Министерство здравоохранения Красноярского края
краевое государственное бюджетное
профессиональное образовательное учреждение
«Дивногорский медицинский техникум»
Методическая разработка комбинированных уроков
по дисциплине «Английский язык»
для специальностей 34.02.01 Сестринское дело
Раздел 7: Первая медицинская помощь при неотложных состояниях.
Разработчик:
Рыжкова Наталья Сергеевна,
преподаватель английского языка
Дивногорск 2022
В настоящем методическом пособии представлены методическая разработка и дидактические материалы для студентов для проведения комбинированных уроков по теме: Первая медицинская помощь при неотложных состояниях дисциплин "Иностранный язык - английский" в структуре подготовки специалистов среднего звена по специальности 34.02.01 Сестринское дело на 3 курсе в 6 семестре.
Содержание:
Пояснительная записка…………………………………………………………...4
Bleeding 9
Fainting 10
Burns 12
Poisoning 14
Insect bites and strings 17
Fractures 21
Sunstroke 24
Список литературы 26
Пояснительная записка
Уважаемые студенты!
Настоящее методическое пособие разработано для практических занятий по теме: «Первая медицинская помощь при неотложных состояниях», в соответствии с рабочей программой дисциплины «Иностранный язык (Английский) на 3 курсе 6 семестре, в соответствии требованиям ФГОС СПО, учебного плана техникума по специальности 34.02.01 Сестринское дело.»
Пособие включает перечень профессиональных текстов, практических заданий по темам, лексический материал.
Целью данного методического пособия научить студентов использовать иностранный язык как средство получения, расширения и углубления системных знаний по специальности, а также как средство формирования навыка повседневного и профессионального иноязычного общения.
Исходя из данной цели, основными задачами самостоятельной работы студентов по иностранному языку являются:
уметь
- общаться (устно и письменно) на английском языке на профессиональные и повседневные темы;
- переводить (со словарем) английские тексты профессиональной направленности;
- самостоятельно совершенствовать устную и письменную речь, пополнять словарный запас.
знать
- лексический (87 лексических единиц) и грамматический минимум, необходимый для чтения и перевода со словарем иностранных текстов профессиональной направленности.
Освоенные Вами умения и знания по теме помогут Вам в формировании общих и практических компетенций, таких как:
ОК 4. Осуществлять поиск и использование информации, необходимой для эффективного выполнения профессиональных задач, профессионального и личностного развития.
ОК 5. Использовать информационно-коммуникационные технологии в профессиональной деятельности.
ОК 6. Работать в коллективе и команде, эффективно общаться с коллегами, руководством, потребителями.
ПК 1.1. Проводить мероприятия по сохранению и укреплению здоровья населения, пациента и его окружения.
ПК 1.2. Проводить санитарно-гигиеническое просвещение населения.
ПК 2.2. Осуществлять лечебно-диагностические вмешательства, взаимодействуя с участниками лечебного процесса.
ПК 2.3. Сотрудничать с взаимодействующими организациями и службами.
ПК 2.7. Осуществлять реабилитационные мероприятия.
ПК 2.8. Оказывать паллиативную помощь.
ПК 3.1. Оказывать доврачебную помощь при неотложных состояниях и травмах.
ПК 3.2. Участвовать в оказании медицинской помощи при чрезвычайных ситуациях.
ПК 3.3. Взаимодействовать с членами профессиональной бригады и добровольными помощниками в условиях чрезвычайных ситуаций.
Методические требования к заданиям по чтению и переводу профессионально-ориентированных текстов:
Критерии оценки: За перевод текста и ответы на вопросы студент может получить максимум 5 баллов. При оценке текста преподаватель обращает внимание на беглость чтения, точность перевода и правильность ответов на вопросы. Под точностью перевода понимают не буквальный (дословный), а адекватный перевод. Адекватный перевод – это точная и полная передача смыслового содержания иностранного текста средствами русского языка. Если студент допускает большое количество ошибок при переводе и ответах на вопросы, ему разрешается выполнить задание еще раз.
Различные виды чтения контролируются при устном собеседовании по прочитанному тексту, или при проверке выполненных упражнений к тексту в тетради студентов.
2. Выполнение лексико-грамматических упражнений (закрепление полученных знаний происходит, например, при ответе на вопросы по содержанию, выборе правильных ответов, при нахождении эквивалентов русских слов и выражений в иноязычном тексте, при выписывании тематической лексики, при заполнении пропусков недостающими фразами из текста и т.д.);
Методические требования к лексико-грамматическим заданиям:
Критерии оценки: Задания по грамматике иностранного языка должны быть представлены в письменном виде. За выполнение заданий этого типа студент может получить максимум 5 баллов (каждое задание содержит по 10 предложений, т.е. одно правильно выполненное предложение оценивается в 0.5 балла). При проверке заданий по грамматике исправляются все ошибки, но учитываются ошибки только на контролируемую тему.
Если студент допустил большое количество ошибок, ему разрешается выполнить работу еще раз.
Текущий контроль осуществляется через проверку тетрадей с домашним заданием. Проверяется усвоение лексико-грамматического материала по темам.
Промежуточный контроль предполагает выполнение студентами лексико-грамматических тестов 1 раз в семестр.
3. Овладение лексическим минимумом специальности (при усвоении определенного объёма профессиональной лексики);
Требования к овладению лексическим минимумом специальности:
При проверке лексического минимума, студент отвечает устно (где проверяется произношение слов и выражений) и письменно (где проверяется орфография и словообразование).
Критерии оценки: Методические требования к умению применять усвоенную профессиональную лексику в диалогической и монологической речи:
За задания данного типа студент может получить максимум 5 баллов. Задания на проверку навыков устной речи проверяются с использованием следующих оценочных шкал:
| Тип задания | Проверяемые умения | Требуемый объем | Критерии оценивания |
| Монологическое высказывание | Умение высказываться по теме в виде монолога, лично построить своё высказывание в соответствии с поставленной коммуникативной задачей | 10 -15 фраз | Решение коммуникативной задачи (содержание) -1 балл
Взаимодействие с собеседником -1 балл
Лексическое оформление речи -1 балл
Грамматическое оформление речи -1 балл
Произношение -1 балл |
| Диалог | Умения начать, поддержать и закончить беседу, предлагать варианты к обсуждению, выражать свою аргументированную точку зрения и отношение к обсуждаемому вопросу, принимать совместное решение | Не менее 10 реплик |
Методические требования к заданиям творческого характера:
Творческие задания или проекты оцениваются при защите. Защита проекта может проходить в различных формах:
- Устная презентация созданного продукта.
- Показ созданного видеофильма.
- Выпуск стенгазеты.
Критерии оценки выполнения проекта (демонстрации и защиты презентации):
Максимальная оценка – 5 баллов:
- соблюдение структуры презентации;
- соблюдение соотношения текстовой части и иллюстраций;
- соблюдение требований к тексту
- соответствие иллюстраций содержанию текста
- выступающий ясно и четко излагает тему, не читает со слайдов, отвечает на вопросы.
BLEEDING
Words:
-
bleeding - кровотечение
-
severe - тяжелый
-
loss - потеря
-
case - случай
-
blood transfusion - переливание крови.
Bleeding can lead to a severe loss of blood. The best way to stop bleeding is by direct pressure with a clean cloth. If the bleeding is from the arm or the leg, the limb can be kept in a raised position. If the bleeding is from a nose, put a cold compress on the nose. It will stop the blood. Ice placed on the nose also stops bleeding. In severe case doctors make blood transfusion.
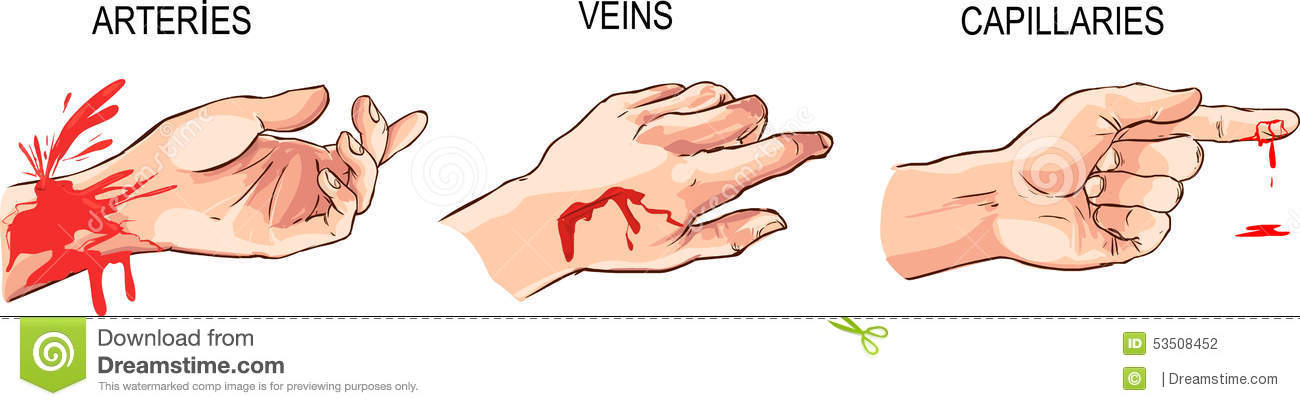
-
Spurting blood
-
Pulsating flow
-
Bright red color
-
Steady
-
Slow flow
-
Dark red color
-
Slow, even flow
-
Bright red color
Ex.1 Find English equivalents.
лучший способ остановить кровотечение, потеря крови, чистая ткань, поднятое положение, кровотечение из носа, остановить кровотечение, переливание крови.
Ex.2 Find Russian equivalents.
Bleeding from the arm or the leg; cold compress; severe case; severe loss of blood; direct pressure; to put a compress on
Ex.3 Answer the questions.
-
What can lead to a severe loss of blood?
-
What is the best way to stop the bleeding?
-
What do the doctors in severe cases?
Ex.4 Describe the picture.
1.

2.
Ex.5 Make your «First Aid Guide».
FAINTING
Words:
-
fainting - обморок
-
cause - причина; вызывать
-
emotion - душевное волнение
-
want of food - голод
-
fatigue - усталость
-
lose consciousness - терять сознание
-
brain - мозг
-
to feel dizzy - чувствовать головокружение
-
weak - слабый
-
shallow - поверхностный
-
slow - медленный
-
to lay - (laid) положить
-
flat - плоско
-
to loose - зд. ослабить
-
to cover - покрывать
-
to sprinkle - брызгать
-
sweat - пот, испарина
-
ammonia - нашатырный спирт.

The cause of fainting may be different: strong emotion, want of food, fatigue or pain. In fainting person loses consciousness. Blood doesn't get to the brain. The face of a person before fainting gets very pale and sweat appears on his forehead. He feels dizzy and weak. His breathing is shallow. His pulse is weak and slow.
If you help a person who lost his consciousness:
-
Lay the person flat on his back.
-
Raise his feet a little.
-
Loose his dress.
-
Cover him warmly and open the window.
-
Sprinkle cold water on his face.
-
Give the person to breathe in ammonia water.
Ex.1 Find English equivalents.
Сильные эмоции; терять сознание; кровь не поступает в мозг; лицо становится бледным; уложить на спину; поднять ноги; побрызгать водой; ослабить одежду; тепло укрыть.
Ex.2 Find Russian equivalents.
the cause of fainting; wait of food; the face gets pale; sweat appears; he feels diszy; shallow breathing; weak pulse; slow pulse
Ex.3 Answer the questions.
-
What may be the cause of fainting?
-
What does person lose in fainting?
-
What appears on his forehead before fainting?
-
What does person feel?
-
How can you help a person who lost his consciousness?
Ex.4 Read and play the dialogues.
Ann: What’s the matter with you?
A man: I was fishing here, suddenly I saw a fish and ran to catch it, fell down and couldn’t stand on my leg
Ann: Bad luck! What do you complain of?
A man: I feel a pain my foot is out of joint.
Ann: You look pale. Keep your spirits. Thing will come right. I’ll put a splint for the broken limb and call in an ambulance.
Sweta: What is the cause of fainting?
Ann: There are many causes: strong emotion, want of food, fatigue or pain and soon.
Sweta: What is the way to help the person?
Ann: Lay a person flat on his back, raise his head a little, loose his dress, cover him warmly and open the window. Sprinkle cold water on his face. Give the person to breathe in ammonia water a rub his temples.
Sweta: Thank you. I think I must call in an ambulance.
Ex.5 Make your «First Aid Guide».
BURNS

Words:
-
burn - ожог
-
electric fire- электрический камин
-
to catch fire - загораться
-
scream - крик
-
flame - пламя
-
carpet - ковер
-
to go out - потухать
-
piece - кусок
-
burnt - сожженный
-
clothes - платье, одежда
-
ambulance - машина скорой помощи
-
to wrap - завертывать
-
tablecloth - скатерть
-
to heal - заживлять, излечивать
Burns are caused by the dry heat from flames, electricity, lighting, chemicals and radiation (for example, in sunburn). Scalds are caused by moist heat from boiling liquids or steam. Burns and scalds are serious injuries and can result in infection, scarring and, in extreme cases, death.
Signs and symptoms:
• Skin looks red and blistered if only the outer layers are affected
• Skin looks dark red, blackened or charred if all the layers of skin are burnt
• Pain if the burn or scald is superficial, but it may be absent if nerve ends have been damaged
• Shock if burns or scalds are extensive.
Action:
1. Remove the casualty from danger and the source of heat if you can do so
without becoming a casualty yourself.
2. If the casualty’s clothes are on fire, protect yourself by holding a blanket or rug in front of yourself as you approach him or her.
3. If the casualty is unconscious, place him or her in the recovery position, check the airway, breathing and pulse and begin AR or CPR if necessary.
4. Carefully remove clothing, jewellery from the affected area.
5. Cool the burnt area with cold, but not icy, water, ideally by placing the burn under gently running water for at least 10 minutes.
6. Cover the burn with a sterile, non-adherent dressing, and then lightly apply a bandage.
7. If the casualty is conscious and thirsty, give him or her water to sip slowly.
8. Rest the casualty comfortably, supporting any burnt limb
9. For all expect minor burns and scalds, seek medical aid immediately
Ex.1 Read the text.
John's mother stood near the electric fire and her dress caught fire. John heard her scream and ran into the room. "Lie down!" he ordered and covered the flame with a carpet. The flames went out without air. "Don't worry, mother," he said. "You'll be all right."
"Do not take the pieces of burnt dress off your leg. Get into the bath with your clothes on." John helped her.
"Keep your leg under the water for ten minutes," he said. He telephoned for an ambulance." When John's mother got out оf the bath, he wrapped her leg in a clean cotton tablecloth. Every 10 minutes he gave her drink. Soon the ambulance came and took her to hospital. Because John knew First Aid for burns his mother was not badly hurt and her leg soon healed.
Ex.2 Find English equivalents.
Одежда загорелась; вбежал в комнату; без воздуха; держать ногу под водой; позвонить в скорую; давать пить каждые 10 минут.
Ex.3 Find Russian equivalents.
Lie down; to cover the flame; to wrap the leg in a clean cotton tablecloth; to take to the hospital; First Aid for burns; badly hurt
Ex.4 Answer the questions.
-
Why did John's mother scream?
-
What did John order?
-
What did he say about the pieces of burnt dress?
-
What did he say about mother’s leg?
Ex.5 Describe the picture.
Ex.6 Make your «First Aid Guide».
POISONING
Words:
-
swallow - глотать
-
inject – впрыскивать, вводить
-
to be exposed – подвергаться воздействию
-
harmful – вредоносный, опасный для здоровья
-
occur by accident – происходить случайно
-
carbon monoxide gas – угарный газ
-
over-the-counter – продаваемые без рецепта
-
illicit – незаконный
-
household – домашний
-
airway – дыхательный путь
-
rescue breathing – искусственное дыхание
-
CPR - СЛР, сердечно-лёгочная реанимация (искусственное дыхание и закрытый массаж сердца)
-
empty – опустошать
-
stomach – желудок
-
fume – газ, пар, испарения

Poisoning is caused by swallowing, injecting, breathing in, or otherwise being exposed to a harmful substance. Most poisonings occur by accident.
Immediate first aid is very important in a poisoning emergency. The first aid you give before getting medical help can save a person's life.
Items that can cause poisoning include: carbon monoxide gas, certain foods, chemicals in the workplace, drugs, including over-the-counter and prescription medicines (such as an aspirin overdose) and illicit drugs such as cocaine, cleaning products, household and outdoor plants (eating toxic plants), insecticides, paints
First Aid. Seek immediate medical help!
For poisoning by swallowing:
-
Check and monitor the person's airway, breathing, and pulse. If necessary, begin rescue breathing and CPR.
-
Try to make sure that the person has indeed been poisoned. It may be hard to tell. Some signs include chemical-smelling breath, burns around the mouth, difficulty breathing, vomiting, or unusual odors on the person. If possible, identify the poison.
-
Do NOT empty person’s stomach unless told to do so by a health care professional.
-
If the person vomits, clear the person's airway. Wrap a cloth around your fingers before cleaning out the mouth and throat. If the person has been sick from a plant part, save the vomit. It may help experts identify what medicine can be used to help reverse the poisoning.
-
If the person starts having convulsions, give convulsion first aid.
-
Keep the person comfortable. The person should be rolled onto the left side, and remain there while getting or waiting for medical help.
-
If the poison has spilled on the person's clothes, remove the clothing and wash the skin with water.
For inhalation poisoning:
-
Call for emergency help.
-
If it is safe, open windows and doors to remove the fumes.
-
Take several deep breaths of fresh air, and then hold your breath as you go in. Hold a wet cloth over your nose and mouth.
-
Do not light a match or use a lighter because some gases can catch fire.
-
After rescuing the person from danger, check and monitor the person's airway, breathing, and pulse. If necessary, begin rescue breathing and CPR.
-
If necessary, perform first aid for eye injuries or convulsion first aid.
-
If the person vomits, clear the person's airway. Wrap a cloth around your fingers before cleaning out the mouth and throat.
-
Even if the person seems perfectly fine, get medical help.
Ex.1 Find English equivalents.
Обмотайте ткань вокруг пальца, кусочки растений, проверьте и следите за дыхательными путями человека, химический запах дыхания, необычный запах, проверить пульс, первая помощь при конвульсиях, нелегальные наркотики, человек выглядит в порядке.
Ex.2 Find Russian equivalents.
occur by accident, over-the-counter and prescription medicines, burns around the mouth, identify, wash the skin with water, deep breaths of fresh air, first aid for eye injuries, clean out the mouth and throat
Ex.3 Answer the questions.
-
What can cause the poisoning?
-
What to do if the poison has spilled on the person's clothes?
-
What to do if the person vomits?
-
Do you need to keep the person comfortable?
-
What to do if the person starts having convulsions?
Ex.4 Read and retell the text.
A doctor was invited to see a family of three persons. Approximately, half an hour before the attack of illness all of them had eaten some food which was evidently not quite fresh.
All the members of the family became nauseated; they vomited and had violent pains in the stomach. At the examination food poisoning was diagnosed. Gastric lavage with large amounts of boiled water was instituted immediately. Two patients were put to bed and given some medicine. Heating pans were applied to their feet .They obtained almost immediate relief and were allowed get up.
The third patient was taken to the hospital in an ambulance. He was retained there because of persistent nausea, vomiting, diarrhea and marked prostration. A strict diet, bed regime and a proper therapy helped the patient and in a week he was discharged from the hospital in a good condition.
NOTES
1. approximately– приблизительно, примерно
2. attack – приступ
3. evidently – очевидно
4. nauseate – тошнить
5. vomit – рвать
6. violent – сильный
7. gastric lavage – желудочный зонд
8. heating pans – грелки с горячей водой
9. prostration – бессилие, слабость
10. to be discharged – быть выписанным
Ex.1 Put in order.
1. To see, a family, a doctor, of three persons, was invited.
2. Their feet, to, heating, were applied, pans.
3. To the hospital, in an ambulance, third, was taken, the patient.
4. Became, all, of, nauseated, the members, the family.
5. Were, two, to, some, patients, bed, and put, medicine, given.
Ex. 2 Translate the sentences, using the text.
Осмотреть семью из 3-х человек; примерно за полчаса до начала болезни; не совсем свежий; сильные боли в желудке; большое количество кипяченой воды; быстрое облегчение; постоянная тошнота; постельный режим.
Ex.3 Answer the questions. 1. What happened to the family of three persons? 2. Had they eaten some food which was not fresh? 3. What did they complain of? 4. What kind of medicine did they take? 5. Why did they obtain immediate relief? 6. What did they use to become healthy again? 7. When was the third patient discharged?
Ex.4 Say it in English.
Что с вами случилось? Вы плохо выглядите. Что вы ели за обедом? Была ли пища свежей? Какая у вас температура? Вам необходимо остаться в постели. Примите лекарство. Вас необходимо госпитализировать. У вас понос? Вы должны соблюдать строгую диету, постельный режим и правильное лечение. Через неделю вас выпишут.
Ex.5 Put the words according to the text:
1. A doctor was…to see a family. 2. The family became… 3. Two patients were… and given some medicine. 4. The third patient was… in an ambulance. 5. In a week he was… from the hospital in a good condition.
Ex.6 Make your «First Aid Guide».
INSECT BITES AND STRINGS

Words:
-
fire ant-муравей
-
wasp-оса
-
hornet- шершень
-
mite-клещ
-
numbness-онемение
-
tingling-покалывание
-
stinger-жало
-
venom sac-мешочек с ядом
-
hive- улей
-
emergency kit-аптечка
-
floral-patterned-узор на ткани в виде цветов
Insect bites and stings can cause an immediate skin reaction. The bite from fire ants and the sting from bees, wasps, and hornets are usually painful. Bites caused by mosquitoes, fleas, and mites are more likely to cause itching than pain. Insect and spider bites cause more deaths from poisoning than bites from snakes.
Considerations. In most cases, bites and stings can be easily treated at home.
Some people have extreme reactions that require immediate medical treatment to prevent death.
Certain spider bites, such as the black widow or brown recluse, can be serious and life-threatening. Most spider bites, however, are harmless. If bitten by an insect or spider, bring it for identification if this can be done quickly and safely.
Symptoms. Symptoms depend on the type of bite or sting. They may include pain, redness, swelling, itching, burning, numbness, tingling
Some people have severe, life-threatening reactions to bee stings or insect bites. This is called anaphylactic shock. This condition can occur very quickly and lead to rapid death if not treated quickly.
Symptoms of anaphylaxis can occur quickly and affect the whole body. They include: chest pain, face or mouth swelling, difficulty swallowing, difficulty breathing.

First Aid
For severe reactions:
-
Check the person's airways and breathing. If necessary, call ambulance and begin rescue breathing and CPR.
-
Reassure the person. Try to keep him or her calm.
-
Remove nearby rings and constricting items because the affected area may swell.
-
Use the person's EpiPen or other emergency kit, if they have one. (Some people who have serious insect reactions carry it with them.)
-
If appropriate, treat the person for signs of shock. Remain with the person until medical help arrives.
General steps for most bites and stings:
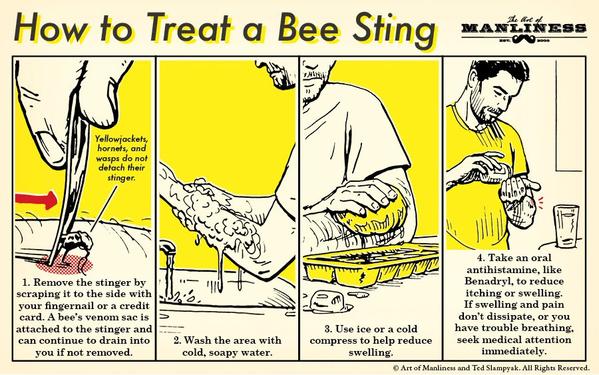
- Remove the stinger by scraping the back of a credit card or other straight-edged object across the stinger. Do not use tweezers -- these may squeeze the venom sac and increase the amount of venom released.
- Wash the site thoroughly with soap and water.
- Place ice (wrapped in a washcloth) on the site of the sting for 10 minutes and then off for 10 minutes. Repeat this process.
-If necessary, take an antihistamine, or apply creams that reduce itching.
-Over the next several days, watch for signs of infection (such as increasing redness, swelling, or pain).
DO NOT
-
Do NOT apply a tourniquet.
-
Do NOT give the person stimulants, aspirin, or other pain medication unless prescribed by the doctor.
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Call 911 of your local emergency number if someone with a sting has the following symptoms:
-
Trouble breathing, wheezing, shortness of breath
-
Swelling anywhere on the face or in the mouth
-
Throat tightness or difficulty swallowing
-
Feeling weak
-
Turning blue
If you had severe, body-wide reactions to a bee sting, your doctor should send you to an allergist for skin testing and therapy. You should receive an emergency kit to carry with you wherever you go.
Prevention
-
Avoid rapid, jerky movements around insect hives or nests.
-
Avoid perfumes and floral-patterned or dark clothing.
-
Use appropriate insect repellants and protective clothing.
-
Use caution when eating outdoors, especially with sweetened beverages or in areas around garbage cans, which often attract bees.
-
If have severe allergies to insect bites or stings, you should have an emergency kit and EpiPen. Make sure your friends and family know how to use it if you have a reaction.
Ex.1. Find English equivalents.
укусы насекомых и жалящих; блохи и клещи; пауки; можно вылечить в домашних условиях; безвредный; предоставить для опознания; скоропостижная кончина; близлежащие кольца; тщательно вымыть водой с мылом; признаки инфекции; повязка; резкие движения; сладкие напитки; шприц с дозой антидота; убедиться, что друзья и семья знают.
Ex.2. Find Russian equivalents.
immediate skin reaction; to have extreme reactions; redness, swelling, itching, burning, numbness, tingling; if not treated quickly; airways and breathing; person's EpiPen; tweezers; scraping the back of a credit card; to apply creams that reduce itching; throat tightness; turning blue; to use appropriate insect repellants.
Ex.3. Answer the questions.
-
What can insect bites and stings cause?
-
What bite is usually painful, cause itching?
-
Certain spider bites, such as the black widow or brown recluse, can be serious and life-threatening, can’t they?
-
Can a bite cause anaphylactic shock?
-
What are the symptoms of anaphylactic shock?
-
Do you know the first aid at severe reactions?
-
Why is it prohibited to apply a tourniquet or give person stimulants?
-
What are the special signs in patient’s condition for contacting a medical professional?
-
How can a person prevent insect bites and stings?
Ex. 4 Check out the posters and discus it.

Ex.5 Make your «First Aid Guide».
FRACTURES
Words:
1. fracture – перелом
2. to break – ломать, перелом
3. bone – кость
4. closed – закрытый
5. open – открытый
6. to complain of – жаловаться на
7. to move – двигаться
8. comminuted fracture – оскольчатый перелом
9. single fracture – единичный перелом
10. greenstick fracture – прелом по типу зеленой веточки
11. complete fracture – полный перелом
12. to appear – появляться
13. splint – шина
14. to bind - перевязывать
15. X-rays – рентгеновы лучи
16. plaster cast – гипсовая повязка
17. limb – конечность
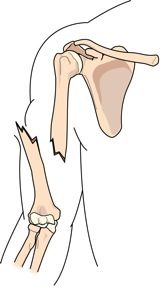
Your bones are tough stuff — but even tough stuff can break. Like a wooden pencil, bones will bend under strain. But if the pressure is too much, or too sudden, bones can snap. You can break a bone by falling off a skateboard or crashing down from the monkey bars. When a bone breaks it is called a fracture. The word “fracture” means a break in a bone.
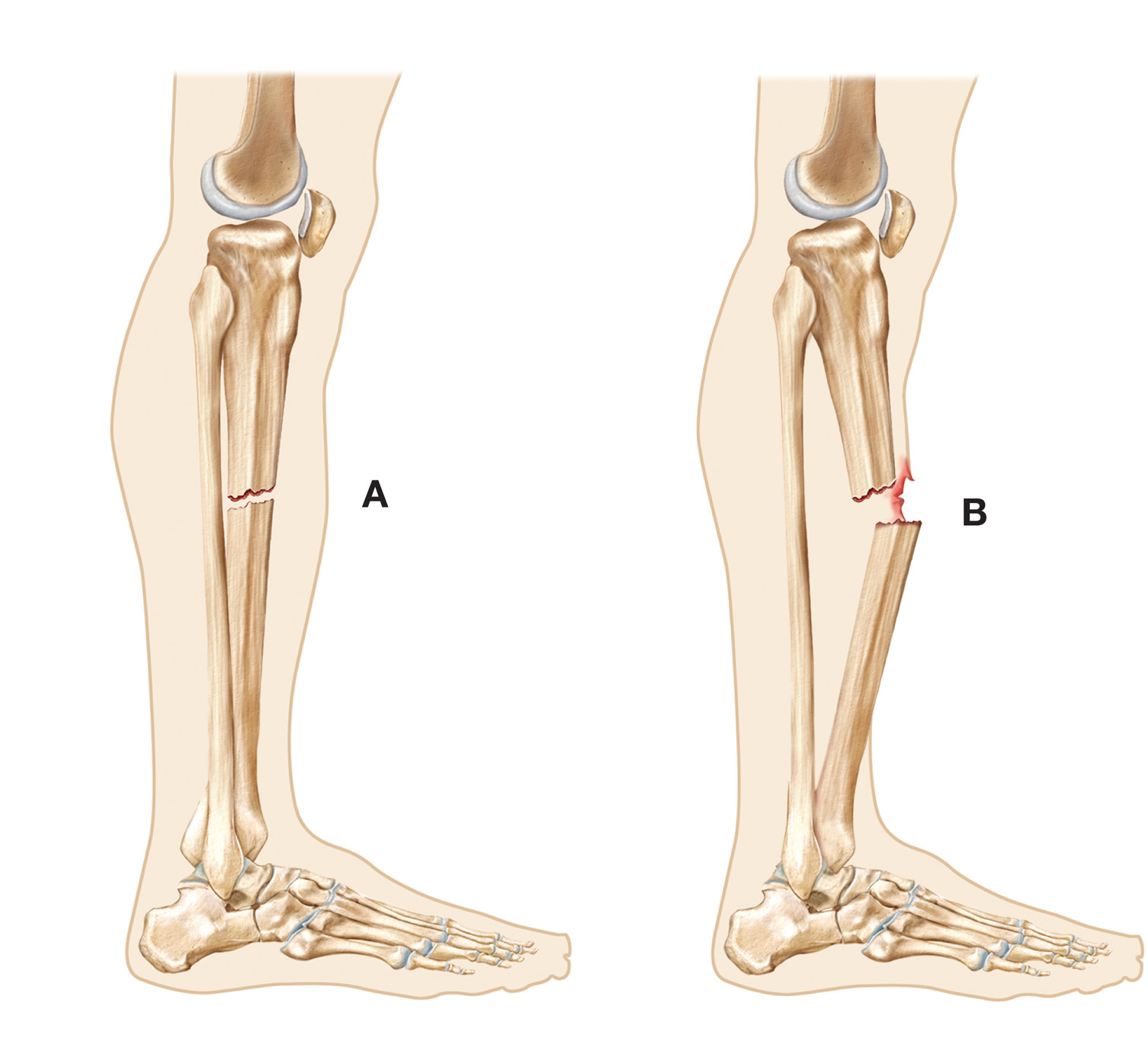
There are two kinds of fractures: closed and open. In a closed fracture there is no wound on the skin. In an open fracture there is a wound. Open fractures are more serious than closed ones.
Doctors describe fractures in the following ways:
-
A complete fracture is when the bone has broken into two pieces.
-
A greenstick fracture is when the bone cracks on one side only, not all the way through.
-
A single fracture is when the bone is broken in one place.
-
A comminuted fracture is when the bone is broken into more than two pieces or crushed.
-
A bowing fracture, which only happens in kids, is when the bone bends but doesn't break.
If a person breaks his arm or leg he complains of pain in the place of the break. The pain becomes more severe if he presses the place or tries to move. If you think you or someone else has broken a bone, the most important things to do are to:
-
stay calm
-
make sure the person who is hurt is as comfortable as possible
-
do not let the person move
-
use a splint for the broken limb
-
bind the splints to the limb but not at the place of the fracture
-
call the emergency number in your area
One super-important tip: If you're not sure what bone is broken or you think the neck or back is broken, do not try to move the injured person. Wait until a trained medical professional has arrived.
Doctors use X-rays to see the break and put plaster casts on the broken limbs. The special bandage that will keep the bone in place for the 1 to 2 months it will take for the break to mend.
Ex.1 Find English equivalents.
Нет раны на коже, более серьёзный, жаловаться на боль, становиться более сильной, пытаться двигаться, не позволяйте, наложите шину, на сломанные конечности.
Ex.2 Find Russian equivalents.
To bend under strain, by falling off a skateboard, a break in a bone, more serious, a wound on the skin, an open fracture, a closed fracture, a comminuted fracture, a single fracture, a greenstick fracture, a complete fracture, to see the break, to put plaster casts/
Ex.3 Answer the questions.
1. What does the word “fracture” mean?
2. What kinds of fractures do you know?
3. What fracture is more serious?
4. When does the pain become more severe?
5. How can you help the person with fracture?
6. What do the doctors do with fractures?
Ex.4 What kind of fractures do you see?
Ex.5 Make your «First Aid Guide».
SUNSTROKE

Words:
1. sunstroke – солнечный удар
2. dry – сухой
3. headache – головная боль
4. to cool – охлаждать
5. sponge – губка
6. to keep up – поддерживать
7. blood circulation - кровообращение
It is very dangerous to fall asleep in the open air when the sun is hot or to be in the hot sun for a long time without a hat. You may get sunstroke.
When a person has sunstroke, he has a high temperature. His skin is very hot, dry and red. He has a bad headache ant can even lose consciousness. Sunstroke can cause death. One must avoid walking in excessive heat conditions during the summers. It is important to stay cool.
If you help a person who has sunstroke:
1. Take the patient into a cool and shady place.
2. Put him on his back.
3. Raise his head and shoulders a little.
4. Put cold cloth on his head.
5. Cool his body with cold water.
6. Rub his skin with a sponge to keep up blood circulation.
If you are suffering heatstroke alone:
1. Get into a shady, cool (preferably air-conditioned) area.
2. Call emergency services. Even if you still feel like you are hanging in there, you may start going into shock and be unable to call for help when you really need it. Prolonged heat stroke damages the brain, heart, kidneys, and muscles, so it’s better to be safe than sorry.
3. Remove any extra clothing (hat, shoes, socks) to aid in the cooling process.
4. Get in a cold bath, shower, stream, or pond if possible. Otherwise, put a cool, wet rag on the back of your neck, on your groin, and/or in your armpits. If you can, mist and fan yourself to promote evaporative cooling.
5. Lie down and raise your feet by about a foot (30cm). This will help you avoid potential shock.
6. Replenish your fluids and electrolytes. If you have it, slowly sip Gatorade to counteract both dehydration and the loss of salts through sweating, but don’t drink quickly or you could induce shock. If you don’t have Gatorade, sip plain water; trying to hunt down the right beverage in a panic will hurt more than help.
7. Calm yourself. Minimize your agitation by breathing deeply and focusing your thoughts away from what is happening to you.
During the summer, we try to go to the sea to get a welcome dose of sunshine and warmth. To make sure we stay undamaged, we must be aware of the danger of heat or sunstroke in advance and take the necessary measures.
Ex.1 Find English equivalents.
На открытом воздухе, высокая температура, сухая красная кожа, сильная головная боль, потерять сознание, перенести в прохладное помещение, слегка приподнять голову, обтереть кожу губкой, принять холодный душ, поднять ноги на 30 см., успокойтесь, восполните недостаток жидкости, жаловаться, остаться невредимым.
Ex.2 Find Russian equivalents.
In the open air, the sun is hot, to get a sunstroke, a high temperature, to lose consciousness, a cool and shady place, blood circulation, to start going into shock, to raise your feet, replenish your fluids, to get a welcome dose, necessary measures.
Ex. 3 Answer the questions.
1. What symptoms of sunstroke do you know?
2. Have you ever had a sunstroke?
3. What must we do to help a person who has a sunstroke?
4. Can sunstroke cause death?
5. What must you do if you are suffering heatstroke alone?
Ex.4 Make your «First Aid Guide».
Список литературы:
-
Козырева Л.Г. Английский для медицинских колледжей и училищ: учебное пособие.- Р/н/Д: Феникс, 2017
-
Марковина И.Ю. Английский язык. Вводный курс [Электронный ресурс] : учебник.- М.: ГЭОТАР-Медиа, 2016.
-
Марковина И.Ю. Английский язык для мед. колледжей и училищ.- М.: Академия,2017
Интернет ресурсы:
-
https://www.medicinenet.com/broken_bone_types_of_bone_fractures/article.htm
-
https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/15241-bone-fractures
-
https://www.webmd.com/brain/understanding-fainting-basics
-
https://www.mayoclinic.org/first-aid/first-aid-burns/basics/art-20056649
-
https://www.webmd.com/first-aid/thermal-heat-or-fire-burns-treatment
-
https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/insect-bites-and-stings/treatment/#:~:text=First%20aid%20for%20insect%20bites%20and%20stings&text=Wash%20the%20affected%20area%20with,this%20can%20help%20reduce%20swelling.
-
https://healthywa.wa.gov.au/Articles/F_I/First-aid-for-bites-and-stings
29






































