Ministry of Education and Science of the Republic of Kazakhstan
M. Auezov South Kazakhstan State University
FACULTY OF “PHYSIOLOGICAL TRAINING AND SPORT”
CHAIR OF “PSYCHOLOGY AND DEFECTOLOGY”
Presentation
The theme : The concept of organizational culture
Prepared by: Ni Y.
Group: FK-17-3R
Checked by: Isabayeva A.S.
Shymkent - 2019
и
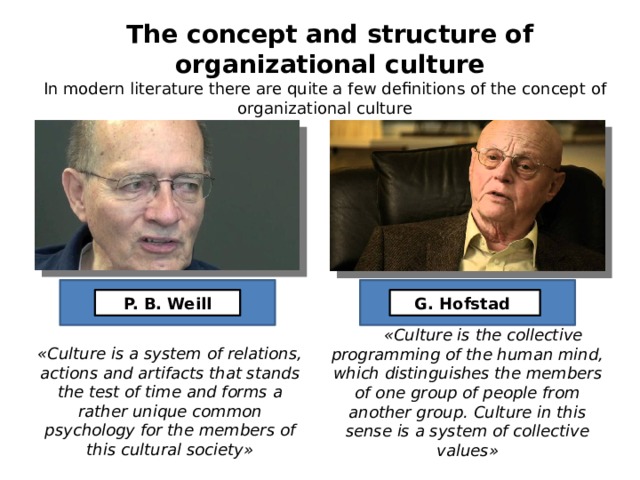
The concept and structure of organizational culture
In modern literature there are quite a few definitions of the concept of organizational culture
P. B. Weill
G. Hofstad
«Culture is the collective programming of the human mind, which distinguishes the members of one group of people from another group. Culture in this sense is a system of collective values»
«Culture is a system of relations, actions and artifacts that stands the test of time and forms a rather unique common psychology for the members of this cultural society»
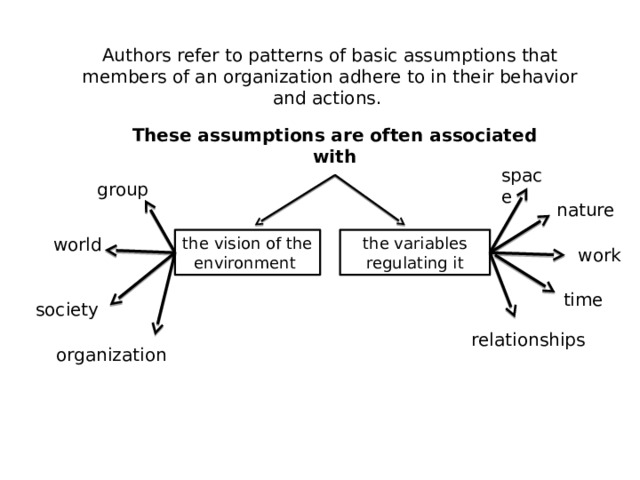
Authors refer to patterns of basic assumptions that members of an organization adhere to in their behavior and actions.
These assumptions are often associated
with
space
group
nature
world
the variables regulating it
the vision of the environment
work
time
society
relationships
organization
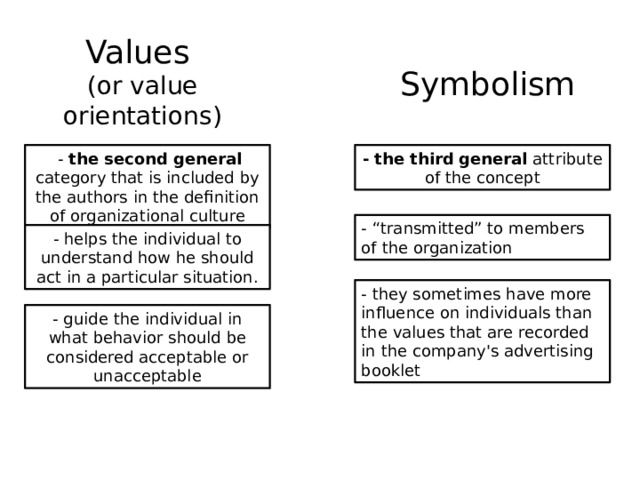
Values (or value orientations)
Symbolism
- the second general category that is included by the authors in the definition of organizational culture
- the third general attribute of the concept
- “transmitted” to members of the organization
- helps the individual to understand how he should act in a particular situation.
- they sometimes have more influence on individuals than the values that are recorded in the company's advertising booklet
- guide the individual in what behavior should be considered acceptable or unacceptable
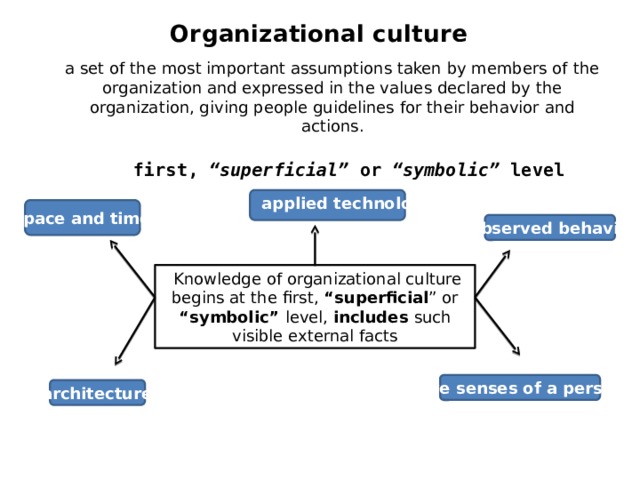
Organizational culture
a set of the most important assumptions taken by members of the organization and expressed in the values declared by the organization, giving people guidelines for their behavior and actions.
first, “superficial” or “symbolic” level
applied technology
space and time
observed behavior
Knowledge of organizational culture begins at the first, “superficial ” or “symbolic” level, includes such visible external facts
five senses of a person
architecture
- The perception is conscious and depends on the will of the people
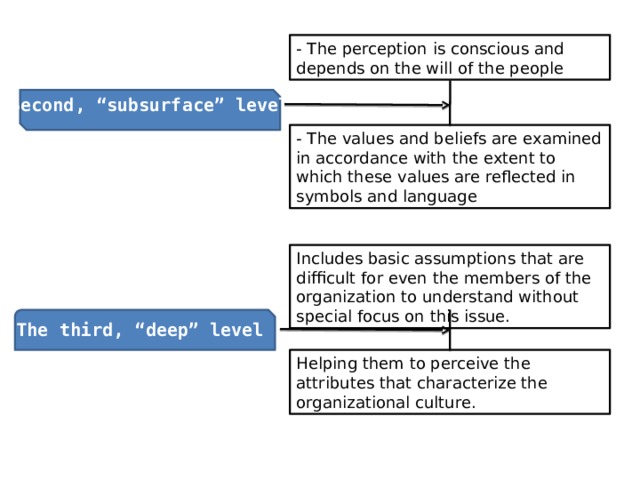
Second, “subsurface” level
- The values and beliefs are examined in accordance with the extent to which these values are reflected in symbols and language
Includes basic assumptions that are difficult for even the members of the organization to understand without special focus on this issue.
The third, “deep” level
Helping them to perceive the attributes that characterize the organizational culture.
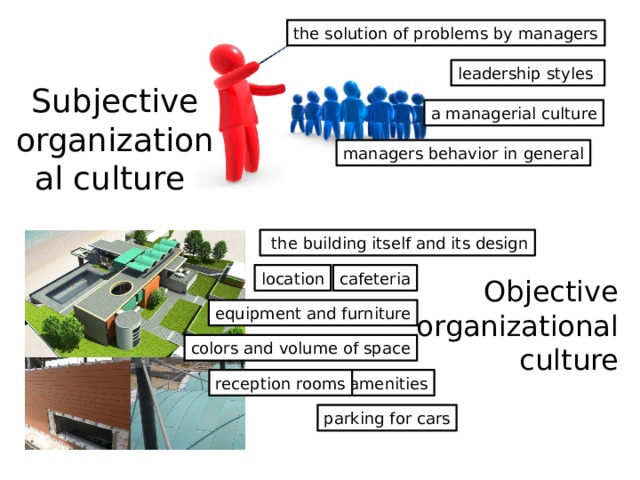
the solution of problems by managers
leadership styles
a managerial culture
Subjective organizational culture
managers behavior in general
the building itself and its design
location
cafeteria
Objective organizational culture
equipment and furniture
colors and volume of space
amenities
reception rooms
parking for cars

The main characteristics of the organizational (corporate) culture
McDonald’s was formed by R. Kroc , who headed the company until 1984
The main conditions for success:
High quality, qualified service and cleanliness
The fundamental principles of the company:
Do not compromise the company, use only the best ingredients for cooking
Today's leaders, fully embraced by the philosophy of R. Kroc, usually come to decisions that are in many ways similar to those that Kroc took during his leadership. This largely explains the McDonald’s phenomenon, symbolizing stability.
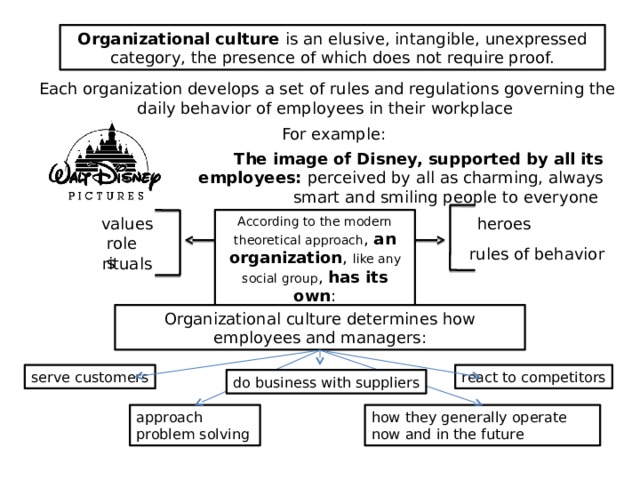
Organizational culture is an elusive, intangible, unexpressed category, the presence of which does not require proof.
Each organization develops a set of rules and regulations governing the daily behavior of employees in their workplace
For example:
The image of Disney, supported by all its employees: perceived by all as charming, always smart and smiling people to everyone
heroes
According to the modern theoretical approach , an organization , like any social group , has its own :
values
roles
rules of behavior
rituals
Organizational culture determines how employees and managers:
react to competitors
serve customers
do business with suppliers
how they generally operate now and in the future
approach problem solving
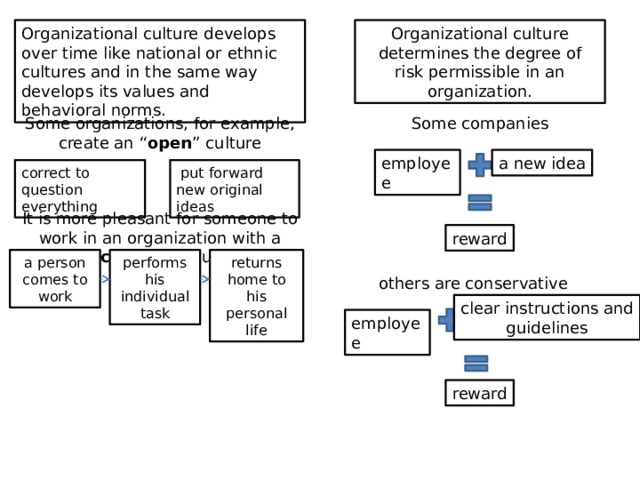
Organizational culture develops over time like national or ethnic cultures and in the same way develops its values and behavioral norms.
Organizational culture determines the degree of risk permissible in an organization.
Some organizations, for example, create an “ open ” culture
Some companies
a new idea
employee
correct to question everything
put forward new original ideas
It is more pleasant for someone to work in an organization with a “ closed ” culture
reward
returns home to his personal life
a person comes to work
performs his individual task
others are conservative
clear instructions and
guidelines
employee
reward
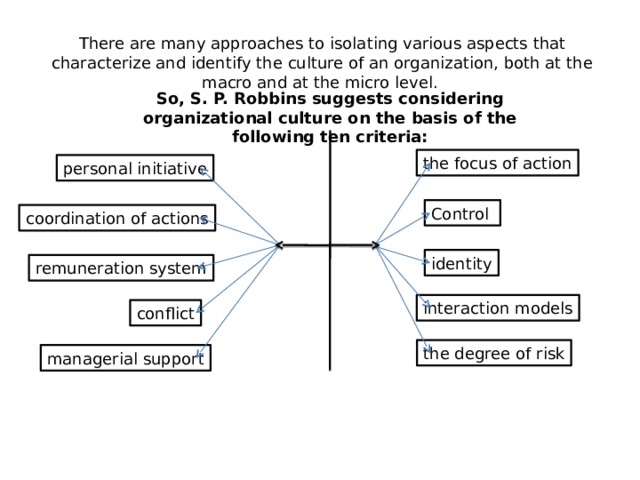
There are many approaches to isolating various aspects that characterize and identify the culture of an organization, both at the macro and at the micro level.
So, S. P. Robbins suggests considering organizational culture on the basis of the following ten criteria:
the focus of action
personal initiative
Control
coordination of actions
identity
remuneration system
interaction models
conflict
the degree of risk
managerial support





































