МИНИСТЕРСТВО ЛЕСНОГО ХОЗЯЙСТВА
И ОХРАНЫ ОБЪЕКТОВ ЖИВОТНОГО МИРА НИЖЕГОРОДСКОЙ ОБЛАСТИ
Государственное бюджетное профессиональное
образовательное учреждение Нижегородской области
«КРАСНОБАКОВСКИЙ ЛЕСНОЙ КОЛЛЕДЖ»
(ГБПОУ НО «КБЛК»)
МЕТОДИЧЕСКИЕ УКАЗАНИЯ
по дисциплине «Иностранный язык (Английский язык)»
для студентов I курса 7 часть
Тема 1.8 Родная страна: географическое положение, столица,
крупные города, регионы; система образования, достопримечательности, культурные особенности (национальные и популярные праздники, знаменательные даты, традиции, обычаи); страницы истории.
Составили:
преподаватели
иностранного языка
Воронина М.В.,
Булкина Т.А.
Красные Баки
2024 год
Lesson 1
The Russian Federation
№1. Read, translate the text and answer the questions:
The Russian Federation is the largest country in the world. It occupies about one-seventh of the earth’s surface. It covers the eastern part of Europe and the Northern part of Asia. Its total area is about 17 million square kilometers, the population is about 145 million. The country is washed by 12 seas of 3 oceans: the Pacific, the Arctic and the Atlantic. In the south Russia borders on China, Mongolia, Korea, Kazakhstan, Georgia and Azerbaijan. In the west it borders on Norway, Finland, the Baltic States, Belorussia, the Ukraine. It also has a sea-border with the USA.
There is hardly a country in the world where such a variety of scenery and vegetation can be found. We have steppes in the south, plains and forests in the midland, tundra and taiga in the north, highlands and deserts in the east. There are two great plains in Russia: the Great Russian Plain and the West Siberian Lowland. There are several mountain chains on the territory of the country: the Urals, the Caucasus, the Altai and others. The largest mountain chain, the Urals, separates Europe from Asia.
There are over two million rivers in Russia. Europe’s biggest river, the Volga, flows into the Caspian Sea. The main Siberian rivers – the Ob, the Yenisei and the Lena – flow from the south to the north. The Amur in the Far East flows into the Pacific Ocean. Russia is rich in beautiful lakes. The largest lakes are Lake Peipus, Lake Khanka, Lake Ladoga, Lake Onega. The world’s deepest lake (1,600 metres) is Lake Baikal. It is much smaller that the Baltic Sea, but there is much more water in it than in the Baltic Sea. The water in the lake is so clear that if you look down you can count the stones on the bottom.
Russia has one-sixth of the world’s forests. They are concentrated in the European north of the country, in Siberia and in the Far East. On the vast territory of the country there are various types of climate, from arctic in the north to subtropical in the south. In the middle of the country the climate is temperate and continental. Russia is very rich in oil, coal, iron ore, natural gas, copper, nickel and other mineral resources.
Russia is a parliamentary republic. The Head of State is the President. The legislative powers are exercised by the Duma. The capital of Russia is Moscow. It is its largest political, scientific, cultural and industrial centre. It is one of the oldest Russian cities. At present, the political and economic situation in the country is rather complicated. There are a lot of problems in the national economy of the Russian Federation. The industrial production is decreasing. The prices are constantly rising, the rate of inflation is very high. People are losing their jobs because many factories and plants are going bankrupt. But in spite of the problems Russia is facing at present, there are a lot of opportunities for this country to become one of the leading countries in the world. I’m sure that we, the younger generation, can do very much to make Russia as strong and powerful as it used to be.
Where is Russia located?
What is the population of Russia?
What countries does Russia border on?
What kind of surface can you find in Russia?
Where does the Volga flow into?
What is the capital of Russia?
№2. Define whether these statements are False or True. Correct them:
1) Russia is a small country.
2) It occupies about one seventh of dry land.
3) Its total area is over 150 million square kilometers.
4) Russia is washed by three oceans.
5) Russia is located in the taiga.
6) The Urals is the longest mountain chain. It separates Europe from Asia.
7) There are one type of climate on the territory of Russia.
8) The Baikal is the deepest lake in the world.
9) Russia has four natural resources.
10) The Russian Federative Republic is a Monarchy.
№3. Complete the sentences:
1. The total area of Russia is ………
2. The country is washed by ……….
3. The symbols of Russia are……..
4.Most part of Russia has ………………climate with cold winters and hot summers.
5.The deepest lake in the world is ……
№4. Match the words with the opposites meaning
| shallow high rich far wide cold damp long vast | poor dry near short deep small low narrow warm |
№5. Write the names of the cities and when they were founded.
| City | Date of foundation |
| St. Petersburg Nizhniy Novgorod Yaroslavl Vladimir Rostov Pskov Suzdal Novgorod |
|
№6. Study the material “Word-formation”:
В английском существует шесть основных способов словообразования (word formation):
1) с помощью приставок (prefixes): compose → decompose, write → rewrite.
2) с помощью суффиксов (suffixes): to train → trainer, to cut → cutter.
3) переход слова из одной части речи в другую (conversion): to interview → an interview.
4) сложение слов (compounds): block + chain = blockchain, well + read = well-read.
5) аббревиатуры (abbreviations): personal computer → PC, video blog → vlog.
6) заимствования (loan words): pizza (из итальянского), sushi (из японского).
1. Суффиксы существительных, образованных от глагола
-er/or (суффикс деятеля): write — writer, invent — inventor
-tion (суффикс процесса): invent — invention
-ing: mean — meaning
2. Суффиксы существительных, образованных от прилагательного
-ness: kind — kindness
-ance/ -ence (соответствующие прилагательные имеют суффиксы: -ant/ -ent): important — importance, different — difference
Суффиксы существительных можно разделить на две группы: суффиксы субъекта деятельности и суффиксы абстрактных существительных.
Субъект деятельности
-er/-or - описывают роль занятий человека: driver, director
-an, -ian - указывает на профессии или страны происхождения: historian, Australian
-ist - указывает на принадлежность к соц. течению: socialist, capitalist
-ant, -ent - помогают образовать существительное от глагола: student, migrant
-ee - помогают образовывать отглагольные существительные: employee, referee
-ess - суффикс существительных женского рода: waitress, princess
Абстрактные существительные
-ity - абстрактное понятие: activity
-ance, -ence, -ancy, -ency - находиться в каком-то состоянии: defence, reliance
-ion, -tion, -sion - абстрактное понятие: admission, promotion
-ism- социальное течение: racism
-hood - какое-то объединение: childhood, neighbourhood
-ure - образует существительные от глаголов: pressure
-dom - какое-то объединение: kingdom
-ment - обозначает результат действия: disappointment
-ness - абстрактное понятие: happiness
-ship - образует существительные от других существительных: friendship
№7. Form nouns using suffixes -er/-or and translate them:
direct, drive, sail, write, instruct, use, edit, work, translate, dance, act, read, invent, play, conduct, buy, construct, mix, collect, listen
№8. Form nouns using suffixes -ness and translate them:
polite, sad, dark, fresh, cold, happy, white, ill, kind, blind, weak, rich, bright, good, black
№9. Form nouns using suffixes -tion and translate them:
educate, communicate, collect, invent, celebrate, protect, translate, decorate, exhibit, inform, act, explain, demonstrate, migrate, locate
Lesson 2
National symbols of Russia
№1. Translate the words:
symbol, flag, anthem, coat of arms, symbolic, purity, perfection, constancy, faith, loyalty, bloodshed, crown, orb, scepter, state, power, unity, nobility, frankness, chastity, honesty
№2. Read and translate the text:
The national flag of Russia is a tri color flag-white color which lies on the top, blue in the middle and red on the bottom. White stands for nobility and frankness; blue symbolizes loyalty, honesty, chastity and scarlet represents self-sacrifice, generosity and love. While some Russians believe that red means the land, blue stands for sky, and white symbolizes heaven. The current Russian flag was adopted on August 21, 1991 just before the country became an independent state. Most historians trace the origin of Russia’s flag to Peter the Great. In 1699, out of hundreds of different flags, Peter selected the flag similar to the flag of the Netherlands — white, blue and red flag. His design was used as a Russian maritime flag for merchant ships and then it was adopted as the civil flag of Russia in 1883.
The two-headed eagle first appeared in Russia, during the time of Moscovia, in the 15th century. Two-headed eagle has been the symbol of the monarchy of Russia for more than four hundred years. But with the advent of Russian revolution and dethroning of the Tsar Empire, it was on the verge of extinction. In 1993, under the initiative of President Boris Yeltsin it was again adopted on 30th November 1993. The two heads of the eagle stands for the two parts of vast Russian empire — European and Asian, which are believed to be an important part of the country of Russia. There are three historical crowns of Peter the Great above the two-headed eagle (they are symbols of the sovereignty both in Russia as a whole and in its parts). The eagle holds in claws scepter and orb as embodiment of State power and united state. On its chest there is a horseman – Russian St. George – who is killing an evil snake with his spear. That is one of the oldest symbols of victory of Russia against all its enemies, symbol of the struggle of good against evil, light against gloom.
For a long time Russia had no anthem. The various church hymns and military marches were used to honour the Russia up to 1816, when the ―Молитва русских― («Prayer of the Russians») by Russian poet V. Zhukovskii was chosen as the national anthem. The second official anthem ―Боже, царя храни― was presented in 1833, on December 25th, when the nation celebrated the expulsion of the French from Russia. That anthem existed until the October revolution of 1917 and was replaced to the new anthem of the victorious proletarian revolution — «International» — in 1918. In 1944, the national anthem of Russia was accepted. The music was composed by Alexander Alexandrov and the lyrics were written by Russian Federalist Sergey Mikhalkov. After the collapse of the Soviet Union, in 1993, a government commission and President Yeltsin offered a new national anthem («Patriotic Song») by M. Glinka. However this anthem was unpopular and didn’t inspire Russians. People preferred the old Soviet anthem instead of it.
№3. Fill in the gaps and write the texts “Flag of the Russian Federation”: use the words: constancy, faith and loyalty, white, three, blue, red, energy and bloodshed
The flag has … wide stripes on it. The stripes are white, … and … . The colours of the flag are symbolic. … is peace, purity, perfection, blue is … , red is … .
№4. Fill in the gaps and write the texts “The Double-Headed Eagle”: use the words: Russia, symbol, orb, horseman, the sign of state power
The double-headed eagle is the emblem of … . There are three crowns above the heads. The eagle has a scepter the symbol of … , and an … , the …of unity. You can see … on the chest of the eagle. It is the symbol of love for the homeland.
№5. Are these statements true or false? Correct the false ones.
1. The composer of the anthem of the Russian Federation was Mikhail Glinka.
2. The song is an adaptation of the anthem of the Soviet Union
3. The author of the lyrics was A. Alexandrov.
4. The public attitude of the anthem was different.
5. President Vladimir Putin decided that Alexandrov's music was to be restored, and that new lyrics should be written for it.
№6. Study the material “Word-formation”:
1. Суффиксы прилагательных, образованных от существительных
-ful (выражает наличие качества; beautiful, colourful)
-less (выражает отсутствие качества: colourless, useless)
-ous (слова франц. происхождения, аналог ful: courageous, famous)
-al (central, formal)
-y (cloudy, dirty)
-ic (poetic, domestic)
-ish (выражает национальную принадлежность: Scottish, English, а также слабая степень качества: brownish -коричневатый, reddish -красноватый)
2. Суффиксы прилагательных, образованных от глаголов
-able /-ible (выражает возможность подвергнуться действию, указанному глаголом:
to change – changeable; to eat – eatable)
-ive (active, talkative)
-ent /-ant (different, important)
№7. Form adjectives using suffixes -al and translate them:
science, culture, continent, politics, industry, economy, nation, history, academy, architect, person, center, logic, mechanics, digit, education, addition, biology, territory
№8. Form adjectives using suffixes –y and translate them:
rain, fog, cloud, wind, frost, snow, dirt, sun, fun, ice, sand, noise, dust, health
№9. Form adjectives using suffixes –ful and translate them:
beauty, power, hope, use, harm, colour, care, thank, peace, success, help, faith, doubt
№10. Form adjectives using suffixes –ent and translate them:
differ, confide, depend, compete, excel, insist, obey, violence
№11. Form adjectives using suffixes –ous and translate them:
danger, fame, adventure, humour, mystery, courage, fury, glory, luxury, mountain
№12. Change the words in brackets in adjectives:
1) It covers the … (EAST) part of Europe and the … (NORTH) part of Asia.
2) It is its largest … (POLITICS), … (SCIENCE), … (CULTURE) and … (INDUSTRY) centre.
3) Russia is rich in … (BEAUTY) lakes.
4) Moscow is famous for its … (HISTORY) and … (ARCHITECT) monuments that were built by outstanding architects.
5) Russia is a … (PARLIAMENT) republic.
Lesson 3
Moscow
№1. Match the words in the left and right columns:
| 1. Moscow State University 2. the Arbat 3. Petrovskiy Passage 4. the Tretyakov Gallery 5. the Tomb of the Unknown Soldier 6. the Bolshoy 7. Luzhniki 8. Metropol 9. Praga 10. Pushkinsky | a. department store b. theatre c. stadium d. cinema e. educational institution f. restaurant g. hotel h. museum i. monument j. street |
№2. Read and translate the text
Moscow, the capital of Russia, is one of the largest cities in the world. It was founded in 1147 by the prince Yuri Dolgorukiy. Moscow stands on the banks of the Moskva River. About 12 million people live in the city.
Moscow is famous for its historical and architectural monuments that were built by outstanding architects. The Red Square is the central and the most beautiful square in Moscow. It is the place of parades, meetings and demonstrations. There is a Cathedral of St. Basil (Василий Блаженный) built in 1552 on the Red Square. It is a masterpiece of Russian architecture.
The heart of Moscow is the Kremlin. There is a wonderful architectural ensemble with three cathedrals, the Bell tower Ivan the Great, palaces, fortress walls and twenty towers inside the Kremlin. The most famous of the towers is the Spasskaya Tower with a big clock. The Kremlin with golden domes and towers makes a strong impression on tourists.
Several skyscrapers decorate Moscow, including Moscow University and the Ministry of Foreign Affairs. Moscow is a scientific and cultural center with a lot of institutes, universities, libraries, museums. The city`s cultural life is very rich and various. Moscow has a lot of cinemas, clubs, concert halls, more than a hundred drama and musical theatres, including the Bolshoi Theatre, the Art Theatre, the Maly Theater, the Vakhtangov Theater. Moscovites [ˈmʌskəʊvaɪts] are proud of their museums: the Tretyakov Gallery, Pushkin Museum of Fine Arts and many literary museums. A lot of people visit Tretyakov Art Gallery admiring beautiful pictures of Russian painters. There are a lot of stadiums, swimming pools, tennis courts and sport grounds in Moscow.
№3. Find the word and phrases in the text:
был основан, стоять на берегах, известный, выдающийся архитектор, шедевр русской архитектуры, золотые купола, производить сильное впечатление на …, научный и культурный центр, гордиться чем-либо, любоваться картинами.
№4. Insert the missing words:
1. Moscow stands ____ ____ ____ of the Moskva River.
2. Moscow is ____ for its historical and architectural monuments that were built by _____ architects.
3. It is a __________ of Russian architecture.
4. The Kremlin with _____ _______ and towers makes a strong ______ on tourists.
5. Several _______ decorate Moscow.
6. Moscovites are ___ __ their museums.
7. A lot of people visit Tretyakov Gallery _____ beautiful pictures of Russian painters.
№5. Answer the questions
What is the capital of Russia?
When was Moscow founded?
Who founded Moscow?
What river does Moscow stand on?
What is the population of Moscow?
What is the heart of Moscow?
What tower is the symbol of Russia?
When was St. Basil`s Cathedral built?
Name the most famous museums in Moscow.
Name the most famous theatres in Moscow.
№6. Are these statements true or false? Correct the false ones.
Moscow is a small town in Russia.
Moscow is the capital of the UK.
Moscow is one of the most interesting and famous cities in Europe.
The Tretyakov Gallery is in London.
The Kremlin stands in Red Square in Moscow.
Moscow stands on the Moskva – river.
Arbat Street is in the center of Moscow.
Red Square is in London.
Spasskaya tower is in France.
Moscow is not a political and business centre.
Hermitage is in Moscow.
Tourists in London always visit The Bolshoi Theatre.
№7. Study the material “Past Progressive”:
1) Past Continuous или Past Progressive Tense — это прошедшее длительное время.
2) Обозначает действие, которое происходило в определённый момент в прошлом.
3) Указатели времени: at that time yesterday – в тот момент вчера, at 5 o’clock – в 5 часов, when he came – когда он пришёл.
4) Вспомогательные глаголы: was (ед. ч.), were (мн. ч.)
5) Положительное предложение:
ед.ч. V4
 was
was 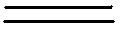
мн.ч. V4 V4 = Ving
 were
were 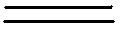
6) Отрицательное предложение:
ед.ч. V4
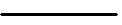 was not
was not 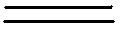
мн.ч. V4
 were not
were not 
7) Общий вопрос:
ед.ч. V4
Was 
 ?
?
мн.ч. V4
Were 
 ?
?
8) Специальный вопрос:
ед.ч V4
Wh. was 
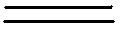 ?
?
мн.ч. V4
Wh. were 
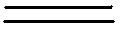 ?
?
9) Прибавление окончания к глаголу: do+ing=doing
Исключения: - y + ing=ying: playing, studying
- e + ing=ing: making, taking
- ee + ing=eeing: seeing, agreeing
-ie + ing=ying: lying, dying, tying
run+ing=running, put+ing=putting, stop+ing=stopping
№8. Insert was or were in the sentences:
1. She … staying at home the whole day.
2. The children … doing their homework when their father came back from the office.
3. Tom … speaking to his daughter when I saw him.
4. I … waiting for you at four yesterday.
5. It … raining heavily from morning till night yesterday.
6. We … discussing this problem at five o’clock yesterday.
№9. Open the brackets using Past Progressive and translate them:
1. Yesterday about six o’clock she (to walk) towards Oxford Street.
2. I (to read) a book when they came in.
3. While you (to wait) for an answer, a knock came at the outer door.
4. The sun (to shine) when we went out.
5. At ten o’ clock she (to walk) her dog in the park.
№10. Make sentences negative and interrogative:
1. They were preparing for their examinations in December.
2. Ann was speaking to him for an hour.
3. My sister was playing the piano the whole evening.
4. The children were skiing the whole day.
5. I was reading a book when he came.
Lesson 4
Sights of Russia
№1. Read and translate the text
The island of Onekotan lies to the southwest of Kamchatka. It is an uninhabited Russian island contains an active volcano. Krenitsyn Volcano (вулкан Креницына) is a volcano in a volcano 1324 meters in height. It is located in the middle of the lake in the island. It is an island with an island. Volcano is surrounded by beautiful nature and clean air that can make a trip to the island unforgettable.
The Manpupuner Rock Formations (столбы выветривания, Мань-пупу-нёр) are 7 gigantic, oddly-shaped stone pillars located on a flat landscape. About 200 million years ago this area was a high mountain. But rain, snow, wind, cold and heat gradually destroyed the mountain. The pillars are also called the “Seven Giants” or “Seven Strong Men”. Rock climbers from around the world have tried to scale their impossible sides.
The Mirny Diamond Mine (алмазная шахта «Мирная») is the second largest manmade hole in the world. It is located on the outskirts of Mirny, a small town in Eastern Siberia. For half a century it produced a huge mass of high-quality diamonds for Russia. It was closed in 2011. The hole is 525 meters deep and 1,25 kilometers across. It’s a very cool place to visit in Russia.
The Baskunchak is a salt lake, with an area of about 115 square km. It’s located in Astrakhan region not far from the Caspian Sea. The lake has played an important role in Russia’s economy since the 8th Century. Today, the Baskunchak provides over 80% of Russia’s salt. This lake has no kind of living plants, seaweeds, birds or insect as the salt water kills them all.
Kungur Ice Cave (Кунгурская пещера) is one of the most famous and popular tourist attractions of the Urals. This is a true wonder of nature. The length of cave is about 5700 meters. The cave is available for visitors, but not completely – only 1500 meters are specially equipped and cleaned. The temperature in cave is always freezing: -2-3 degrees in summer and below -20 in winter. Everything here will give you unforgettable impressions.
Chara Sands (Чарские пески) is a real miracle of Russian nature. It is one of the smallest deserts in the world. It’s just 3 kilometers wide and 6 kilometers long. The desert is surrounded by taiga and marshes. Sand chains are very beautiful; they look like frozen waves. Sand-dune may reach up to 700 meters in length, and to 30 meters in height. Also you can see two small lakes – Alyonushka and Taiga in the North-Eastern part of the desert.
The island of Kizhi is located in Lake Onego. It is famous for the biggest ensemble of wooden architecture in the world. Kizhi Museum looks like a fairytale castle. The age of Kizhi Pogost (Кижский Погост) is about 300 years. Kizhi Museum includes two 18th century wooden churches. The Kizhi Pogost is a unique monument of Russian wooden architecture.
The Kamchatka Peninsula is one of the most amazing places on our planet. It is located in Russian Far East. The Valley of Geysers in Kamchatka is one of the largest geyser fields in the world. Geysers are rather unusual for our country; generally, they meet in the USA (in Yellowstone Park), Iceland and New Zealand. The Valley of Geysers is unique in Eurasia. There are over 20 large geysers and many thermal springs on the 6 kilometers area. The Valley attracts a lot of interest from scientists and tourists.
The Baikal is the biggest lake in Russia. It contains 20% of the world's fresh water. The water in the Baikal is completely transparent, and you can see some objects at depths of about 40 meters. There are thousands of varieties of plants and animals in the lake. Three quarters of them cannot be found anywhere else in the world. The Baikal is the deepest lake on the Earth – the greatest depth is 1637 meters. Lake Baikal is the most famous natural sight in Russia because of purest air, unique landscapes, and incredible beauty.
Lena Pillars (Ленские столбы) are vertical rocks located on the right bank of the Lena River, two hundred kilometers from Yakutsk. They stretch 40 kilometers along the river. The height of pillars can reach 200 meters. Each pillar looks like medieval tower or mysterious castle. The age of Lena Pillars is about 500,000 years. They have been under UNESCO protection since 2012.
The name of Altai comes from Mongolian “Altan”, which means “golden”. The Altai Mountains area is 845,000 square kilometers. They cover large territory of four countries: Russia (largest part), Kazakhstan, Mongolia and China. Altai’s landscape rich in contrasts. You can see steppes, taiga, tundra and even glaciers. The main sight of interest is the two-peak Belukha Mountain. It is 4,506 meters in height and constantly covered with the snow and ice. The Altai Mountains are really one of the most magnificent places, amazing by their incredible beauty.
The Solovetsky Islands (Solovki) are located in the western part of the White Sea, not far from the Arctic Circle. The Solovki consist of six big islands and many small islands. There is a famous Solovetsky monastery on the island. It was built in the first half of the 15th century. The monastery is a medieval historical and cultural monument. The Solovetsky Archipelago also is famous for its unusual landscape, including hills, lakes, and gullies.
№2. Fill in the table using the text:
| № | Sightseeing | Place | Numbers | Interesting fact |
| 1 | Krenitsyn Volcano | Kuril islands | 1324 m in height | A volcano in a volcano |
| … |
|
|
|
|
| 12 |
|
|
|
|
№3. Fill in the gaps:
1. Krenitsyn Volcano is a volcano in a … .
2. The Manpupuner Rock Formations are 7 oddly-shaped … pillars.
3. The Mirny Diamond Mine is located in … .
4. Baskunchak plays an … role in Russia’s economy.
5. The … in Kungur Ice cave is always freezing.
6. Chara Sands is one of the … deserts in the world.
7. Kizhi Museum looks like a … .
8. The Valley of Geysers is … in Eurasia.
9. Baikal is the …. lake in Russia.
10. The age of Lena pillars is about … .
11. The Altai Mountains cover vast territory of four countries: … .
12. Solovetsky monastery is a medieval … monument.
№4. Match two columns:
| 1 | Krenitsyn volcano | a) 5700 meters in length |
| 2 | Manpupuner Rock Formations | b) 6 km area |
| 3 | The Mirny Diamond Mine | c) 3 km wide |
| 4 | Lake Baskunchak | d) 1324 meters in height |
| 5 | Kungur Ice Cave | e) 1637 meters depth |
| 6 | Chara Sands | f) 40-70 km |
| 7 | Kizhi Pogost | g) 1,25 km across |
| 8 | The Valley of Geysers | h) 15th century |
| 9 | Lake Baikal | i) 7 stone pillars |
| 10 | Lena Pillars | j) 300 years |
| 11 | Altai Mountains | k) 115 square km |
| 12 | Solovetsky Islands | l) 845,000 square km |
№5. Study the material “Passive Voice”:
В английской грамматике существует два залога: действительный (активный) и страдательный (пассивный). Если подлежащее само выполняет действие, мы относим его к категории действительного залога, например, «мама часто печет пироги». В предложении видно, кто именно выполняет действие, поэтому мы переводим его в одном из времен действительного залога, в данном случае - в настоящем простом времени - “mother often bakes cakes”.
Рассмотрим другое предложение, например, «мне часто звонят», или «мне подарили подарок». В данном случае, не ясно кто именно выполняет действие, т.е. звонит и дарит подарок. Не подлежащее выполняет действие, оно испытывает воздействие со стороны другого лица. В страдательном залоге внимание обращают на результат действия.
Для образования форм страдательного залога простых времен (Indefinite / Simple tenses) используется глагол to be + participle II (третья форма глагола). «To be» в данном случае является подвижной частью этой формулы, меняющей свою форму в зависимости от времени, лица и числа подлежащего, а причастие всегда остается неизменным.
В отрицательных предложениях частица not ставится после вспомогательного глагола, а если их несколько, то после первого из них.
В вопросительных предложениях вспомогательный глагол (или первый из них) выносится на место перед подлежащим.
Дополнение в предложении с глаголом-сказуемым в пассивном залоге употребляется с предлогом by или with. Это дополнение соответствует русскому дополнению в творительном падеже без предлога. Дополнение с предлогом by выражает действующее лицо или действующую силу. Дополнение с предлогом with выражает орудие действия.
| Passive Voice |
|
| Simple | Progressive | Perfect | Perfect Progressive |
| Present | am is + V3 are | am is + being V3 are | have + been V3 has |
______ |
| Past | was + V3 were | was + being V3 were |
had been +V3 |
______ |
| Future | shall +be V3 will |
__________ | shall + have been V3 will |
______ |
В страдательном залоге не употребляются следующие глаголы:
Непереходные глаголы, т.к. при них нет объекта, который испытывал бы какое-то воздействие (напр. live, work, arrive)
Глаголы-связки be (быть), become (становиться)
Глагол have
№6. Write the form of participle II (=V3)
say, know, tell, write, complete, build, sit, whitewash, lay, speak, use, answer, place, follow, construct, translate, buy, decorate, found, find, send, develop, listen
№7. Translate into Russian and define the tense:
1. They are sending for the doctor.
2. The doctor is being sent for.
3. He asked me a question.
4. The question was asked.
5. Special attention is being paid to the grammar.
6. This paper has been just received.
7. I will write a letter to my friends in Britain.
8. The letter will be soon written.
9. The tiles are being laid in the bathroom.
10. They are buying the furniture for the kitchen.
11. They will be speaking about this problem with you tomorrow at five.
12. The new apartment house is being constructed in our street.
13. The armchair was placed in the sitting room.
14. They are playing tennis.
15. Football is played in winter in Great Britain.
№9. Translate into English using Passive Voice:
Им задали три трудных вопроса вчера на уроке.
Нам всем дат билеты на выставку каждый год.
Эти журналы должны быть возвращены в библиотеку на следующей неделе.
Ее отправили в больницу два дня назад.
Все ваши сочинения будут возвращены на будущей неделе.
На этой фабрике делают очень красивые сумки каждый день.
Lesson 5
The Past of Our Motherland
№1. Read and translate the text:
Alexander is a Muscovite and he knows a lot about the history of Moscow. Moscow is the capital of Russia and of the Moscow region. It is the administrative centre of the Central district. It is situated on the Moscow River. Moscow is Russia's largest city and the leading economic and cultural centre. Moscow is governed by a city council and a mayor and is divided into boroughs. The heart of Moscow is the Kremlin, a walled city in itself. Its walls represent the city limits as of the late 15th century. The hub of the Russian railway network, Moscow is also a port and has several civilian and military airports.
Adjoining the Kremlin in the east there is Red Square. It originally was a marketplace and a meeting spot for popular assemblies. Red Square is still used as a parade ground and for demonstrations. One of the most wonderful examples of Russian architecture is St Basil's Cathedral. In front of the cathedral there stands a monument to the liberators Minin and Pozharskiy. The village of Moscow was first mentioned in the Russian Chronicles in 1147. And this year it was founded by Yuri Dolgorukiy. In the 15th century Moscow became the capital of the Russian national state, and in 1547 Grand Duke Ivan IV became the first Tsar.
Built largely of wood until the 19th century, Moscow suffered from numerous fires. The most well-known of them occurred during Napoleon's occupation in 1812. Rebuilt, Moscow developed as a major textile and metallurgical centre. During the 19th and early 20th centuries it was the principal centre of the labour movement and social democracy. During World War II, Moscow was the goal of the German offensive. Although the German columns were stopped only about 40 km from the city's centre, Moscow suffered virtually no war damage. The city hosted the Olympic Games in 1980. In the 1990s the city began to attract foreign investment and became increasingly westernized. Many reconstruction projects were launched. Nowadays Moscow is even more beautiful with its modern cafes, shops and offices of European standard.
№2. Are these statements true or false? Correct the false ones:
1. Moscow is governed by a mayor.
2. Moscow has several ports.
3. Minin and Pozharskiy founded Moscow in 1147.
4. The monument to Yuri Dolgorukiy stands in Red Square.
5. St Basil's Cathedral is located within the territory of the Kremlin.
6. The first Russian Tsar was Ivan the Terrible.
7. In the 15th century Moscow became the capital of the Russian Federation.
8. During World War II Moscow was occupied by the German troops.
9. Moscow suffered from numerous fires. The most known of them occurred during World War II.
10. In the 1980s many reconstruction projects were launched.
№3. Put the verbs in the correct form.
1. Prince Yuri Dolgorukiy (to want) to celebrate some successful negotiations and was looking for a place to celebrate a feast. The place (to happen) to be Moscow.
2. In 1237 the Mongols (to burn) the city to ashes.
3. In 1328 Moscow (to earn) the status of capital of the Russian region.
4. In 1571 the Mongols (to attack) the city again and (to burn) in completely.
5. A severe plague (to ruin) the city in 1654 It (to kill) a lot of inhabitants.
6. In 1712 Moscow (to lose) its capital status to St. Petersburg.
7. In 1812 the war with Napoleon (to lead) to big fires in Moscow destroying almost everything.
8. On the 12th March 1918 the City of Moscow (to become) the capital of Soviet Russia.
9. When the USSR (to divide) in the year 1991, the city (to continue) to be the capital of Russia.
10. Moscow (to celebrate) its 850 Anniversary in 1997 and today (to be) one of the more respected cities in the world.
№4. Match the events with their dates:
1. The foundation of Moscow a. 1812
2. The defeat of Tartar hordes b. 1941-1945
3. The capital of the united state c. 1918
4. Moving the capital to St. Petersburg d. the 13th century
5. The main target of Napoleon's attack e. 1147
6. The capital of the revolutionary Russia f. the 16th century
7. The heroic struggle against Hitler's troops g. 1712
№5. Choose and write full right answer:
1. Who baptized Russia?
- Vladimir I
- Alexander I
- Catherine II
- Nicholas II
2. What Russian tsar was called Terrible?
- Vladimir
- Nicholas
- Ivan
- Elisabeth
3. The civil uprising freed Moscow from the Polish in …
- 1612
- 1480
- 1380
- 1812
4. Alexander II is well-known in Russia because:
- he had a lot of wives
- he liberated the peasants
- he won a lot of wars
- he fought against Napoleon
5. What happened in Russia in year 1812?
- The war against the Turkish Empire broke out
- The peasants were liberated
- The war against Napoleon broke out
- The World War I broke out
6. The Russian Revolution took place in:
- 1905
- 1915
- 1917
- 1918
7. Lenin's real first name and surname were:
- Alexander Ivanov
- Vladimir Ulyanov
- Ivan Denisov
- Sergei Kropotkin
8. Why is Mikhail Gorbachev so famous?
- he organized the perestroika
- he organized a great repression
- he started a war in Chechnya
- he was a political dissident
9. What happened during the period of 1991–1993 in Russia?
- economic crisis
- coups d'état attempt
- terrorist attacks
- great repressions
10. When did Putin become a president?
- in 1991
- in 1995
- in 2000
- in 2008
| Passive Voice |
| Present Simple | Past Simple | Future Simple |
| am is + V3 (-ed) are
| was + V3 (-ed) were | shall be + V3 (-ed) will be |
№6. Complete the sentences using Present Simple Passive:
1. English and French…(speak) all over the world.
2. The newspaper ... (deliver) at about 7 o’clock every morning.
3. How often ... (these competitions /hold)?
4. What country... (your car/make)?
5. These goods... (not import) from foreign countries.
6. The classroom ... (decorate) for the party every three months.
7. A lot of invitations ... (send) to our friends.
8. Dinner … (cook) by our parents in the kitchen.
9. The boys ...(ask) to take part in the school concert.
10. Some extra money … (spend) for presents every Christmas.
№7. Complete the sentences using Past Simple Passive:
1.The poem … (write) by Lord Byron.
2. … (this novel/write) by a French or an English writer?
3. When … (your composition/write)?
4. My bike ... (not repair) last week.
5. The album … (record) a month ago.
6. This play … (perform) by the actors perfectly last Sunday.
7. The film … (not direct) by a famous person.
8. Where … (you/ send) after school yesterday?
9. When ... (the telephone/ invent)?
10. A new house … (build) near the sport centre last year.
№8. Open the brackets using Future Simple Passive:
The postbox … (to empty) tomorrow.
The stamps … (to postmark) at the post office next week.
The letters … (to sort) into the different towns soon.
The mail … (to load) into the train next Friday.
The mailbags … (to unload) after their journey in an hour.
The bags … (to take) to the post office tomorrow.
The letters … (to sort) into the different streets in a week.
The letters … (to deliver) tomorrow.
№9. Open the brackets using Simple Passive tenses:
Mushrooms (to gather) in autumn.
We (to invite) to a concert last Saturday.
His new book (to finish) next year.
Many houses (to build) in our town every year.
The dog (to find) by my sister yesterday.
This bone (to give) to my dog tomorrow.
This text (to translate) at the last lesson.
Tom always (to ask) at the lessons.
This work (to do) tomorrow.
This bone (to give) to my dog next week.
Lesson 6
Customs of Russia
№1. Translate the definitions:
Holiday is an official day when you do not have to go to school or work.
Custom is a habit or tradition.
Tradition is a custom or way of behaving that has continued for a long time in a group of people or a society.
Festival is a special day or period when people celebrate something, especially a religious event.
№2. Read and translate the text:
Shrovetide is an ancient festival dating from pagan times. The Christian historians say that those were really "mad" days in the past. People wore funny masks and costumes, sometimes, men wore women's clothing and vice versa. It was a merry festival, when delicious food and a lot of wine was consumed.
Shrovetide or Maslenitsa is the holiday when Russians say “goodbye” to winter and welcome spring. It lasts for a week before Lent. People celebrate it at the end of February or at the beginning of March. At first it was a festival that celebrated the arrival of spring and the start of work on the land. It included a lot of feasts and rituals (burning a doll of straw symbolizing winter, lighting fires, leaving festival food on the ancestors' graves). The main food at Shrovetide were bliny. The fist fighting was one more great fun that helped to get warm or cold winter days.
Later, the Orthodox Church included Shrovetide among its festivals. In Orthodox calendar Shrovetide is called the Cheese Week, a week before Lent, when they don’t eat meat but milk, eggs and cheese are allowed. Holy Church sees the Cheese Week as a week of humility and penitence.
Nowadays it’s time of singing, dancing and fun. People dress up, invite their friends, their nearest and dearest to see each other. People go for sleigh rides, go sledging and play in the snow. People have snow fights, burn bonfires, have a tug-of-war in the snow and lots more. There’s a lot to eat, too – especially blinis (or pancakes). You can eat them with sour cream, fish, caviar or butter, sugar, honey.
№3. Read the text again and decide if the statement is true or false:
1. Before Christianity people celebrated Shrovetide.
2. People sometimes exchanged their clothes.
3. Work in the fields usually began after this holiday.
4. People liked fist fighting because they were brave and strong.
5. The main meal at Cheese Week was BLINY WITH MEAT
6. Shrovetide is an important Orthodox holiday
№4. Answer the questions:
1) What kind of dress did women of common people wear in ХVПI-ХIХ centuries? It was а sleeveless dress with high skirt and stripes. What is it?
2) What kind of shoes, made of straw, wore men and women in ХVП~ХIХ centuries?
3) What kind of famous Russian doll, made of wood, with beautiful decoration can you name? How many pieces does it have?
4) What famous dishes from Russian cuisine do you know?
5) What is the name of special Russian kettle, which is used for boiling water for tea in ХVП-ХIХ centuries?
№4. Read the text and fill the gaps using the words: celebrate, singing, chickens, bucket, hidden, wearing, white, bunny, Santa, Easter.
Christians 1) ____ the resurrection of Christ on Easter Sunday/ Many churches hold Easter 2) _____ services. Churches are decorated with 3) ____ lilies and are filled with people 4) _____ new Easter outfits. The choir and congregation join in. 5) ____ special hymns of joy. For many children the excitement of receiving an Easter 6) ____ filled with goodies and hunting for eggs 7) ____ by the Easter rabbit is topped only by the excitement of receiving gifts from 8) ____ at Christmas. Did you ever wonder why the Easter 9) ____ brings the eggs instead of the Easter chicken? After all, 10) ___ not rabbits lay eggs.
№5. Match the holidays and their descriptions:
| New Year’s Eve is a night when … | … people honour women by giving them flowers and presents. |
| April 1st is a day when … | … people play tricks on friends. |
| February 23rd is a holiday when … | … pupils and students start the new academic year. |
| March 8th is a day when … | … people in our country honour workers. |
| Victory Day is a holiday when … | … people have parties and stay up until midnight to see the new year in. |
| September 1st is a day when … | … people have parades and ceremonies to honour those who died in the Great Patriotic War. |
| Easter is a religious holiday when … | …people honour members of the armed forces. |
| Labour Day is a holiday when… | … many people have gatherings eating dyed eggs, paskha and kulich. |
| Christmas is a religious holiday when… | … people have parties, light candles and give each other gifts. |
№6. Read the text and answer the questions:
Almost every nation and country have a reputation of some kind. First, let’s speak about Russian people. The main traits of their characters that differ them from other people are hospitality, their «open heart», «golden hands», and wise Russian fairy-tales reflect this wisdom. Our people are hardworking, patient, never loosing hope for better life. The Russians are talented people. Russia gave the world-famous names of Pushkin and Lermontov, Chaikovsky and Repin, thousands of names of world-famous poets, writers, composers, scientists. All of them are the pride of the nation because they sang the beauty of our nature and people.
Our country is famous for Russian traditional specific crafts and its skilled craftsmen. Painted boxes of Palekh, coloured shawls of Pavlov Posad, clay toys of Dymkovo, laces of Vologda are known all over the world. The names of Gzhel and Khokhloma are considered to be the symbols of Russia as well as matryoshkas and samovars. The history of Khokhloma goes back into the 17th century. Producing of tableware - dishes, spoons, mugs was begun at that time in the villages of Syomino and Khokhloma in the Nizhny Novgorod Province, on the banks of the great Russian river Volga. Many carpenters, painters have been working since then reviving traditions of old masters. The Khokhloma style is characterized by using plant elements in painting the tableware. The prevailing colours are black, yellow, golden, green and red. And nowadays this craft is sure to be saved, it will be developed and brought into the future by the new generation of painters.
Now we celebrate the forgotten holidays - Troitsa, Maslenitsa, the Easter. We again sing Russian folk songs and chastushki, dance Barinya and perform khorovods, ride in troikas. Traditional Russian cooking is world-famous for such dishes as okroshka, shi, pelmeni, kurnik, kvas. We begin to build and reconstruct churches. The example of it is the building of the Cathedral of Christ the Saver in Moscow. It is the symbol of reviving human feelings, national pride and patriotism.
What are the main traits in Russian people’s character?
What specific Russian crafts do you know?
What is Khokhloma style characterized by?
What is traditional Russian cooking?
№7. Change the underlined active verbs into the passive form:
Adam hit the ball. - The ball was hit by Adams.
Someone is ringing the bell. - The bell ………………………
Mom washes the carpet. - The carpet ………………… by Mom.
Children should drink milk. - Milk ……………………… by children.
I have paid my checks. - Checks …………………………… by me.
Tim will write a story. - A story ………………………… by Tim.
Tom needs to do this work. - This work needs ……………
Dina may invite some friends. - Some friends ……………… by Dina.
№8. Change the following sentences from active into passive:
1. The lawyer will give you some advice.
2. Sue asked the policeman for directions.
3. The pirates had found the treasure.
4. Peter is going to take the package later.
5. Someone has already stopped the machine.
6. The coach always encourages the trainees.
7. Meg needs to wipe the floor right now.
8. The employees might suggest new rules.
№9. Change the following negative sentences from active into passive:
1. We didn’t notice the new changes.
2. The store won’t deliver the furniture.
3. They haven’t collected the taxes yet.
4. The students didn’t study the poem well.
5. We don’t accept credit cards here.
6. Tim wasn’t planting trees at seven.
7. You shouldn’t water this plant daily.
8. They are not interviewing the applicants.
№10. Change the following questions from active into passive:
1. Did the driver hit the boy yesterday?
2. Will the police question all the suspects?
3. Have you signed the house contract?
4. Do people speak English in Spain?
5. Who broke the vase in the sitting room?
6. Are you roasting chestnuts now?
7. Can you reach the top of this mountain?
8. Was Jim playing the piano very loudly?

























