Parts of Speech
Voronina M.V.

Adjectives
Adverbs
Verbs
Prepositions
Conjunctions
Pronouns
Parts of speech
Nouns
Interjections
The parts of speech explain how a word is used in a sentence.
There are eight main parts of speech (also know as word classes): nouns , pronouns , verbs , adjectives , adverbs , prepositions , conjunctions and interjections .

Parts of Speech
NOUN - (Naming word)
PRONOUN - (Replaces a Noun)
VERB - (Action Word)
A noun is the name of a person, place, thing or idea.
Examples of nouns: London, table, happiness, hope
A pronoun is used in place of a noun or noun phrase to avoid repetition.
A verb shows an action or state of being. A verb shows what someone or something is doing.
PREPOSITION - (Shows relationship)
Example sentences: Steve lives in Sydney.
Examples of pronouns: I, you, me, him, this, those
Examples: go, speak, live, walk, have, like, are, is
A preposition shows the relationship of a noun or pronoun to another word. They can indicate time, place, or relationship.
Example sentences: Mary is tired. She wants to sleep.
Example sentences: I like English. I study and play.
Examples: at, on, in, from, between, about, under
Example sentences: I left my keys on the table.

Parts of Speech
ADJECTIVE - (Describing word)
ADVERB - (Describes a verb)
CONJUNCTION - (Joining word)
An adjective describes, modifies or gives more information about a noun or pronoun.
Examples: big, happy, green, young, fun, crazy
An adverb describes/modifies a verb, an adjective or another adverb. It tells how, where, when, how often or to what extent. Many adverbs end in -LY
A conjunction joins two words, ideas, phrases or clauses together in a sentence and shows how they are connected.
INTERJECTION - (Expressive word)
Example sentences: The little girl had a pink hat.
Examples: slowly, very, always, never, too, here
Examples: and, or, but, because, since, if.
An interjection is a word or phrase that expresses a strong feeling or emotion. It is a short exclamation.
Example sentences: I am usually busy.
Example sentences: I was hot and exhausted but I still finished the marathon.
Examples: Ouch! Wow! Great! Help! Oh! Hey! Hi!
Example sentences: Wow! I passed my English test. Great! – Ouch! That hurt.

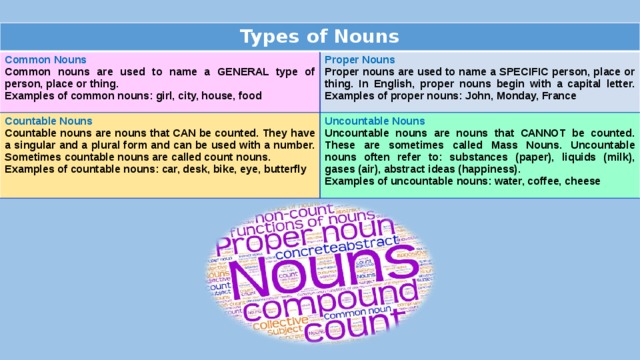
Types of Nouns
Common Nouns
Common nouns are used to name a GENERAL type of person, place or thing.
Proper Nouns
Countable Nouns
Examples of common nouns: girl, city, house, food
Proper nouns are used to name a SPECIFIC person, place or thing. In English, proper nouns begin with a capital letter. Examples of proper nouns: John, Monday, France
Countable nouns are nouns that CAN be counted. They have a singular and a plural form and can be used with a number. Sometimes countable nouns are called count nouns.
Uncountable Nouns
Examples of countable nouns: car, desk, bike, eye, butterfly
Uncountable nouns are nouns that CANNOT be counted. These are sometimes called Mass Nouns. Uncountable nouns often refer to: substances (paper), liquids (milk), gases (air), abstract ideas (happiness).
Examples of uncountable nouns: water, coffee, cheese

Types of Nouns
Concrete Nouns
Concrete nouns are nouns which refer to people and things that exist physically and that at least one of the senses can detect (can be seen, felt, heard, smelled/smelt, or tasted).
Abstract Nouns
Compound Nouns
Examples of concrete nouns: dog, tree, ball, water
Abstract nouns are nouns that have no physical existence and are not concrete. They refer to ideas, emotions or concepts so you CANNOT see, touch, hear, smell or taste something that is an abstract noun. Many abstract nouns are uncountable.
Compound nouns are two or more words that create a noun. Compound nouns are sometimes one word (haircut), words joined by a hyphen (son-in-law) or as separate words (bus stop).
Collective Nouns
Examples of abstract nouns: love, time, speed
Examples of compound nouns: toothbrush, rainfall
Collective nouns are words that refer to a set or group of people, animals or things.
Examples of collective nouns: staff, team, crew, herd, flock, bunch

There are several different kinds of pronouns, including:
- Personal pronouns (e.g., he, they)
- Demonstrative pronouns (e.g., this, these)
- Interrogative pronouns (e.g., which, who)
- Indefinite pronouns (e.g., none, several)
- Possessive pronouns (e.g., his, your)
- Reciprocal pronouns (e.g., each other, one another)
- Relative pronouns (e.g., which, where)
- Reflexive pronouns (e.g., itself, himself)
- Intensive pronouns (e.g., itself, himself)

In fact, there are more than ten different types of verbs that are grouped by function.
- Compound Verbs
- Finite and Non-finite Verbs
- Auxiliary Verbs
- Stative Verbs
- Modal Verbs
- Participles , Gerunds & Infinitives
- Regular and Irregular Verbs
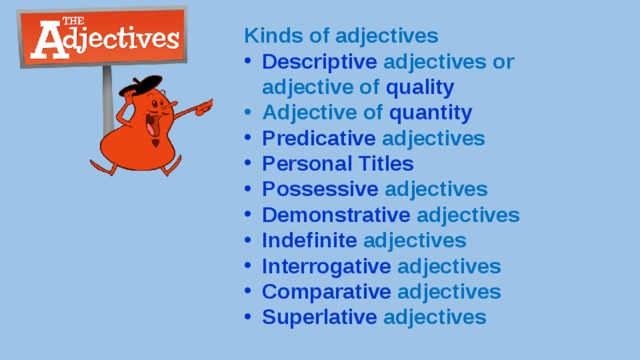
Kinds of adjectives
- Descriptive adjectives or adjective of quality
- Predicative adjectives
- Personal Titles
- Possessive adjectives
- Demonstrative adjectives
- Indefinite adjectives
- Interrogative adjectives
- Comparative adjectives
- Superlative adjectives

Types of Adverbs
There are many types of adverbs, such as:
Adverbs of Frequency - always, sometimes, never, once a week, etc.
Adverbs of Manner - carefully, slowly, loudly
Adverbs of Time - tomorrow, now, this year, next week, soon, then
Adverbs of Place/Location - here, there, above, everywhere
Adverbs of Degree - very, extremely, rather, almost, nearly, too, quite
Adverbs of Quantity - a few, a lot, much
Adverbs of Attitude - fortunately, apparently, clearly

The types of preposition are as follows:
- Preposition for Time
- Preposition for Place
- Preposition for Direction
- Preposition for Agent
- Preposition for Instrument
- Prepositional Phrase

Conjunctions can be categories basically in three types. All the three types of conjunctions are given below
- Coordinating conjunctions
- Subordinating conjunctions

Interjection is divided into following types on the basis of way to express interjections in the sentence such as:
greeting (hey, hello, hi, etc.),
joy (hurrah, wow, hurray, etc.),
surprise (ha, what, hey, ah, oh, eh, etc.),
approval (well done, bravo, brilliant, etc.), sorrow (alas, ouch, ah, oh, etc.),
attention (look, behold, listen, hush, etc.).









































