СДЕЛАЙТЕ СВОИ УРОКИ ЕЩЁ ЭФФЕКТИВНЕЕ, А ЖИЗНЬ СВОБОДНЕЕ
Благодаря готовым учебным материалам для работы в классе и дистанционно
Скидки до 50 % на комплекты
только до
Готовые ключевые этапы урока всегда будут у вас под рукой
Организационный момент
Проверка знаний
Объяснение материала
Закрепление изученного
Итоги урока

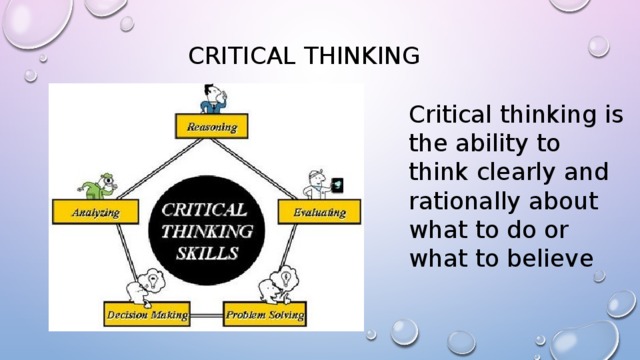
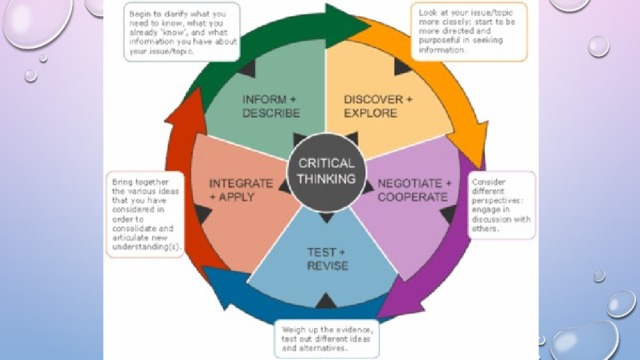
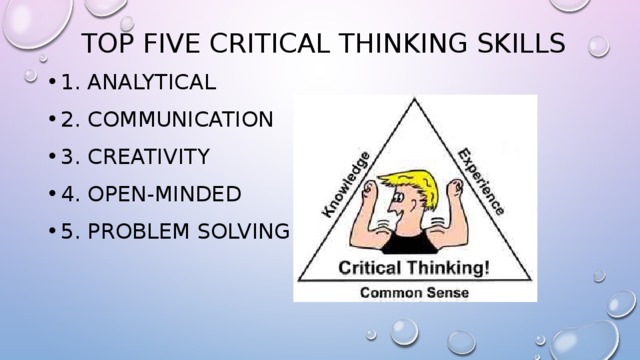
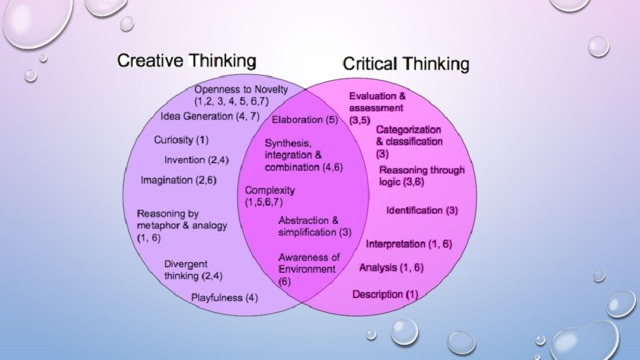
Summary Critical Thinking (presentation)
Категория:
Английский язык
11.05.2018 23:18
© 2018, Kabulova Zhanar Shokanovna 1851 22