, light and clean. We have our meals there.
3. There is also another difference between old and modern ones. Nowadays it is very unusual to find three generations living under one roof as they used to do in the past. Relatives, as a rule, live separately and don't often meet one another. Our parents and grandparents usually suffer from lack of attention and respect from their children and grandchildren, although they try not to show it. They really don't need much, just a telephone call or a visit once a week will make them happy.
4. They use systematic methods of study to make observations and collect facts. They develop theories that help them order and unity facts. Such theories consist of general principals or laws that attempt to explain how and why something happens or happened. A theory is considered to become a part of such knowledge if it has been tested experimentally and proved to be true.
5. Today it is possible to book a holiday to a seaside resort on the other side of the world. Staying at home, you can book it through the Internet or by phone. The plane takes you straight there and within some hours of leaving your country. Now we can do it by different means of transport: by plane, by ship, by train, by car and even on foot.
№2. Read the texts again from exercise №1. Are these statements true or false? Rewrite true statements and correct the false ones.
Now we can travel by different means of transport except the traveling on foot.
The reading room is equipped with laptops.
To make observations and collect facts scientists use systematic methods of study.
It is very usual to find three generations living under one roof.
Exercises make you feel and look worse.
№3. Put the words in the right order to make the sentence.
you, like, ship, Why, don’t, travelling, by?
is, sport, Fortunately, getting, more, in, our, popular, country.
What, skills, language, is, the, way, to, best, improve, your, and, habits?
Relatives, as a rule, separately, and live, meet, don’t, often, one another.
most, People, with, the, creative, fresh mind, and, ideas, will get, better, career chances
№4. Insert the article: a / an / the / -
… Pacific Ocean is very … deep.
He seems to be … clever man.
… James Grey is … brightest student in our … class.
They had … amazing time in Paris.
№5. Write the right form of degree of comparison
Germany is ___ than Poland. (big)
You are the ___ girl I’ve ever met. (good)
The New Year is ___ holiday in the year. (wonderful)
It was the ___ day in my life. (bad)
№6. Поставьте глагол в нужную форму, образуйте отрицательную и вопросительную формы:
I … (to draw) a picture already.
She … just … (to give) his bicycle to his brother.
We … (to buy) a computer recently.
№7. Поставьте глагол в нужную форму, образуйте отрицательную и вопросительную формы:
I ... (to have) breakfast before I went to college.
We …(to know) the results of the test by four o’clock.
The performance … (to finish) by eight o’clock in the evening.
№8. Переделайте предложения в косвенную речь:
He advised, “Take the umbrella.”
She said, “He is my friend.”
He asked, “When do you finish your work?”








 dress code indicates conformity, a sense of belonging and to a degree a sense of discipline. It creates an atmosphere of uniformity. It gives you a method to identify yourself with a larger group through the way you dress. Above all, it clears confusion for most people as to what is expected of them – no one wants to be that person who is underdressed or worse, overdressed. When there are set rules, it is easy to follow them.
dress code indicates conformity, a sense of belonging and to a degree a sense of discipline. It creates an atmosphere of uniformity. It gives you a method to identify yourself with a larger group through the way you dress. Above all, it clears confusion for most people as to what is expected of them – no one wants to be that person who is underdressed or worse, overdressed. When there are set rules, it is easy to follow them.

















