Просмотр содержимого документа
«Презентация по английскому языку на тему "Ливерпульский университет"»

University of Liverpool

The University of Liverpool is a public university based in the city of Liverpool, England. Founded as a college in 1881, it gained its Royal Charter in 1903 with the ability to award degrees and is also known to be one of the six original 'red brick".

It comprises three faculties organised into 35 departments and schools. It is a founding member of the Russell Group, the N8 Group for research collaboration and the university management school is triple crown accredited.

It was the world's first university to establish departments in oceanography, civic design, architecture, and biochemistry at the Johnston Laboratories.
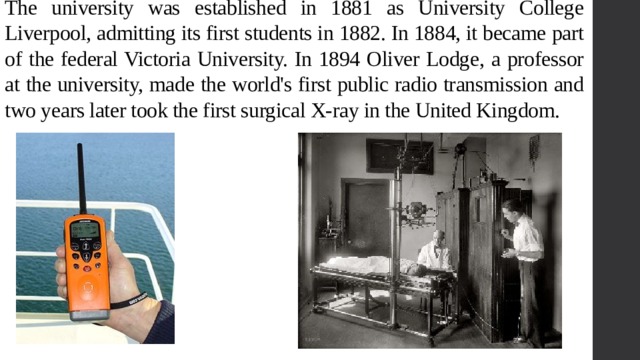
The university was established in 1881 as University College Liverpool, admitting its first students in 1882. In 1884, it became part of the federal Victoria University. In 1894 Oliver Lodge, a professor at the university, made the world's first public radio transmission and two years later took the first surgical X-ray in the United Kingdom.


The main site is divided into three faculties: Health and Life Sciences; Humanities and Social Sciences; and Science and Engineering. The Veterinary Teaching Hospital (Leahurst) and Ness Botanical Gardens are based on the Wirral Peninsula. There was formerly a marine biology research station at Port Erin on the Isle of Man until it closed in 2006.

Nobel Prize winners
Sir Ronald Ross (awarded the Nobel Prize in Medicine in 1902) for his work with malaria.

Charles Barkla (awarded the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1917) for discovering the electromagnetic properties of X-rays.

Sir Charles Sherrington (awarded the Nobel Prize in Physiology/Medicine in 1932) for his research into neurons.

Sir James Chadwick (awarded the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1935) for discovering neutrons.

Sir Robert Robinson (awarded the Nobel Prize in Chemistry in 1947) for his research into anthocyanins and alkaloids.

Har Gobind Khorana (awarded the Nobel Prize in Physiology/Medicine in 1968) for his work on the interpretation of the genetic code and its function in protein synthesis.

Rodney Porter (awarded the Nobel Prize in Physiology/Medicine in 1972) for his discovery of the structure of antibodies.

Ronald Coase (awarded the Nobel Prize in Economics in 1991) for his discovery and clarification of the significance of transaction costs and property rights for the institutional structure and functioning of the economy.

Joseph Rotblat (awarded the Nobel Peace Prize in 1995) for his efforts with nuclear disarmament.

Martin Lewis Perl (awarded the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1995) for his discovery of the tau lepton.

University of Liverpool










































