МИНИСТЕРСТВО ЛЕСНОГО ХОЗЯЙСТВА
И ОХРАНЫ ОБЪЕКТОВ ЖИВОТНОГО МИРА НИЖЕГОРОДСКОЙ ОБЛАСТИ
Государственное бюджетное профессиональное
образовательное учреждение Нижегородской области
«КРАСНОБАКОВСКИЙ ЛЕСНОЙ КОЛЛЕДЖ»
(ГБПОУ НО «КБЛК»)
МЕТОДИЧЕСКИЕ УКАЗАНИЯ
по дисциплине «Иностранный язык
в профессиональной деятельности (Английский язык)»
для студентов IV курса 2 часть
«Инструкции по технике безопасности при ремонте
и вождении автомобиля. Я хочу быть техником»
для специальности 23.02.07 «Техническое обслуживание
и ремонт двигателей, систем и агрегатов автомобилей»
| РАССМОТРЕНО: на заседании предметно-цикловой комиссии общеобразовательных дисциплин ПРОТОКОЛ № от « » сентября 2021г. Председатель ПЦК____________________ | Составили: преподаватели иностранных языков Воронина М.В., Булкина Т.А.
|
Красные Баки
2021
Lesson 1
Vehicle safety instructions
№1. Read, translate the text:
One of the most sophisticated technological advances on our planet has become a crucial part of everyday human life. The progression and development of the automobile has led to an increase in the dangers related to its operation. Today’s modern vehicles are equipped with many devices that help prevent serious injury in the event of a crash, or help avoid an accident all together. Most average drivers may recognize the names of some common safety devices in their vehicle, but many lack the knowledge of how these devices effectively work in providing them with a safe driving experience each day.
The term active safety is increasingly being used to describe systems that use an understanding of the state of the vehicle to both avoid and minimize the effects of a crash. These include braking systems, like brake assist, traction control systems and electronic stability control systems, that interpret signals from various sensors to help the driver control the vehicle. Additionally, forward-looking, sensor-based systems such as advanced driver-assistance systems including adaptive cruise control and collision warning/avoidance/mitigation systems are also considered as active safety systems under this definition.
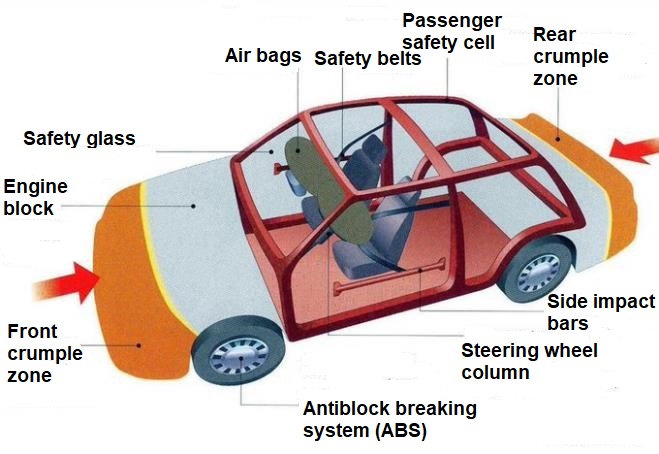
Passive safety is a combination of the design and performance properties of a car aimed at reducing the severity of a traffic accident. Most passive safety systems are triggered during a collision, when active safety systems could not help the driver prevent or avoid a collision. Includes the following elements:
high-strength cabin cage;
energy-absorbing elements of the front and rear parts of the car body, crumpling on impact (embedded deformation zones or soft body bumpers);
seat belts, including inertial ones with pretensioners;
inflatable airbags, including those built into seat belts;
folding steering column;
trauma-safe pedal assembly - in the event of a collision, the pedals are separated from the attachment points and reduce the risk of damage to the driver's legs;
crumpled or soft elements of the interior;
active seat head restraints that protect against serious injuries to the neck of the crew when the car is hit from behind;
safety glass - hardened, which, when destroyed, crumble into many non-sharp fragments and triplex;
safety arches, reinforced front roof pillars and the upper frame of the windshield in roadsters and convertibles;
transverse bars in the doors, etc.;
protection against the penetration of the engine and other units into the cabin (their removal under the bottom).
Emergency warning systems (e.g. Era Glonass)
For the first time, passive safety as one of the principles of car design was introduced by Béla Bareni.
№2. Translate the following word combinations:
equipped with many devices, combination of the design, properties of a car, the severity of a traffic accident, parts of the car body, crumpling on impact, separated from the attachment points, the risk of damage, elements of the interior, protect against serious injuries, crumble into fragments, protection against the penetration.
№3. Fill the table using the text:
| Examples of active safety | Examples of passive safety |
| 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. | 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. |
№4. Write out 5 regular and 5 irregular verbs from the text, write 3 forms of every verbs:
Example: translate – translated – translated (переводить)
read- read – read (читать)
№5. Write what these vehicle safety components are used for:
№6. Write out from the text 10 plural nouns with singular forms and translate them:
Example: vehicles – vehicle (транспортное средство)
№7. Write out from the text 10 words with suffixes or prefixes and translate them:
Example: deformation (деформация) – deform (деформировать) – form (формировать)
№8. Write out from the text 10 adjectives. Write 3 degrees of comparison:
Example: sharp - sharper - sharpest
Lesson 2
Причастие: функции
№1. Study the material:
Причастие — это неличная форма английского глагола, которая обладает свойствами глагола (является частью сказуемого), наречия и прилагательного. Это главное отличие причастий от инфинитива и герундия, ведь они близки по значению к глаголу и существительному.
У причастия в английском есть две основные формы:
Причастие настоящего времени (Present Participle или Participle I)
Причастие прошедшего времени (Past Participle или Participle II).
Функции причастия настоящего времени:
1. Для образования продолженных времен: то есть всех времен глагола Continuous, а также для Perfect Continuous.
They are watching a new movie – Они смотрят новый фильм.
I have been waiting for you – Я ждал тебя.
2. В качестве прилагательного для существительного:
Причастие определяет существительное, показывает его признак (как это обычно делает прилагательное)
3. Для обозначения одновременных действий
Когда два действия происходят одновременно и выполняют их одно лицо или предмет, то одно из действий выражается причастием.
He stayed at home doing homework. – Он остался дома, делая домашнее задание
Также причастием можно описать ситуации, когда одно и то же лицо совершает действие сразу после другого действия:
Finishing breakfast, he left the cafe. – Закончив завтрак, он вышел из кафе.
4. Для выражения обстоятельства причины
Причастие может быть использовано в составе причастного оборота, которое начинается с союзов as, since, because. В этом случае причастный оборот объясняет причину действия.
Knowing that his mother was late, he didn’t clean the room. – Зная, что мама опаздывает, он не убрался в комнате.
5. В качестве сложного дополнения (Complex Object) c глаголами восприятия
Сложное дополнение может использоваться с инфинитивом или причастием настоящего времени:
I heard you coming. – Я слышал, как ты пришел.
Функции причастия прошедшего времени:
1. Для образования совершенного времени: Present Perfect, Past Perfect, Future Perfect.
Вспомогательные глаголы для их образования — have, has, had, will have. К ним добавляется третья формы глагола V3 (то есть причастие прошедшего времени) или глагол с окончанием -d/-ed.
2. Для образования страдательного залога (Passive voice):
3. Для выражения именной части составного сказуемого после глаголов: to be (быть), to read (читать), to look (выглядеть), to take (брать), to become (становиться), и др. В этом случае Past Participle переводится на русский язык страдательным причастием, прилагательным или наречием:
4. В качестве определения, причем оно может находиться как перед существительным, так и после него:
5. Для обозначения обстоятельства времени и причины. В этом случае причастие отвечает на вопрос «когда?». А в функции обстоятельства причины на вопросы: «почему?», «по какой причине?».
When he was asked for help, Jim called the police. – Когда его попросили о помощи, Джим вызвал полицию.
6. В качестве сложного дополнения с существительным в общем падеже или местоимением в объектном падеже:
I want the work done immediately. – Я хочу, чтобы работа была сделана немедленно.
№2. Переведите на русский язык, обращая внимание на причастия настоящего времени.
1. The girl standing at the window is my sister.
2. Having been sent to the wrong address the letter didn’t rich him.
3. He sat in the arm-chair thinking.
4. She came up to us breathing heavily.
5. The hall was full of laughing people.
6. The singing girl was about fourteen.
7. Having read the book I gave it to Pete.
8. The large building being built in our street is a new school – house.
9. Having finished the experiment the students left the laboratory.
10. Being busy, he postponed his trip.
№3. Раскройте скобки, употребив причастие настоящего времени в активной и пассивной форме.
1. (To impress) by the film, they kept silent.
2. (To lose) the book, the student couldn’t remember the topic.
3. He spent the whole day (to read) a book.
4. (To travel) around America for a month, she returned to England.
5. He watched Mike (to go) out of the door and (to cross) the street.
6. The question (to discuss) now is very important.
7. (To pack) in the beautiful box the flowers looked very lovely.
8. (To descent) the mountains, they heard a man calling for help.
9. (To reject) by everybody he became a monk.
10. (To show) the wrong direction, the travelers soon lost their way.
№4. Раскройте скобки, употребив Indefinite или Perfect Participle I. Переведите.
1. (To write) out all the words, I started to learn them.
2. (To buy) food, they left supermarket.
3. (to bark) dog doesn’t bite.
4. She entered the room (to smile).
5. (To drink) coffee she was talking to her friend.
6. (To find) the keys, we were able to open the door.
7. (To make) the report, Tom left the room.
8. (To see) her he raised his hat.
9. My task (to finish), I went to bed.
10. While (to learn) the pronunciation of the words we learned their meaning.
№5. Переведите на русский язык, обращая внимание на причастие прошедшего времени.
1. He doesn’t like boiled milk.
2. I remember well his words said at the meeting.
3. We don’t like the book bought last week.
4. The stolen things were returned to the owner.
5. Asked about this event, he replied nothing.
6. The explanation given was not complete.
7. When burnt, coal produces heat.
8. The results received were of great importance for the further work.
9. When reconstructed the theatre looked more beautiful than before.
10. She showed us a list of the newly published books.
№6. Раскройте скобки, употребив причастие прошедшего времени. Переведите.
1. The letter (to write) by him was very long.
2. We are interested in the goods (to produce) by this factory.
3. She didn’t understand the word (to say) by him.
4. He didn’t see the things (to keep) in her box.
5. I don’t like the video (to buy) yesterday.
6. This is the house (to build) many years ago.
7. The question (to put) to the professor was important.
8. When (to offer) to work abroad, he refused.
9. The article on agriculture (to publish) in this magazine was written by Smith.
10. You can get the book (to recommend) by our teacher in the library.
Lesson 3
Инструкции по технике безопасности
№1. Read, translate the text:
Using this Manual
Please take the time to get acquainted with your vehicle by reading this Operator’s Manual. We recommend that you read and understand this manual from beginning to end before you operate this equipment. This manual contains useful information for the safe and efficient operation of this equipment. It also provides service information, with an outline for performing safety checks and basic preventive maintenance inspections. We have tried to present the information you’ll need to learn about functions, controls, and operation - and to present it as clearly as possible. We hope you’ll find this manual easy to use.
Your vehicle may not have all the features or options mentioned in this manual. Therefore, you should pay careful attention to the instructions that pertain to just your vehicle. In addition, if your vehicle is equipped with special equipment or options not discussed in this manual, consult your dealer or the manufacturer of the equipment.
Safety Alerts
Please read and follow all of the safety alerts contained in this manual. They are there for your protection and information. These alerts can help you avoid injury to yourself, your passengers and help prevent costly damage to the vehicle. Safety alerts are highlighted by safety alert symbols and signal words such as “WARNING”, “CAUTION”, or “NOTE”. Please DO NOT ignore any of these alerts.
Warnings
 The safety message following this symbol and signal word provides a warning against operating procedures which could cause death or injury. They could also cause equipment or property damage. The alert will identify the hazard, how to avoid it and the probable consequence of not avoiding the hazard.
The safety message following this symbol and signal word provides a warning against operating procedures which could cause death or injury. They could also cause equipment or property damage. The alert will identify the hazard, how to avoid it and the probable consequence of not avoiding the hazard.
Hot engine oil can be dangerous. You could be burned. Let the engine oil cool down before changing it. Failure to comply may result in death, personal injury, equipment or property damage.
 Cautions
Cautions
The safety message following this symbol and signal word provides a caution against operating procedures which could cause equipment or property damage. The alert will identify the hazard, how to avoid it, and the probable consequence of not avoiding the hazard.
Continuing to operate your vehicle with insufficient oil pressure will cause serious engine damage. Failure to comply may result in equipment or property damage.
 Notes
Notes
The message following this symbol and signal word provides important information that is not safety related but should be followed. The alert will highlight things that may not be obvious and is useful to your efficient operation of the vehicle.
Pumping the accelerator will not assist in starting the engine.
№2. Translate the following word combinations:
руководство оператора, использовать оборудование, полезная информация, безопасная работа, проверка профилактического обслуживания, пристальное внимание, следовать предупреждениям, избежать травм, подсвечиваться символами, сигнальное слово, нанести ущерб, привести к смерти, серьёзные повреждения, эффективная работа.
№3. Match the words with their translations:
| 1) эксплуатационный отказ 2) внезапный отказ 3) безотказность 4) наработка на отказ 5) надежность 6) сохраняемость 7) взаимозаменяемость | a) fail-free operation b) mean time to failure c) reliability d) conservability e) sudden failure f) interchangeability g) field failure |
№4. Match the English equivalents to these terms by choosing one of them:
1. Эксплуатационный отказ
a) technological failure b) field failure c) gradual failure
2. Сохраняемость
а) reliability b) repairability c) conservability
3. Отказ
a) malfunction b) total fail lure c) dependent failure
4. Безотказность
a) reliability b) trouble – free file c) fail – free operation
5. Постепенный отказ
a) technological failure b) gradual failure c) partial failure
№5. Translate the sentences
1. Отказ, после которого использование объекта по назначению невозможно (для восстанавливаемых объектов – невозможно до проведения восстановления).
2. Событие, заключающееся в нарушении работоспособного состояния объекта. То есть неспособность выполнять заданную функцию с параметрами, установленными требованиями технической документации.
3. Свойство автомобиля работать без интенсивного изнашивания отдельных деталей, механизмов и систем, вызывающего прекращение эксплуатации автомобиля.
4. Объём работы или срок эксплуатации, на который рассчитывается объект. После исчерпания ресурса безопасная работа устройства не гарантируется, ему требуется капитальный ремонт или замена.
5. Разрушение поверхности металла под действием ударов газовых пузырьков, образующихся в обтекающем изделии высокоскоростном потоке жидкости при перепадах давления.
№6. Complete the sentences with given verbs:
Operate, use, specialize, design, divided, work, study
1. We will…thoroughly mechanical engineering.
2. Mechanical engineers…principles such as heat, force.
3. Engineers in this field…, and… machinery of all types.
4. They also…on a variety of manufactured goods.
5. The field is…into machinery, mechanisms, materials, hydraulics.
6. Some of them…in particular types of machines.
№7. Make up comparative and superlative forms of the adjectives and adverbs in the expressions listed below and translate them:
Important properties, pure metals, much experience, new solutions, long service life, good protection, well-known metals, useful devices, high efficiency, bad results, a modern truck, a large team of designers.
№8. Translate these sentences into Russian. Write out the comparative and superlative forms of the adjectives and adverbs:
1. Metals are the most widely used materials in industry.
2. In general, a metal with small grains will be harder and stronger than one with coarse grains.
3. Small amounts of other metals, less than 1 per cent, are often added to a pure metal.
4. Toughness is different from strength: the toughest steels are different from the ones with highest tensile strength.
5. Plastics are lighter and more corrosion-resistant, but they are not usually as strong as metals.
6. Hot-worked products have better ductility and toughness than the un-worked casting.
7. Rolling is the most common metalworking process.
8. Medium-carbon steels containing from 0.2 to 0.4 per cent carbon are tougher and are used as structural steels.
9. In operations that involve stretching, the best alloys are those which grow stronger with strain.
10. Metals such as copper and aluminium are more ductile in such operations than other metals.
Lesson 4
How To Become A Mechanic: Step To Step Guide
№1. Read and translate the text:
Below you will find the best hacks on how you can become a successful auto mechanic. In the next few lines, you will learn exactly the best things that have worked for most successful guys in the field.
Carefully carry out your research
Before you dive into the pursuit of your new career, it is very important you sit down and do some research and calculations. Find people who are already in the field and find out what exactly they are doing. Find out if there are any challenges they may be going through or they have gone through in the past. Then leverage their knowledge and experiences and learn how not to encounter such challenges. You cannot dispute this fact, it is good to have good dreams but knowing exactly where to take that dream is another. Take out some time to really learn what is involved. Once the focus is narrowed, it will be easier to move to the next step.
Complete a Secondary or High School Education
Before you carry on with your dream of being a mechanic, it is very important you, first of all, complete your secondary education or at least complete a General Education Development program. You would really need the credentials you acquire from here to be able to move on and enroll in a certificate or degree program.
Find a Vocational College and Enroll
This is the next thing that should fall in place. Remember while carrying out your detailed research, this is one of the things you will also need to find out: the best vocational schools for your program. Not all vocational schools may meet your standards. So, after you must have researched and figured out the best school for you, then you will need to enroll and start taking your lessons. There are so many places where you can find these schools.
Automobile manufacturers, vocational schools, and community colleges have training programs that award associate’s degrees or certificates of completion in automotive service technology. Some of the courses aspiring mechanics should take include electronics, hands-on automotive repair, computers, math, and English, etc.
Get Certified
While you are in your vocational college, ensure to really pay attention to every bit of detail. Endeavor to be serious in your studies and try to learn all you can. Remember, it is your performance that determines whether you will get certified or not. So if you are really passionate about your new career, putting all your best so as you can get certified is one of the best things you would do for yourself. Your certificate is what majorly qualifies you as a professional and not just any kind of guy try to play around with spanners, bolts, and nuts. Certification through the National Institute for Automotive Excellence is the standard for mechanics.
Develop yourself beyond the classroom
Even after you have completed your program, keep working and developing yourself. Do not rely alone on what your instructors tell you in class. Read more books, see videos, attend conferences where great minds in the field converge. learn from the best. You see, technologies change fast, so it’s very important to keep up with the latest techniques and engine features. If you must stand out in your chosen career, then this learning will continue throughout your career walk.
Keep learning, don’t burn out
The next big thing that will happen to you is to get a good job. Now, in your new job, be open to employer training. They are a very important component of your making as a successful mechanic. Employer. training for mechanics typically lasts for a couple of months. You’ll work with experts like lubricant workers, trainee technicians, or automotive helpers during your training. It’s important that you learn to work independently and as part of a team during the training.
The Big Dream Master Mechanic
When you have gone through all of the necessary training and have gotten the required skills, I can bet you, you are on your high way to becoming a master certified auto mechanic. When you have been endorsed, it is unarguable that you soon be the big dream master mechanic you have always dreamt to become.
№2. Match the words with their definitions:
| 1. Electrician | a) is able to adjust the engine speed when switching speeds gearbox. |
| 2. Autorestart | b) thoroughly versed in the motor. Able to determine the damage, guided sounds and the main symptoms when the unit. |
| 3. Painter | c) identify the cause of damage to the car through full diagnostic. |
| 4. A mechanic for diagnosis | d) performs paint work. He handles the car anti-corrosion agents and polishes the vehicle for paint. |
| 5. Master engine repair | e) working on straightening the body in the event of dents and irregularities and other defects of the car by extruding and drawing the surface using special tools. He engaged in the plaster of the car and prepare it for painting works. |
| 6. Repair transmissions Master | f) fixes a problem in the electronics, responsible for the basic commands.: start, turning on and off lights and air conditioning. |
№3. Translate into Russian:
Requirements for the role
If you want to work as a mechanic, you should:
mandatory to have a medium- special education;
a thorough understanding of the structure of the car and the characteristics of parts and materials;
to be able to handle instruments and tools, and other equipment, necessary for car repair and diagnostics.
Job responsibilities
It needs to accept incoming vehicles, knowing the cause of treatment to the service center.
Using precision equipment mechanic is required to diagnose the vehicle.
To find the damage and repair the devices, whether it's gearbox, fuel system, suspension or other components and assemblies
The mechanic also prepares a car for painting works and produces painting.
The duties of the specialist include receiving cash for the performed services.
The employee is obliged to keep clean your working place.
The mechanic must perform the orders and instructions of the mechanic.
№4. Put in prepositions where necessary.
1. A car mechanic specializes … automobile repair.
2. Mechanics should be knowledgeable in working … all parts of cars.
3. This job involve the replacement … some parts.
4. Nowadays mechanics need to have more knowledge than … the past.
5. Most dealerships provide diagnostic computers … each technician.
№5. Write out 5 regular and 5 irregular verbs from the text, write 3 forms of every verbs:
Example: translate – translated – translated (переводить)
read- read – read (читать)
№6. Write out from the text 10 plural nouns with singular forms and translate them:
Example: vehicles – vehicle (транспортное средство)
№7. Write out from the text 5 words with suffixes or prefixes and translate them:
Example: deformation (деформация) – deform (деформировать) – form (формировать)
№8. Write out from the text 5 adjectives. Write 3 degrees of comparison:
Example: sharp - sharper - sharpest
№9. Choose the right variant of translation:
a) rotation - вращать, вращение, вращательный;
b) fundamentally - основной, в основном, основа;
c) difference - различие, различать, различный;
d) lubrication - смазка, смазывать, смазывающий;
e) transmission - передача, передавать, передаточный;
f) differential - дифференциал, дифференцировать, дифференциальный;
g) driver - водитель, водить, водительский.
Lesson 5
Герундий: функции
Герундий (Gerund) — это неличная форма глагола, которая выражает название действия и сочетает в себе признаки глагола и существительного. Соответственно, на русский язык герундий обычно переводится существительным или глаголом (чаще неопределенной формой глагола). Формы, подобной английскому герундию, в русском языке нет.
Герундий, как и причастие настоящего времени, образуется путем прибавления к основе глагола в неопределенной форме окончания -ing:
to read — reading
to play — playing
to run — running
to tie – tying
to see – seeing
to dance – dancing
Отрицательная форма образуется при помощи частицы not, которая ставится перед герундием: He enjoys not working. — Ему нравится не работать.
Формы герундия
Герундий имеет простую (Simple) и перфектную (Perfect) формы, а также может употребляться в активном и пассивном залоге.
|
| Active (Активный залог) | Passive (Пассивный залог) |
| Indefinite (Simple) | writing | being written |
| Perfect | having written | having been written |
| Verbs which are usually followed by a gerund: acknowledge, admit, adore, anticipate, appreciate, avoid, celebrate, confess, contemplate, delay, deny, describe, detest, discuss, dislike, dread, endure, enjoy, fancy, finish, imagine, involve, keep, justify, mention, mind, miss, omit, postpone, practise, quit, recall, recommend, regret, report, resume, risk, suggest, tolerate, understand. | Verbs which are usually followed by an infinitive: afford, agree, appear, arrange, ask, attempt, care, choose, claim, come, consent, dare, decide, demand, deserve, determine, elect, expect, fail, get, hate, help, hesitate, hope, hurry, intend, learn, manage, mean, need, offer, plan, prepare, pretend, promise, refuse, resolve, say, seem, tend, threaten, want, wish. |
Герундий в предложении может выступать в качестве подлежащего, дополнения или именной части составного сказуемого, так как он может выполнять те же функции, что и существительное.
Подлежащее (главный член предложения)
Smoking can destroy your health. – Курение может уничтожить твое здоровье.
Дополнение (второстепенный член предложения)
Jane likes making people happy. – Джейн любит дарить людям счастье.
Именная часть составного сказуемого (главный член предложения)
Our duty is taking care of those, who need help. – Наш долг – это забота о тех, кому нужна помощь.
№1. Add –ing to the verbs and translate them.
read, write, take, sit, play, look, swim, jump, run, go, do, buy, help, eat, clean, make, speak, sleep, listen, talk, fly, lie, die, come, shop, live, sing, dance, work, have, cry, put, use, stop, drive, win.
№2. Complete with a gerund or an infinitive
1. She agreed ……….. (pay) the electricity bill the following week.
2. Hector dislikes ………… (go) to the opera.
3. Martin admitted ………. (steal) the money from the safe.
4. Elizabeth didn’t need ……. (do) the final exams.
5. I regretted ………… (forget) to call my grandfather for his birthday.
6. Your aunt wished ………. (visit) Australia in Summer.
7. Please, avoid ………… (touch) the wires with wet hands.
8. Your friend seems ………. (be) very busy today.
9. We suggested ………………… (sell) our apartment at the seaside.
10. She postponed ………………… (make) a decision for the new shop.
№3. Translate into Russian
He always suggested staying here.
The job involves travelling to Germany once a month.
I proposed having party at the beach.
I promised to care for the cat but I’m not much good at babysitting.
He is capable of standing on his head and playing the saxophone.
You’d better start digging the garden.
Writing letters is more boring than phoning.
It is not worth helping him do this job.
My wife apologized for being late.
I’m very excited about attending tomorrow’s game.
№4. Translate into English
Мой дядя бросил курить и сейчас предпочитает есть.
Пожалуйста, прекратите шептаться.
Мне нравится быть одному. Я никогда не чувствую себя одиноко.
Я перешел дорогу, не посмотрев.
Подумай хорошо (carefully), прежде чем принять решение.
Попробуй нажать на кнопку!
Как насчет последнего стаканчика?
Она закончила красить свою квартиру.
Ты можешь представить свою жизнь без ТВ?
Я правда не могу терпеть ждать автобус.
№5. Choose the right form:
1. I want (to see/seeing) Paris.
2. We enjoy (to swim/swimming).
3. I would like (to live/living) in a small town.
4. I hope (to visit/visiting) you next week.
5. My brother hates (to help/helping) me with my homework.
6. We stayed in the house until it stopped (to rain/raining).
7. I don’t really mind (to cook/cooking).
8. We would prefer (to buy/buying) a new house.
9. I love (to travel/travelling) by train.
10. We like (to learn/learning) English.
№6. Choose gerund or infinitive
I am planning (to visit/visiting) my granny next week.
When they finish (to eat/eating) their lunch, they’ll go to the office.
He suggested (to buy/buying) some food.
Does Sally enjoy (to go/going) to the gym?
Don’t put off (to write/writing) a report till the end of the month.
John refused (to answer/answering) my question.
My brother intends (to get/getting) married soon.
I think she didn’t mean (to hurt/hurting) you.
Keep (to beat/beating) the eggs.
Fred can’t afford (to travel/travelling) this year.



















