27
ВВЕДЕНИЕ
Данные методические указания предназначены для студентов 2-го курса специальности «Электромеханики» факультета МТС.
Основная задача методических указаний – помочь студентам в совершенствовании приобретенных ранее знаний студентов, в расширении словарного запаса, кроме того методические указания будут способствовать развитию навыков и умений.
Методические указания состоят из 6 видеоуроков, каждый из которых содержит упражнения для закрепления лексики соответствующий рабочей программе, а также творческие задания коммуникативной направленности. Лексический материал содержит как профессиональную терминологию, так и лексические единицы и словосочетания из общей направленности, которые студенты смогут использовать в разговоре на различные темы. Также содержится дополнительный материал и мини-словарь к каждому уроку, которые помогут студентам расширить словарный запас по изучаемым текстам. К методическим указаниям прилагаются ключи для реализации контроля и самоконтроля уровня сформированности лексической компетенции студентов.
CONTENTS
ВВЕДЕНИЕ……….................................................................................1
Half-wave rectifier……………………………………………………...3
Electromechanical relay…………………………………………….......5
Circuit breaker and fuse…………………………………………...……8
How electric motors work………………………………………………9
Hydroelectric Power Plant…………………………………………….11
Nuclear Power Plants………………………………………………….14
Mini-dictionary………………………………………………………..17
Appendix………………………………………………………………21
Keys……………………………………………………………………29
БИБЛИОГРАФИЕСКИЙ СПИСОК……………………………...…42
Half-wave rectifier
I. Pre-watching tasks:
1. Try to remember your general knowledge and answer the following questions:
What is Half-wave rectifier? How does it work? What purpose does it serve for?
2. Read the words and translate them. Consult your mini dictionary if it’s necessary.
| transformer diode rectifier capacitor a.c. inefficient suppress straight
|
II. After-watching tasks:
1. Answer the following questions:
1) What parts does the half-wave rectifier consist of?
2) Why does only half of the voltage come through?
3) Why did the half of the a.c. wave disappear after the diode?
4) What is happening when the capacitor is connected after the diode?
5) What’s the effect of the capacitor?
6) Why is it inefficient?
| capacitor Rectifiers direct current(DC) Electric power transformer conductors electric circuit |
2. Fill in the gaps with the words from the box below.
a) A __________is an electrical device that transfers energy between two or more circuits through electromagnetic induction.
b) _________ have many uses, but are often found serving as components of DC power supplies and high-voltage direct current power transmission systems.
c) ____________ is the rate at which electric energy is transferred by an ___________.
d) A __________ consists of two __________ separated by a non-conductive region.
e) Virtually all electronic devices require __________.
3. Open the brackets using the correct form of the verb. Pay attention to the tenses and voice (active/passive):
a) In half wave rectification of a single-phase supply, either the positive or negative half of the AC wave (to pass), while the other half (to block).
b) Because only one half of the input waveform (to reach) the output, mean voltage (to be) lower.
c) Half-wave rectification (to require) a single diode in a single-phase supply, or three in a three-phase supply.
d) Half-wave rectifiers (to produce) far more ripple than full-wave rectifiers.
e) Much more filtering (to need) to eliminate harmonics of the AC frequency from the output.
4. Work with a partner. Try to explain the following terms in English. Give their English equivalents. The information in the appendix may be helpful.
1. transformer
2. diode.
3. capacitor.
4. a.c.
5. d.c.
Electromechanical relay
I. Pre-watching tasks:
1. Try to remember your general knowledge and answer the following questions:
What is a relay? Where are relays used? What types of relays do you know?
2. Match Russian and English equivalents. Consult your mini dictionary if it’s necessary.
| relay
| провод катушки |
| actuate
| электромагнитное поле |
| frame
| металлический стержень |
| coil wire
| легкий каркас |
| metal core | наматывать |
| armature | приводить в действие |
| contact
| катализатор |
| wind
| корпус |
| electromagnetic field
| реле |
II. After-watching tasks:
1. Answer the following questions:
1) What is an electromechanical relay?
2) What are the basic parts and of the electromechanical relay?
3) What circuits does electromechanical relay involve?
4) How might the relay be described as?
2. See if you can spot the fake facts.
1) A relay is a mechanically operated switch.
2) An armature is responsible for the passage of current.
3) An electromagnet is a type of magnet in which the magnetic field is produced by electric current.
4) An electromagnetic field (also EMF or EM field) is a physical field produced by electrically charged objects.
5) Electric shock is a useful experience for a young specialist.
3. Open the brackets using the correct form of the verb. Pay attention to the tenses and voice (active/passive):
a) A relay (to be) an electrically operated switch.
b) Many relays (to use) an electromagnet (to operate) mechanically a switch.
c) Relays (to use) where it (to be) necessary (to control) a circuit by a low-power signal or where several circuits (must/ to control) by one signal.
d) The first relays (to use) in long distance telegraph circuits as amplifiers.
e) They (to repeat) the signal coming in from one circuit and re-transmitted it on another circuit.
4. Work with a partner. Try to explain the following terms in English. The information in the appendix may be helpful.
1) electromagnet
2) armature
3) relay
Circuit breaker and fuse
I. Pre-watching tasks:
1. Try to remember your general knowledge and answer the following questions:
What is a circuit breaker? What is a fuse? What types of circuit breakers do you know?
2. Read the words and translate them. Consult your mini dictionary if it’s necessary filament
| porcelain ceramic metallic lever circuit breaker fuse switching mechanism solenoid bimetallic plate current corruption capacity rating resettable |
II. After-watching tasks:
1. Answer the following questions:
1) Fuses are made of:
2) What means is switching mechanism with a metallic level actuated by?
3) What are the thermal magnetic circuit breakers?
4) Why are fuses considered to be safer?
5) What is the advantage and disadvantage of fuses?
6) And what is the advantage and disadvantage of the circuit breakers?
2. Put the words in a correct order.
a) automatically, electrical, A, is, operated, an, switch ,circuit breaker;
b) resistance, low, A, fuse, resistor, a, type, of, is;
c) sizes, made, Circuit, in, varying, breakers, are.
3. Open the brackets using the correct form of the verb. Pay attention to the tenses and voice (active/passive):
a) Its basic function (to be) (to detect) a fault condition and (to interrupt) current flow.
b) Unlike a fuse, which (to operate) once and then (must/to replace), a circuit breaker (can/ to reset) to resume normal operation.
c) Circuit breakers (to make) in varying sizes.
d) It (to act) as a sacrificial device (to provide) over current protection.
e) Its essential component (to be) a metal wire or strip that (to melt) when too much current (to flow) through it, interrupting the circuit that it (to connect).
4. Explain the main difference between a circuit breaker and fuse? The information in the appendix may be helpful.
How electric motors work
I. Pre-watching tasks:
1. Try to remember your general knowledge and answer the following questions:
What is an electric motor? What purpose does it serve for? Where can they be used?
2. Read the words and translate them. Consult your mini dictionary if it’s necessary.
| electric motor produce motion vacuum cleaner windshield wipers conveyor belt brush graphite transmit commutator split ring output shaft depend upon/on |
II. After-watching tasks:
1. Answer the following questions:
1) What is an electric motor?
2) Give the examples of the devices operated with the electric motors you’ve seen in the video.
3) What is a brush? What’s its use?
4) What is the commutator connected to?
5) What does the direction of the motion depend upon?
2. See if you can spot the fake fact:
a) An electric motor is an electric machine that converts electrical energy into mechanical energy.
b) The reverse conversion of mechanical energy into electrical energy is done by an electromagnetic field.
c) Motors can be used only in cars.
d) Electric motors are replacing hydraulic cylinders in airplanes and military equipment.
e) There are no such motors as non-magnetic motors.
3. Open the brackets using the correct form of the verb. Pay attention to the tenses and voice (active/passive):
a) In normal motoring mode, most electric motors (to operate) through the interaction.
b) Small motors (may/ to find) in electric watches.
c) Electric motors (may/ to classify) by electric power source type, internal construction, application, type of motion output, and so on.
d) In an electric motor the moving part (to be) the rotor which (to turn) the shaft (to deliver) the mechanical power.
e) The stator core (to make up) of many thin metal sheets, called laminations.
4. Think of more ways of the electric motor use. The information in the appendix may be helpful.
Hydroelectric Power Plant
I. Pre-watching tasks:
1. Try to remember your general knowledge and answer the following questions:
What do you know about Hydroelectric power plants? What other ways of the producing of energy do you know? Do you think it is an efficient way to produce energy?
2. Match Russian and English equivalents. Consult your mini dictionary if it’s necessary.
| Hydroelectric Power Plant | турбина |
| floodgate | дамба |
| dam | напорный туннель |
| penstock | стержень |
| turbine | генератор |
| shaft | гидроэлектростанция |
| cones | конусы |
| generator | водоспуск, шлюз |
| rotate | вращать |
II. After-watching tasks:
1. Answer the following questions:
1) How is the electricity produced in Hydroelectric Power Plant?
2) The Hydroelectric Power Plant is…
3) Where is a floodgate situated?
4) What are the parts of the Hydroelectric Power Plant?
2. Fill in the gaps with the words from the box below.
| harm Hydroelectricity renewable damming hydropower produced cost source |
a) ________________ is the term referring to electricity generated by _________.
b) It is the most widely used form of _________ energy.
c) Hydropower is __________ in 150 countries
d) The ____ of hydroelectricity is relatively low, making it a competitive _______ of renewable electricity.
e) However, _______ interrupts the flow of rivers and can ______ local ecosystems.
3. Open the brackets using the correct form of the verb. Pay attention to the tenses and voice (active/passive):
a) Hydropower (to use) since ancient times.
b) Many small hydroelectric power stations (to construct) by commercial companies in mountains near metropolitan areas.
c) Hydroelectric power stations (to continue) to become larger throughout the 20th century.
d) An underground power station (to use) generally at large facilities.
e) Annual electric energy production (to depend on) the available water supply.
4. Explain how the Hydroelectric Power Plant works. The information in the appendix may be helpful.
Nuclear Power Plants
I. Pre-watching tasks:
1. Try to remember your general knowledge and answer the following questions:
What is nuclear power? What spheres is it used in? Is it useful rather than harmful?
2. Read the words and translate them. Consult your mini dictionary if it’s necessary.
| nuclear power plant thermal power station turbine building containment building cooling tower pressurized water reactor fuel assembly fuel rod fuel pellet enriched uranium chain reaction steam generator/heat exchanger water circulation system reactor pressure vessel
|
II. After-watching tasks:
1. Answer the following questions:
1) What is a nuclear power plant?
2) What are the most important buildings and facilities of a nuclear power plant?
3) What is the PWR?
4) What is a fuel assembly composed of?
6) How many fuel assemblies can be found in a pressurized water reactor?
7) Where is the actual nuclear fuel found?
8) What is a fuel pellet composed of?
9) For what purpose is water needed?
10) Why does not the water boil?
11) What is the other way to call a heat exchanger?
12) Where does actually the water boil?
13) Why are the water circulation systems kept separate and through this why does the water in a primary circulation system never leave the containment building?
2. Match the element of the nuclear power plant with their measure characteristics.
| containment building | 200 meter tall |
| cooling tower | 5 meters length, diameter 23 centimeters |
| reactor pressure vessel | 12 meters tall, 25 centimeters thick |
| the water pressure | 570 Fahrenheit |
| Fuel rod | meter thick reinforced concrete |
| the heat of the water inside the reactor pressure vessel | 160 Bars |
3. Open the brackets using the correct form of the verb. Pay attention to the tenses and voice (active/passive):
a) A nuclear power plant (to be) a thermal power station
b) The use of nuclear power as a source of domestic energy (to increase) significantly over the past decade
c) These (can, to range) from environmental impact.
d) Nuclear power plants (to be) usually considered to be base load stations
e) Another significant effect (to be) the increased amount of sulfur dioxide in the air which (to cause) acid rain.
4. Try to think over the quote by Gerhard Uhlenbruck which is given at the beginning of the video? Do you agree with him? Why? The information in the appendix may be helpful.
Mini-dictionary
Half-wave rectifier
a transformer – трансформатор
a diode – диод
a rectifier – ректификатор, выпрямитель
a capacitor – конденсатор
a.c. – переменный ток
d.c. – постоянный ток
inefficient – неэффективный
to suppress – подавлять
straight – прямой
Electromechanical relay
a relay – реле
to actuate – приводить в действие
a frame – корпус
a coil wire – провод катушки
a metal core – металлический стержень
an armature – легкий каркас
a contact – катализатор
to wind – наматывать
electromagnetic field – электромагнитное поле
Circuit breaker and fuse
a filament – волокно
porcelain – фарфор
ceramic – керамика
a metallic lever – металлический рычаг
a circuit breaker – автоматический контактный выключатель
a fuse – плавкий предохранитель
a switching mechanism – механизм переключения
a solenoid – электромагнит
bimetallic – биметаллический
a plate – пластина
How electric motors work
an electric motor – электрический двигатель
to produce – производить, вырабатывать
a motion – движение
a vacuum cleaner – пылесос
windshield wipers – дворники
a conveyor belt – конвейерная лента
a brush – механическая щетка
a graphite – графит
to transmit – передавать, пропускать
a commutator – коммутатор
a split ring – кольцо с прорезью
an output shaft – выводной вал
to depend upon/on – зависеть от
Hydroelectric Power Plant
Hydroelectric Power Plant – гидроэлектростанция
a floodgate – водоспуск, шлюз
a dam – дамба
a penstock – напорный туннель
a turbine – турбина
a shaft – стержень
cones – конусы
a generator – генератор
to rotate – вращать
Nuclear power plant
a nuclear power plant – атомная эелектростанция
a thermal power station – теплоэлектростанция
a turbine building – машинный зал
a containment building – колпак реактора, здание защитной оболочки ядерного реактора
a cooling tower – охлаждающая башня
a pressurized water reactor – водяной ядерный реактор
a fuel assembly – топливная сборка
a fuel rod – топливный стержень
a fuel pellet – топливная таблетка
enriched uranium – обогащенный уран
a chain reaction – цепная реакция
a steam generator / heat exchanger – парогенератор
a water circulation system – система циркуляции воды
a reactor pressure vessel – корпус ядерного реактор
Appendix
The following information may be helpful not only to make exercises but also to stock your mind with knowledge.
Half-wave rectifier.
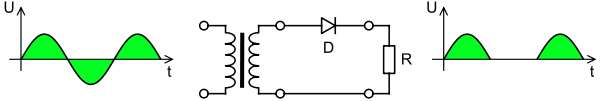
In half wave rectification of a single-phase supply, either the positive or negative half of the AC wave is passed, while the other half is blocked. Because only one half of the input waveform reaches the output, mean voltage is lower. Half-wave rectification requires a single diode in a single-phase supply, or three in a three-phase supply. Rectifiers yield a unidirectional but pulsating direct current; half-wave rectifiers produce far more ripple than full-wave rectifiers, and much more filtering is needed to eliminate harmonics of the AC frequency from the output.
Here is the scheme of half-wave rectifier.
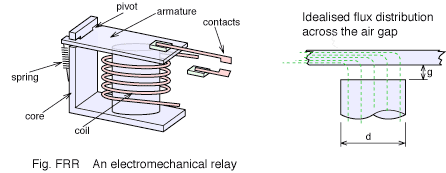
Electromechanical relay
A relay is an electrically operated switch. Many relays use an electromagnet to mechanically operate a switch, but other operating principles are also used. Relays are used where it is necessary to control a circuit by a low-power signal (with complete electrical isolation between control and controlled circuits), or where several circuits must be controlled by one signal. The first relays were used in long distance telegraph circuits as amplifiers: they repeated the signal coming in from one circuit and re-transmitted it on another circuit. Relays were used extensively in telephone exchanges and early computers to perform logical operations
Circuit breaker and fuse
A circuit breaker is an automatically operated electrical switch designed to protect an electrical circuit from damage caused by overload or short circuit. Its basic function is to detect a fault condition and interrupt current flow. Unlike a fuse, which operates once and then must be replaced, a circuit breaker can be reset (either manually or automatically) to resume normal operation. Circuit breakers are made in varying sizes, from small devices that protect an individual household appliance up to largeswitchgear designed to protect high voltage circuits feeding an entire city.
In electronics and electrical engineering, a fuse (from the French fuser, Italian fuso, "spindle"[1]) is a type of low resistance resistor that acts as a sacrificial device to provideovercurrent protection, of either the load or source circuit. Its essential component is a metal wire or strip that melts when too much current flows through it, interrupting the circuit that it connects.

Electric motor
An electric motor is an electric machine that converts electrical energy into mechanical energy. The reverse conversion of mechanical energy into electrical energy is done by an electric generator.
See the scheme of the electric motor on the next page.

What are the uses of Electric Motors?
Motors have a wide variety of uses and are found in cars, clocks, drills, fans, fridges, hair dryers, toothbrushes, vacuum cleaners, water pumps (for fish tanks, central heating, fire fighting)
washing machines, hard disk drives, DVD players, electric vehicles and industrial equipment including extruders, fork-lift trucks, lathes, mills, hoists, robots and winches. We would expect the efficiency of a motor to be between 70 and 85%. The wasted energy is heat and sound.
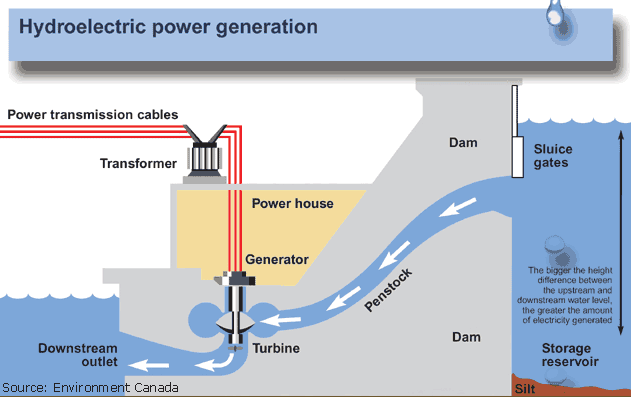
Hydroelectric Power Plant
Hydroelectricity is the term referring to electricity generated by hydropower; the production of electrical power through the use of the gravitational force of falling or flowing water. It is the most widely used form of renewable energy, accounting for 16 percent of global electricity generation – 3,427 terawatt-hours of electricity production in 2010,[1] and is expected to increase about 3.1% each year for the next 25 years.
Hydropower is produced in 150 countries, with the Asia-Pacific region generating 32 percent of global hydropower in 2010. China is the largest hydroelectricity producer, with 721 terawatt-hours of production in 2010, representing around 17 percent of domestic electricity use. There are now four hydroelectricity stations larger than 10 GW: the Three Gorges Dam and Xiluodu Dam in China, Itaipu Dam across the Brazil/Paraguay border, and Guri Dam in Venezuela.[1]
The cost of hydroelectricity is relatively low, making it a competitive source of renewable electricity. The average cost of electricity from a hydro station larger than 10 megawatts is 3 to 5 U.S. cents per kilowatt-hour.[1] It is also a flexible source of electricity since the amount produced by the station can be changed up or down very quickly to adapt to changing energy demands. However, damming interrupts the flow of rivers and can harm local ecosystems, and building large dams and reservoirs often involves displacing people and wildlife.[1] Once a hydroelectric complex is constructed, the project produces no direct waste, and has a considerably lower output level of the greenhouse gas carbon dioxide (CO
2) thanfossil fuel powered energy plants.[2]
Nuclear Power Plants
A nuclear power plant is a thermal power station in which the heat source is a nuclear reactor. As is typical in all conventional thermal power stations the heat is used to generate steam which drives a steam turbine connected to a generator which produces electricity. As of 23 April 2014, the IAEA report there are 435 nuclear power reactors in operation[1] operating in 31 countries.[2] Nuclear power plants are usually considered to be base load stations, since fuel is a small part of the cost of production.[3]

Overview of the question about an impact of the nuclear power.
The use of nuclear power as a source of domestic energy has increased significantly over the past decade and is expected to continue to do so in the years to come. However, the use of this form of energy does not come without a unique set of consequences. These can range from environmental impact, altering to a great extent the balance in the flora and fauna of a region, to causing social problems to do with social consensus and risk perceptions of people living in the vicinity of such a plant. This paper discusses some of the down-sides nuclear power generation is credited for.
Environmental Impact
Perhaps the impact which is easiest to notice is the effect on the environment, particularly in terms of flora and fauna. To start with, the setting up of a nuclear plant requires a large area, preferably situated near a natural water body. This is usually accompanied with clearing of forests which disturbs the natural habitat of several creatures and gradually upsets the ecological balance of the region. Apart from this, studies have shown that due to the heat rejected into the water bodies, there have been significant drops in the populations of several species of fish in certain regions of US. Another significant effect is the increased amount of sulfur dioxide in the air which causes acid rain to form which then leads to contamination of surface water bodies of the region, reduction of productivity of the soil, and has several other negative effects on the region's vegetation and human health.
Social Impact
Setting up a nuclear power plant in any region does not come without concerns and criticism from a wide variety of people. People in such regions fear the threat of being exposed to unusual levels of radiation. The natural water sources in such places are also doubted to contain plant emissions especially if the plant uses the body of water as a heat sink. In addition, during the post 9-11 era, there has also been an increased concern over reactor safety and integrity. As such, a lot of effort has to go into convincing the people living around the plant that it is securely designed with several safety measures. Among other impacts that it can have on the region, plant commissioning in a region causes impairment of aesthetic, recreational and natural conservation values and also significantly lowers the value of the surrounding property.
Keys
Half-wave rectifier
1. Answer the following questions:
1) What parts does the half-wave rectifier consist of?
A transformer, a diode, a capacitor, a lamp.
2) Why does only half of the voltage come through?
Because the other part of the 12 Volts is blocked by the diode.
3) Why the half of the a.c. wave disappeared after the diode.
The diode conducts AC only in one direction.
4) What is happening when the capacitor is connected after the diode?
The voltage rises.
5) What’s the effect of the capacitor?
The AC wave gets more straight.
6) Why is it inefficient?
Because half of the voltage is suppressed be the diode.
2. Fill in the gaps with the words from the box below.
a) A transformer is an electrical device that transfers energy between two or more circuits through electromagnetic induction.
b) Rectifiers have many uses, but are often found serving as components of DC power supplies and high-voltage direct current power transmission systems.
c) Electric power is the rate at which electric energy is transferred by an electric circuit.
d) A capacitor consists of two conductors separated by a non-conductive region.
e) Virtually all electronic devices require DC.
3. Open the brackets using the correct form of the verb:
a) In half wave rectification of a single-phase supply, either the positive or negative half of the AC wave is passed, while the other half is blocked.
b) Because only one half of the input waveform reaches the output, mean voltage is lower.
c) Half-wave rectification requires a single diode in a single-phase supply, or three in a three-phase supply
d) Half-wave rectifiers produce far more ripple than full-wave rectifiers.
e) Much more filtering is needed to eliminate harmonics of the AC frequency from the output.
4. Work with a partner. Try to explain the following terms in English. The information in the appendix may be helpful.
1. A transformer is an electrical device that transfers energy between two or more circuits through electromagnetic induction.
2. A diode is a two-terminal electronic component with asymmetric conductance; it has low (ideally zero) resistance to current in one direction, and high (ideallyinfinite) resistance in the other.
3. A capacitor (originally known as a condenser) is a passive two-terminal electrical component used to store energy electrostatically in an electric field. The forms of practical capacitors vary widely, but all contain at least two electrical conductors (plates) separated by a dielectric (i.e. insulator).
4. In alternating current (AC), the flow of electric charge periodically reverses direction.
5. In direct current (DC, also dc), the flow of electric charge is only in one direction.
Electromechanical relay
1. Match Russian and English equivalents. Consult your mini dictionary if it’s necessary.
| relay
| реле |
| actuate
| приводить в действие |
| frame
| корпус |
| coil wire
| провод катушки |
| metal core | металлический стержень |
| armature
| легкий каркас |
| contact
| катализатор |
| wind
| наматывать |
| electromagnetic field
| электромагнитное поле |
1. Answer the following questions:
1)What is an electromechanical relay?
It is a relay that I actuated electromechanically typically with electromagnet.
2) What are the basic parts and of the electromechanical relay?
The frame, the coil wire, metal core, the armature, the contacts.
3) What circuits does electromechanical relay involve?
The energizing circuit and the contact circuit.
4) How might the relay be described as?
As a single pole single throw or double pole single throw
2. See if you can spot the fake facts.
1) A relay is a mechanically operated switch. F
2) An armature is responsible for the passage of current. F
3) An electromagnet is a type of magnet in which the magnetic field is produced by electric current. T
4) An electromagnetic field (also EMF or EM field) is a physical field produced by electrically charged objects. T
5) Electric shock is a useful experience for a young specialist. F
3. Open the brackets using the correct form of the verb:
a) A relay is an electrically operated switch.
b) Many relays use an electromagnet to mechanically operate a switch.
c) Relays are used where it is necessary to control a circuit by a low-power signal or where several circuits must be controlled by one signal.
d) The first relays were used in long distance telegraph circuits as amplifiers.
e) They repeated the signal coming in from one circuit and re-transmitted it on another circuit.
4. Work with a partner. Try to explain the following terms in English. The information in the appendix may be helpful.
1) An electromagnet is a type of magnet in which the magnetic field is produced by electric current.
2) An armature generally refers to one of the two principal electrical components of an electromechanical machine — generally in a motor or generator— but it may also mean the pole piece of a permanent magnet or electromagnet, or the moving iron part of a solenoid or relay.
3) A relay is an electrically operated switch. Many relays use an electromagnet to mechanically operate a switch, but other operating principles are also used, such as solid-state relays.
Circuit breakers and fuses
1. Answer the following questions:
1) Fuses are made of:
Filament, glass, porcelain or ceramic case.
2) What means is switching mechanism with a metallic level actuated by?
By a solenoid or bimetallic plate.
3) What are the thermal magnetic circuit breakers?
Thermal-magnetic circuit breakers contain two different switching mechanisms, a bimetal switch and an electromagnet.
4) Why are fuses considered to be safer?
Due to their current corruption capacity rating.
5) What is the advantage and disadvantage of fuses?
They are less expensive but need to be replaced.
6) And what is the advantage and disadvantage of the circuit breakers?
Circuit breakers are more expensive but resettable.
2. Put the words in a correct order.
a) A circuit breaker is an automatically operated electrical switch
b) A fuse is a type of low resistance resistor
c) Circuit breakers are made in varying sizes
3. Open the brackets using the correct form of the verb:
a) Its basic function is to detect a fault condition and interrupt current flow.
b) Unlike a fuse, which operates once and then must be replaced, a circuit breaker can be reset) to resume normal operation.
c) Circuit breakers are made in varying sizes.
d) It acts as a sacrificial device to provide over current protection.
e) Its essential component is a metal wire or strip that melts when too much current flows through it, interrupting the circuit that it connects.
4. Explain the main difference between a circuit breaker and fuse? The information in the appendix may be helpful.
They actually do the same thing, protect a circuit in event of an overload. The circuit breaker can be reset and used over and over, where a fuse is a one shot deal and has to be replaced. Fuses are usually found in older buildings where circuit breakers are in newer ones. Circuit breakers are more expensive but resettable. Fuses are less expensive but need to be replaced.
How electric motors work
1. Answer the following questions:
1) What is an electric motor?
It is a machine that uses electric energy to produce motion.
2) Give the examples of the devices operated with the electric motors you’ve seen in the video.
Vacuum cleaners, windshield wipers, conveyor belts.
3) What is a brush? What’s its use?
A block of graphite which transmits current to the commutator which consists of two or more semi-circular split rings.
4) What is the commutator connected to?
Large coil wire called armature and to the output shaft.
5) What does the direction of the motion depend upon?
It depends upon the directions of the field and the current.
2. See if you can spot the fake fact:
a) An electric motor is an electric machine that converts electrical energy into mechanical energy. T
b) The reverse conversion of mechanical energy into electrical energy is done by an electromagnetic field. F
c) Motors can be used only in cars. F
d) Electric motors are replacing hydraulic cylinders in airplanes and military equipment. T
e) There are no such motors as non-magnetic motors. F
3. Open the brackets using the correct form of the verb:
a) In normal motoring mode, most electric motors operate through the interaction.
b) Small motors may be found in electric watches.
c) Electric motors may be classified by electric power source type, internal construction, application, type of motion output, and so on.
d) In an electric motor the moving part is the rotor which turns the shaft to deliver the mechanical power.
e) The stator core is made up of many thin metal sheets, called laminations.
Hydroelectric Power Plant
I. Match Russian and English equivalents. Consult your mini dictionary if it’s necessary.
| Hydroelectric Power Plant | гидроэлектростанция |
| floodgate | водоспуск, шлюз |
| dam | дамба |
| penstock | напорный туннель |
| turbine | турбина |
| shaft | стержень |
| cones | конусы |
| generator | генератор |
| rotate | вращать |
1. Answer the following questions:
1) How is the electricity produced in Hydroelectric Power Plant?
From water.
2) The Hydroelectric Power Plant…
Across a large river.
3) Where is a floodgate situated?
At the bottom of the dam.
4) What are the parts of the Hydroelectric Power Plant?
Floodgate, penstock, turbine, shaft, cones, generator.
2. Fill in the gaps with the words from the box below.
a) Hydroelectricity is the term referring to electricity generated by hydropower.
b) It is the most widely used form of renewable energy
c) Hydropower is produced in 150 countries
d) The cost of hydroelectricity is relatively low, making it a competitive source of renewable electricity.
e) However, damming interrupts the flow of rivers and can harm local ecosystems.
3. Open the brackets using the correct form of the verb:
a) Hydropower has been used since ancient times.
b) Many small hydroelectric power stations were being constructed by commercial companies in mountains near metropolitan areas.
c) Hydroelectric power stations continued to become larger throughout the 20th century.
d) An underground power station is generally used at large facilities.
e) Annual electric energy production depends on the available water supply.
4. Explain how the Hydroelectric Power Plant works. The information in the appendix may be helpful.
Water flows through a penstock and rotates the turbine, the flowing water rotates the turbine which is placed at the end of the penstock. The turbine in turn rotates the shaft that is connected to the cones of a generator. These cones are placed in between strong magnetic poles. The rotating shaft turns the cones.
Nuclear Power Plant
1. Answer the following questions:
1) What is a nuclear power plant?
It is a thermal power station which generate electrical energy.
2) What are the most important buildings and facilities of a nuclear power plant?
The turbine building, the containment building, the cooling tower.
3) What is the PWR?
Pressurized water reactor.
4) What is a fuel assembly composed of?
It is composed of many fuel rods.
6) How many fuel assemblies can be found in a pressurized water reactor?
About 150.
7) Where is the actual nuclear fuel found?
Inside each fuel rod there is a small fuel pellet.
8) What is a fuel pellet composed of?
Enriched uranium or plutonium.
9) For what purpose is water needed?
In order to absorb the thermal energy and keep the chain reaction going.
10) Why does not the water boil?
The pressurizer maintains the water pressure.
11) What is the other way to call a heat exchanger?
Steam generator.
12) Where is actually the water boils?
Inside the heat exchanger.
13) Why are the water circulation systems kept separate and through this why does the water in a primary circulation system never leave the containment building?
Because this water is radioactive since it has been in direct contact with the fuel rods.
2. Match the element of the nuclear power plant with their measure characteristics.
| containment building | meter thick reinforced concrete |
| cooling tower | 200 meter tall |
| reactor pressure vessel | 12 meters tall, 25 centimeters thick |
| the water pressure | 160 Bars |
| fuel rod | 5 meters length, diameter 23 centimeters |
| the heat of the water inside the reactor pressure vessel | 570 Fahrenheit
|
3. Open the brackets using the correct form of the verb:
a) A nuclear power plant is a thermal power station.
b) The use of nuclear power as a source of domestic energy has increased significantly over the past decade.
c) These can range from environmental impact.
d) Nuclear power plants are usually considered to be base load stations.
e) Another significant effect is the increased amount of sulfur dioxide in the air which causes acid rain.
БИБЛИОГРАФИЧЕСКИЙ СПИСОК
1. Луговая А.Л. Английский язык для студентов энергетических специальностей: Учеб. пособие/ А.Л. Луговая –5-е изд., стер.– М.: Высш. шк., 2009.– 160 с.: ил.
2. http://en.wikipedia.org/
Видеоресурсы:
1. Half-wave rectifier: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=w-fZ2PTd7X0
2. Electromechanical relay: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=iEuP-fkyV4s
3. Circuit breaker and fuse: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=LyekAmnJnOA
4. How electric motors work:https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Q2mShGuG4RY
5. Hydroelectric Power Planthttps://www.youtube.com/watch?v=-hooifWJ1jY
6. Nuclear Power Plants: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=_UwexvaCMWA























