
СДЕЛАЙТЕ СВОИ УРОКИ ЕЩЁ ЭФФЕКТИВНЕЕ, А ЖИЗНЬ СВОБОДНЕЕ
Благодаря готовым учебным материалам для работы в классе и дистанционно
Скидки до 50 % на комплекты
только до
Готовые ключевые этапы урока всегда будут у вас под рукой
Организационный момент
Проверка знаний
Объяснение материала
Закрепление изученного
Итоги урока

Практикум по дисциплине для студентов 1 курса профиля : технического, очной формы обучения, Часть 2
Практикум составлен с целью обеспечения необходимым материалом практических занятий со студентами 1 курса технических специальностей очной формы обучения во 2 семестре по дисциплине «Иностранный язык» (английский). Практикум охватывает все темы, указанные в рабочей программе и является продолжением практикума, предназначенного для организации проведения практических занятий в 1 семестре. Он состоит из введения, 10 разделов (Units), начиная с 10 по 19, приложения (ключи к заданиям по аудированию), списка литературы и других источников.
Просмотр содержимого документа
«Практикум по дисциплине для студентов 1 курса профиля : технического, очной формы обучения, Часть 2»
ФЕДЕРАЛЬНОЕ ГОСУДАРСТВЕННОЕ БЮДЖЕТНОЕ ОБРАЗОВАТЕЛЬНОЕ УЧРЕЖДЕНИЕ ВЫСШЕГО ОБРАЗОВАНИЯ
«КЕРЧЕНСКИЙ ГОСУДАРСТВЕННЫЙ МОРСКОЙ ТЕХНОЛОГИЧЕСКИЙ УНИВЕРСИТЕТ»
СУДОМЕХАНИЧЕСКИЙ ТЕХНИКУМ
Цикловая комиссия гуманитарных и социально-экономических дисциплин
Сухарева Н. В.
ИНОСТРАННЫЙ ЯЗЫК
Практикум
для студентов 1 курса специальностей
22.02.06 Сварочное производство
26.02.02 Судостроение
26.02.04 Монтаж и техническое обслуживание судовых механизмов
26.02.05 Эксплуатация судовых энергетических установок
26.02.06 Эксплуатация судового электрооборудования
профиля: технического
очной формы обучения
Часть 2
Керчь, 2019 г.
Cоставитель: Сухарева Н.В., преподаватель высшей категории цикловой комиссии гуманитарных и социально-экономических дисциплин ФГБОУ ВО «КГМТУ» СМТ_________
Рецензент: …………преподаватель высшей категории цикловой комиссии гуманитарных и социально-экономических дисциплин ФГБОУ ВО «КГМТУ» СМТ_________
Методические рекомендации рассмотрены и одобрены на заседании цикловой комиссии гуманитарных и социально-экономических дисциплин СМТ ФГБОУ ВО «КГМТУ»
протокол № ___ от ___________2019 г.
Зав. цикловой комиссии ____________ Р.В. Попова
Методические рекомендации утверждены на заседании методического совета СМТ ФГБОУ ВО «КГМТУ»
протокол № ___ от ___________2019 г.
ФГБОУ ВО «КГМТУ», 2019 г.
СОДЕРЖАНИЕ
ВВЕДЕНИЕ
Unit 10 Healthy Way of Life
Unit 11 Travelling
Unit 12 The State System of the Russian Federation
Unit 13 English-Speaking Countries
Unit 14 Scientific and Technical Progress
Unit 15 Human Activity and the Nature
МОДУЛЬ: ПРОФЕССИОНАЛЬНЫЙ
Unit 16 Achievements and Innovations in Science and Technology
Unit 17 Machines and Mechanisms
Unit 18 Modern Computer Technologies
Unit 19 At an Industrial Exhibition
ВВЕДЕНИЕ
Практикум составлен с целью обеспечения необходимым материалом практических занятий со студентами 1 курса технических специальностей очной формы обучения во 2 семестре по дисциплине «Иностранный язык» (английский). Практикум охватывает все темы, указанные в рабочей программе и является продолжением практикума, предназначенного для организации проведения практических занятий в 1 семестре. Он состоит из введения, 10 разделов (Units), начиная с 10 по 19, приложения (ключи к заданиям по аудированию), списка литературы и других источников.
Разделы состоят из текстов, предлагаемых для чтения, аудирования, а также текстов, которые могут служить основой развития монологической или диалогической речи. Уделяется внимание развитию письменной речи. В практикуме можно найти задания разного уровня сложности, что позволяет включить в учебную деятельность обучаемых с разным уровнем подготовки. Предлагаемый учебный материал представляет определённый интерес для аудитории, так как отражает современные аспекты социальной и культурной жизни общества.
Тексты снабжены словарями и комментариями. Предложенные задания имеют репродуктивный, реконструктивный и творческий уровни. Работа над темой проходит поэтапно с постепенным повышением уровня сложности, что отвечает требованиям методики преподавания дисциплины «Иностранный язык».
Практикум будет полезен как для работы в аудитории, так и для самоподготовки обучаемых по темам, предусмотренным программой.
Unit 10 HEALTHY WAY OF LIFE
Exercise 10.1 Write down the new words in your vocabularies
| spectator amateur soccer[sokə] picture watch an example to play against team important | зритель, наблюдатель любительский футбол портрет наблюдатель пример играть против команда важный |
Exercise 10.2 Read the text and give the title for each paragraph
Sports in Great Britain
The British have a reputation of being mad about sports. In fact they like watching sports more than playing them. The British are spectators and the most popular spectator sports are cricket and football.
Football is the most popular game. Football, or soccer, is an example of a professional game. The game of football was first played in Britain, and later people began to play football in other countries.
There are many amateur soccer players in Britain who play the game on Saturday or Sunday afternoon. Amateur clubs often play against professionals.
Almost every school has its football team and every boy in Britain knows a lot about the game. He can tell you the names of the players in the most popular teams. He has pictures of them and knows the results of many matches.
Rugby is another popular British sport game which is played in other countries. It is also called rugby football. The story is told that in 1823 at Rugby school in England boys were playing football in the normal way, when suddenly one boy picked the ball up and ran with it. That was how a new game was born. There are two forms of rugby football: the amateur game and the professional game. The two games have different rules.
Football is the favourite winter game in Britain and cricket is the favourite summer sport. Amateur cricket has the same rules as the professional game. A typical amateur cricket match takes place on a village green field, an open space in the centre of the village. It is played between two teams — the «home» team and the «visitors» who come from another village.
Exercise 10.3 Translate the word expressions into Russian
to be mad, in fact, to like watching sports, the most popular spectator sports, an example of a professional game, in other countries.
Exercise 10.4 Translate the words expressions into English
любительские клубы, играть против профессионалов, почти каждая школа,
футбольная команда, имена игроков, в большинстве важных команд.
Exercise 10.5 Make the right word combinations using the words from the both columns
1. to know 1 .matches
2. to have 2. boy
3. the results of 3.the game
4. every 4. pictures
5. to play 5. a lot
Exercise 10.6 Finish the sentences
1. Almost every school has its football...
2. Britain knows a lot about...
3. The game of football was first played in ...
Exercise 10.7 Express your agreement or disagreement
Football is an example of only amateur game.
The British have a reputation for being mad about sports.
The most popular spectator sports are cricket and football.
In faсt the British like playing sports more than watching them.
Football is the most popular game.
The game of football was first played in France.
Exercise 10.8 Answer the questions
1. What reputation do the British have?
2. What is the most popular game in Britain?
3. When do amateur soccer players play in Britain?
4. How was rugby football born?
5. What is the British favourite summer sport?
6. How is cricket played?
7. Do you like sports?
8. What sport are you going in for?
Exercise 10.9 Put questions to the underlined words
1. Every boy in Britain knows a lot about football.
2. Every boy knows the results of many matches.
3. Amateur clubs often play against professional clubs.
Exercise 10.10 Make the dialogue of your own about favourite Russian sports according to the sample given below
A Sample Dialogue
A: Do you know anything about football?
B: I know a little.
A: Where was the game played first?
B: The game was first played in Britain.
A: When did people begin to play football in other countries?
B: They began to play football later in other countries.
A: What are the most popular spectator sports?
B: The most popular spectator sports are cricket and football.
A: What is an example of a professional game?
B: Football is an example of a professional game.
A: Does every school have its football team?
B: Almost every school has its football team.
Exercise 10.11 Imagine you are a participant of a competition in Great Britain. Meet a new friend who goes in for sports too. Make a dialogue of your own according to the sample given below. Change underlined words and word expressions
A Sample Dialogue
Sportsmen and Spectators
David: How do you do? I’m David from Briton. And you?
Alex: How do you do? My name’s Alex. I’m from St. Petersburg. Nice to meet you.
David: Nice to meet you too. Are you going to Britain on business?
Alex: Oh, no. I’m going to take part in European Championship in tennis.
David: Are you a tennis player? Ah, that’s why you look so fit and energetic.
Alex: Yes, I practice tennis every day, and I really enjoy it. And what about you?
David: As for me, I’m a good swimmer and runner, but I don’t like to participate in any team. Independent physical exercises help me have a healthy mind in a healthy body.
Alex: I agree with you, but I’m sure that only sports competitions make a person more organized and disciplined and really strong.
Exercise 10.12 Make up questions to the given answers to complete the dialogue
A.: _________________ B.: I am going to my school gym.
A.: _________________ B.: I’ll have my training there.
A.: _________________ B.: I have my training every other day.
A.: _________________ B.: Oleg is my coach.
A.: _________________ B.: He is very good at swimming. Last year he
_________________ was a champion.
A.: _________________ B.: Of course, I do.
A.: _________________ B.: Certainly, you may come if you wish.
A.: _________________ B.: I hope so.
Exercise 10.13 Write down in your vocabulary and try to remember the new words
Vocabulary
| nutrients nutritional value carbohydrates fat saturated fats
unprocessed fats to hide (hid, hidden) crisps tuna additive fertilizers food chain a rumour сancer magined fear taste advertising income a lack of knowledge | питательное вещество питательная ценность углеводы жиры жиры с высоким содержанием насыщенных жирных кислот необработанные жиры прятать хрустящий картофель, чипсы тунец добавка химические удобрения пищевая цепочка молва, слух рак (онкология) надуманный страх вкус реклама доход недостаток знаний |
Exercise 10.14 Read the text. What problem do you think is raised in the text? Define the main idea of the text
Healthy Food
All food is made up of nutrients which our bodies use. There are different kinds of nutrients: carbohydrates, proteins, fats, vitamins and minerals. Different foods contain different nutrients.
Before we cut down on fat, sugar and salt, we have to know a bit more about the kind of food these things might be in. The biggest problem comes when these things are hidden in other foods: biscuits, crisps, sausages, meat pies, soft drinks and so on. The best way is to get into the habit of checking the ingredients and nutritional value on the sides of packets although this isn't always easy to do. Another thing to know is, for example, that we do need fat to live, it's an essential part of our diet and physically we couldn't exist without it. But we all know that to eat much fat is bad for our health. The matter is that there are different kinds of fat. There are fats that are good for us and fats that are bad for us. Eating less of the bad ones and more of the good ones can actually help us to live longer! Bad fats are the saturated fats, found in animal productions, like red meat, butter and cheese.
Friendly fats are the unprocessed fats found naturally in foods like nuts and seeds, olives, avocados and oily fish, including tuna.
One more thing to know is that when food is cooked, its structure changes. It can change the vitamin and nutrient contents of food.
More and more people feel strongly about the way, their food is produced. Nowadays so much of the basic food we eat — meat, fish, fruit and vegetables — is grown using chemicals and additives. Although fertilizers and pesticides have greatly increased the quantity of food and helped to improve its appearance, there is a growing concern about the effects of these chemicals in the food chain. This concern has led to a growth in the demand for organically grown products.
Today there is another problem. It is modified food, which is cheaper that ordinary one. There is a rumour that such food can cause cancer and other problems. Nobody knows, either it is just an imagined fear or a real problem. This problem could be solved and examined, but it will take some time.
The food we eat, depends on lots of things. Taste is a big factor. Culture, religion and health also play a part in what food we eat. Advertising and social factors also have a big influence.
Income is also an important factor. That is why not surprisingly, money, rather than a lack of knowledge about how to eat well, is at the heart of the problem.
Finally, there are three main messages to follow for healthy eating:
First, we should eat less fat, particularly saturated fat. Secondly, we are to cut down on sugar and salt. Thirdly, we must eat more fresh fruit and vegetables.
Exercise 10.15 Answer the questions
What nutrients do you know?
What are the main things to know about the food we eat?
What fats are good?
What fats are dangerous for our health?
What are the main factors that determine the food w eat?
What are three main messages to follow for healthy eating?
Exercise 10.16 Think and tell about your eating habits
• Does your family buy much food?
• Do you sometimes throw it away?
• How much of it do you waste?
• Why is it important for the environment not to waste food?
Exercise 10.17 Put the instructions for the recipe of a tuna sandwich in the correct order
Serve four. Time needed: 15 minutes.
Ingredients: 175 g tin of tuna; 125 g cheese; 1 banana; 200 g mayonnaise; salt and pepper.
a) Mix all the ingredients together.
b) Cut the banana in pieces and put them in the bowl.
c) Open the tin of tuna.
d) Grate the cheese and add it to the tuna.
e) Put the tuna in a bowl and break it up with a fork.
f) Put the mixture on a piece of bread or a roll. It is ready to eat!
g) Mix the mayonnaise with the tuna and cheese.
Exercise 10.18 Think of and suggest your own instructions of making a healthy and tasty dish in writing. Prepare your instruction for your Portfolio
Unit 11 TRAVELLING
Exercise 11.1 Read and translate the text
Travelling
Modern life is impossible without travelling. Almost all people are fond of travelling. Thousands of people travel every day either on business or for pleasure. It is very interesting to see new places, other towns and countries.
There are various means of travelling. People can travel by air, by train, by sea or by road. Of course, travelling by air is the fastest and the most convenient way, but it is the most expensive, too.
Travelling by train is slower than by plane, but it has its advantages. With a train you have speed, comfort and pleasure combined. You can see much more interesting places of the country you are travelling through. Modern trains have comfortable seats. There are also sleeping cars and dining cars that make even the longest journey enjoyable.
Speed, comfort, and safety are the main advantages of trains and planes. That is why many people prefer them for business trips to all other means of travelling.
Travelling by sea or sea voyages are popular mostly as pleasure journeys. Large ships can visit foreign countries and different places of interest.
Many people like to travel by car. It is interesting too, because you can see many places in a short time, you can stop anywhere you wish and spend as much time as you like at any place.
Nowadays a very popular method of travelling is hiking. It is travelling on foot. Walking tours are very interesting.
Vocabulary
| advantage business trip means expensive (air)plain journey sleeping car dining car sea voyage hiking walking tour | преимущество деловая поездка, командировка средство, способ дорогой самолёт путешествие, поездка (по суше) спальный вагон вагон-ресторан морское путешествие, рейс пеший туризм пешая экскурсия |
Exercise 11.2 Find English equivalents for the following Russian expressions
Быть любителем путешествий; командировка; разные способы путешествия; самый дорогой способ путешествия; путешествовать по стране; удобные сидения; приятная поездка; посещать различные достопримечательности; останавливаться, где только пожелаешь; путешествовать пешком
Exercise 11.3 Fill in the gaps with the appropriate form of the verb to be in the Present Simple Tense
Modern life … impossible without travelling. 2. Almost all people … fond of travelling. 3. There … various means of travelling. 4. … there a dining car in the train? 5. Speed, comfort, and safety … the main advantages of trains and planes. 6. Travelling by sea or sea voyages … popular mostly as pleasure journeys. 7. Hiking … travelling on foot. 8. Walking tours … very interesting. 9. I … fond of hiking.
Exercise 11.4 Match the adjectives in the right column with the sentences in the left column
| Travelling by air is … way of journey. … way of travelling is by plane. Travelling by plane is …. Travelling by train is … than by plane. You can see … places of the country. Sleeping cars and dining cars make even … journey enjoyable. Travelling by sea or sea voyages are … too. | the most expensive the longest the fastest popular the most convenient much more interesting slower |
Exercise 11.5 Answer the questions
Why do people travel?
What are the means of travelling?
What are the advantages of travelling by plane?
What are the advantages and disadvantages of travelling by car, train and ship?
Why do many people prefer to travel by car?
How do you prefer to travel and why?
Exercise 11.6 Read the dialogue in pair and translate it. Change the underlined words and expressions to modify the dialogue
At the Travel Agency
Travel Agent: Good morning. Can I help you?
Customer: Yes. I have to go to Moscow for a few days on the 2nd of March.
Travel Agent: On the 2nd of March. And when do you want to come back?
Customer: Returning on the 6th of March.
Travel Agent: Is it just for yourself?
Customer: Yes, it is.
Travel Agent: Do you need accommodation too?
Customer: Yes, please. I’d like a hotel near the centre of the city.
Travel Agent: And do you want to fly business class or economy?
Customer: Can you give me prices for both, please?
Travel Agent: Yes, of course. Well, let’s just have a look at the computer.
Exercise 11.7 Read the dialogues in pairs and translate them. Learn the dialogues by heart
1 At the Airport
a)
Excuse me. Could you tell me where the Aeroflot – Russian Airlines counter is?
Certainly. Just go up the escalator on your right and you’ll see it.
Thank you.
b)
- Good afternoon, sir. I have reserved a ticket from Berlin to London for today’s flight GP 217.
- Good afternoon. What is your name, please?
- I’m Alex Ivanov. Here is my passport.
- Let me see … Oh, yes, Alex Ivanov, flight GP 217. Here is your ticket. Your flight is now boarding at gate 50. Go down concourse D. It’s to your left.
2 Meeting at the Airport
Excuse me … are you Mr. Parker?
Yes.
I’m Alex Ivanov from «Research-and-Production Association "Avrora" (St.-Petersburg). How do you do?
How do you do? Have I kept you waiting?
Oh, no … the plane’s just arrived. Thank you for coming to meet me.
Not at all. Did you have a good trip?
Yes, thank you. I was a bit air-sick, but now I’m O.K.
My car’s just outside the airport. My driver will take your suitcase.
Thank you.
3 At the Railway Station
I’ve found out from this time-table that there are several trains to Brighton daily.
Yes, quit so. The next is at 12.20.
Well, I’ll take it. One ticket, please.
Single or return?
Single, please.
Here you are. The train is leaving from platform 3.
Is there a buffet-car on the train? I’d like to have a snack.
Unfortunately, no. but if you hurry, you can get a snack at a cafeteria in the station. Otherwise you’ll have to do without breakfast.
Thank you very much.
Not at all.
Announcement: The train now standing at Platform 3 is the 12.20 Inter-City service to Brighton.
Exercise 11.8 Study the new words. Think of the topic where they can be used
Vocabulary
| possible blanket dehydration flight flight attendant to fasten ≠ to unfasten seat belt to be safe locker to reach arrival card | возможный одеяло обезвоживание полёт, рейс стюардесса пристёгивать отстёгивать ремень безопасности быть в безопасности запирающийся ящик (шкафчик) добираться, достигать карта прибытия |
Exercise 11.9 Listen to the text and fill in the gaps with the words you hear
On Board an Airplane
- Excuse me. Is it possible to have another … (1), please? I am a little cold.
- Sure. Would you like just one or two?
- One will be enough I think.
- OK. I’ll be right back with your blanket. Would you like anything else?
- Yes. Can I get something … (2) too?
- Sure. We should … (3) dehydration during these long flights. What would you like to drink?
- I’d like some orange … (4), please. And no … (5) in it, of course.
- Oh yes. I’ll bring it to you … (6). By the way you can … (7) your seat belts. It is safe to do so now. And why did you put this … (8) under your seat? I think it is very … (9) for you. You should put it on the shelf above your seat, into the locker.
- OK, thanks. I will do that. Could you tell me how long it’ll take to reach New-York?
- Well, you know it’s a … (10) journey. We still have 6 more hours before landing.
- Will there be any food before we … (11)?
- Sure. We’ll serve another meal in 3 hours. But if you are hungry I can bring you a little … (12) if you want.
- Yes, that would be great.
- No problem. … Here you are, sir. And here is an … (13) for the immigration service. Please, fill in this form before we land. Use … (14) pen, please
- Thank you. But I need a black pen. Could you lend me one?
- One moment, please. Another flight … (15) will be bringing pens around shortly.
- Thanks a lot.
- Enjoy your flight.
Exercise 11.10 Тranslate the following expressions into English.
Что касается меня, то я люблю путешествовать на поезде. В нем не так жарко, как в автобусе, и на железных дорогах почти никогда не бывает пробок (traffic jams). Можно любоваться природой, и прибыть в самый центр города, а не в пригород, как если вы летите самолетом.
Exercise 11.11 Make up а dialogue on the following subjects.
1. Two students plan а trip abroad and choose what transpoгt to take.
2. А tourist agent speaks to а client and suggests different tours. The client doesn't like to travel bу plane.
3. Husband and wife arrive at the railway station of their home town. They see а bus and some taxis and decide what transport to take.
Exercise 11.12 Tell about your last travelling
Unit 12 The State System of the Russian Federation
Exercise 12.1 Study the new words write them down into your note-books
| 1. a state 2. a head to head 3. govern government 4. a branch 5. legislative 6. executive 7. judicial 8. to exercise 9. chamber 10. chairman 11. to elect 12. a vote 13. to initiate 14. a law 15. a bill 16. to approve 17. to sign 18. a treaty 19. to enforce 20. to appoint appointment 21. to act action 22. a court 23. banner 24. to signify 25. ancient 26. to originate 27. succession | государство, штат глава, голова возглавлять управлять правительство ветвь, филиал законодательный исполнительный судебный реализовывать, выполнять палата, камера председатель избирать голосование начинать, инициировать закон законопроект утверждать, одобрять подписывать договор применять, осуществлять назначать назначение действовать действие суд знамя обозначать древний происходить правопреемство |
Exercise 12.2 Match the word expressions in the right- and left hand columns. Study the word combinations by heart
| Parliamentary Republic the Federal Assembly the Upper Chamber the Council of Federation the Lower Chamber the State Duma the Constitutional Court the Supreme Court the Arbitrary Court the Byzantine Empire | Верхняя палата Верховный суд Совет Федерации Византийская империя Парламентская республика Государственная Дума Конституционный суд Федеральное собрание Нижняя палата Арбитражный суд |
Exercise 12.3 Read the text and translate it
The State System of Russia
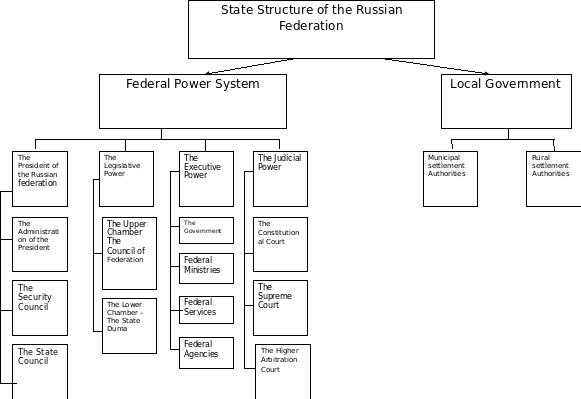
The state power in the Russian Federation is determined as a combination of Parliamentary and Presidential forms of rules. Head of state in this country is the President. The government consists of three branches: legislative, executive and judicial. The President controls each of them.
The legislative power is exercised by the Federal Assembly. It consists of two chambers. The Upper Chamber is the Council of Federation and the Lower Chamber is the State Duma. Each chamber is headed by the Speaker/ Chairman. The members of the State Duma are elected by popular vote for a four-year period. The Council of Federation is not elected. It is formed of the heads of the regions. Legislature is initiated in the Lower Chamber. But to become a law a bill must be approved by the Lower and Upper Chambers and signed by the President. The President may veto the bill. The State Duma may override the veto.
The President makes treaties, enforces laws, appoints the Prime Minister to be approved by the State Duma.
The executive power belongs to the Government, or the Cabinet of Ministers. The government is headed by the Prime Minister. The first action of the Prime Minister on his appointment is to form the Government.
The judicial power belongs to the system of courts. It consists of the Constitutional Court, the Supreme Court, the Arbitrary Court and regional courts.
Today the state banner of the Russian Federation is a three coloured flag. It has three horizontal stripes: white, blue and red. The white stripe symbolizes the peace and purity, the blue one stands for the faith, and the red one signifies energy and blood spilled for the motherland and liberty. It was the first state symbol that replaced the former symbols in 1991. The hymn of Russia was created by Alexander Alexandrov and Sergey Mikhalkov. Now the national coat of arms is a two-headed eagle. It is the most ancient symbol of Russia. It originates from the heraldic emblem of the Ruricovitch signifying the succession of the Russian state from the Byzantine Empire.
Exercise 12.3 Translate the words and word expressions from the text into Russian
Head of state; to consists of three branches; legislative branch; executive branch; judicial branch; to exercise power; to head the chamber; to elect by a popular vote; to approve a bill; to belong to the government; an appointment; the peace and purity; to stand for the faith; to spill blood; the national coat of arms; a two-headed eagle
Exercise 12.4 Find equivalents for the following Russian words and word expressions in the text
Контролировать исполнительную власть; осуществлять законодательную власть; члены Государственной Думы; возглавляться спикером; четырёхлетний период; подписывать закон; наложить вето на законопроект; преодолеть вето; заключить договор; система судов; трёхцветный флаг; обозначать чистоту; национальный герб; двуглавый орёл
Exercise 12.5 Insert the verbs in the brackets in the necessary Active or Passive Voice form
The legislative power (to exercise) by the Federal Assembly.
The Federal Assembly (to consist) of two chambers.
Each chamber (to head) by the Speaker.
The members of the State Duma (to elect) by popular vote.
Legislature (to initiate) in the Lower Chamber.
To become a law a bill must (to approve) by the Lower and Upper Chambers and (to sign) by the President.
The President may (to veto) the bill.
The executive power (to belong) to the Government.
The white stripe (to symbolize) the peace and purity.
The hymn of Russia (to create) by Alexander Alexandrov and Sergey Mikhalkov.
Exercise 12.6 Decide if the statements are true or false
The state power in the Russian Federation is determined as a Parliamentary republic.
The government consists of two branches: legislative and executive.
The Federal Assembly consists of two chambers.
Each chamber is headed by the Administration officer.
The members of the Council of Federation are elected by popular vote for a four-year period.
Legislature is initiated in the Lower Chamber.
The government is headed by the Chairman.
The hymn of Russia was created by Alexander Alexandrov and Sergey Mikhalkov.
Exercise 12.7 Finish the sentences with the appropriate words
| The head of the Russian Federation is… The legislative power is exercised by … The Upper Chamber is … The Lower Chamber is … The Council of Federation is formed of … The President appoints … The executive power belongs to The first action of the Prime Minister on his appointment is … The judicial power consists of the Constitutional Court, the Supreme Court the Arbitrary Court and … The state banner of the Russian Federation has three horizontal stripes: white, blue and … One of the most ancient symbol of Russia is … | the State Duma. regional courts. the Prime Minister the Federal Assembly. to form the Government. the President. red. the Cabinet of Ministers. a two-headed eagle. the heads of the regions. the Council of Federation. |
Exercise 12.8 Answer the questions on the text
How is the state power in the Russian Federation determined?
Who is he head of state in the Russian Federation?
What branches does the government consist of?
What governmental body exercises the legislative power?
What chambers does the Federal Assembly consist of?
Who is each chamber headed by?
How is the State Duma formed?
How is the Council of Federation formed?
What are the main functions of the President?
Who does the executive power belong to?
What courts does the system of courts in the Russian Federation consist of?
What do you know about the state flag of the Russian Federation?
Who created the hymn of Russia?
What does the national coat of arms originate from?
What does this heraldic emblem of the Ruricovitch signify?
Exercise 12.9 Fill in the empty boxes of the Memory Map with the necessary information from the text and tell about the process of making lows in the country

 Veto Approve and …
Veto Approve and …



 Approve Approve
Approve Approve
Discuss Initiate
Upper Chamber – …
Lower Chamber – …
Exercise 12.10 Study the table and make a short report on the theme “The State System of Russia”. Use the following expressions in your report
I’d like to tell you about…
As far as I know…
Firstly…/ Secondly…/ Finally…
On this basis, I can conclude that…
To sum up…
In conclusion I’d like to say that…
Exercise 12.11 Study the new words
| to proclaim revere sovereignty multinational liberty | провозглашать почитать суверенитет многонациональный свобода
|
Exercise 12.12 Read the text and translate it
Constitution of the Russian Federation
The Constitution of the Russian Federation was adopted on the 12ht of December, 1993. More than 58 million voters took part in the referendum on the new Constitution project. The new Constitution came into force on the 25th of December, 1993 when it was officially published. The adoption of the 1993 Constitution marked a new era in the history of the Russian Federation. The Constitution forms the country’s legal foundation, proclaims the President of the Russian Federation the head and lays upon him the responsibility for defending the Constitution, human rights and civil liberties, safeguarding Russia’s sovereignty, independence and territorial integrity, and ensuring the coordinated functioning and cooperation of the state bodies of power. It regulates the procedure for the application of laws and regulations, guarantees equality between men and women, human rights and freedoms, the presumption of innocence. The Constitution guarantees the accessibility and free access to pre-school, basic General and secondary education in state / municipal educational institutions. It assigns Moscow the status of the capital of our state. It sets the ruble as the only legal currency in our country. Some amendments to the Constitution of the Russian Federation were made on the 30th of December, 2008.
We, the multinational people of the Russian Federation, united by a common fate on our land, establishing human rights and freedoms, civic peace and accord, preserving the historically established state unity, proceeding from the universally recognized principles of equality and self-determination of peoples, revering the memory of ancestors who have conveyed to us the love for the Fatherland, belief in the good and justice, reviving the sovereign statehood of Russia and asserting the firmness of its democratic basic, striving to ensure the well-being and prosperity of Russia, proceeding from the responsibility for our Fatherland before the present and future generations, recognizing ourselves as part of the world community, adopt the CONSTITUTION OF THE RUSSIAN FEDERATION.
First Section
Main Provisions
Chapter 1. The Fundamentals of the Constitutional System (Art. 1-16)
Chapter 2. Rights and Freedoms of Man and Citizen (Art. 17-64)
Chapter 3. The Federal Structure (Art. 65-79)
Chapter 4. The President of the Russian Federation (Art. 80-93)
Chapter 5. The Federal Assembly (Art. 94-109)
Chapter 6. The Government of the Russian Federation (Art. 110-117)
Chapter 7. Judicial Power (Art. 118-129)
Chapter 8. Local Self-government (Art. 130-133)
Chapter 9. Constitutional Amendments and Review of the Constitution (Art. 134-137)
Second Section.
Concluding and Transitional Provisions
Exercise 12.13 Answer the questions
Have you ever read the Constitution of the Russian Federation?
When was the present Constitution adopted?
When were some amendments to the Constitution of the Russian Federation made?
Do you think it’s important for you to know this document? Why?
What does the Constitution form and proclaim?
What does the Constitution regulate and guarantee?
Exercise 12.14 Finish the sentences in the table with the words in the right-hand column in the appropriate forms
| Everyone have the right to ... | LIVE |
| Basic general ... shall be compulsory. Parents or guardians shall ensure that children receive a basic general education. | EDUCATE |
| All persons shall be ... before the law and the court. | EQUALITY |
| Everyone shall have the right to use his (her) native language and to a free choice of the language of ..., ... and ... work. | COMMUNICATE EDUCATE CREATE |
| Everyone shall be guaranteed ... of ... and speech. | FREE SPEAK |
| The freedom of the mass media is ... . | GUARANTEE |
| Everyone shall have the right freely to use his (her) labour skills and to choose the type of ... and ... . | ACTIVE OCCUPY |
| Everyone shall have the right to ... . | RESTFUL |
| Everyone shall have the right to ... protection and medical care. | HEALTHY |
Unit 13 English-Speaking Countries
Exercise 13.1 Match English and Russian equivalents
| native language foreign language native speaker thorough knowledge of English to speak poor English to speak English fluently to master the language means of communication to read in original to do one’s best as quick as possible | делать всё возможное хорошее знание английского плохо говорить по-английски как можно быстрее средство общения иностранный язык совершенствовать язык читать в оригинале носитель языка родной язык бегло говорить по-английски |
Exercise 13.2 Suggest sentences of your own using the word expressions in the table
Exercise 13.3 Study the new vocabulary
| bald eagle dense (population) beaver maple leaf urban areas the Southern Cross constellation to stay in close association with the Commonwealth of Nations edging dominion flightless bird kiwi silver fern | белоголовый орёл плотный, густонаселённый бобёр кленовый лист городские районы созвездие Южного Креста оставться в тесном сотрудничестве содружество наций окраина, кайма главенство нелетающая птица киви серебряный папоротник |
Exercise 13.4 Look through the text, write out Proper Names and find out what they mean. Study the new words
Exercise 13.5 Read and translate the text
English-Speaking Countries
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland (the UK) occupies most of the territory of the British Isles. It consists of four main parts which are: England, Scotland, Wales and Northern Ireland. Their capitals are London, Edinburgh, Cardiff and Belfast.
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland is the official name of the state which is sometimes referred to as Great Britain or Britain (after its major isle), England (after its major historic part) or the British Isles.
English is not the only language which people use in the UK. English is the official language. But some people speak Gaelic in western Scotland, Welsh - in parts of northern and central Wales.
The flag of the United Kingdom, known as the Union Jack, is made up of three crosses. The upright red cross is the cross of St. George, the patron saint of England. The white diagonal cross is the cross of St. Andrew, the patron saint of Scotland. The red diagonal cross is the cross of St. Patrick, the patron saint of Ireland. The Welsh flag, called the Welsh dragon, bears the red dragon on the white and green background. St. David as the patron saint of Wales.
The humid and mild climate of Great Britain is good for plants and flowers.
Some of them have become symbols in the UK. Probably you know that the poppy is the symbol of peace, the red rose is the national emblem of England, the thistle is the national emblem of Scotland and the Edinburgh International Festival. The daffodils and the leek are the emblems of Wales, the shamrock (a kind of clover) is the emblem of Ireland.
Except the United Kingdom there are some other countries in the world where people speak English and this language is one of the official ones. The largest and most important of them are the USA, Canada, Australia and New Zealand.
The USA has 50 states. The flag of the USA has 13 red and white stripes, which symbolize the original 13 states. The national symbol of America is the bald eagle; another one is Uncle Sam. 50 stars on the blue field in the left upper corner are for each of the 50 states of the country in our days. The capital of the USA is Washington, D.C. (the District of Columbia). This city was named in honour of the first US president. People of various nationalities live in the USA: the English, the German, the Chinese, the Hindu, the Greek and so on.
The world’s second-largest country is Canada. Though Canada is one of the largest countries in the world, its population isn’t dense. Canada has two official languages – English and French, both spoken by its citizens. The leading cities of Canada are Toronto, Montreal and Vancouver. The capital of Canada is Ottawa. The official head of Canada is the Queen of the United Kingdom. But practically there is a Prime Minister of the Canadian government to rule the country. Emblems of Canada are the beaver and the maple leaf. The colours of Canada are white and red.
Australia – a continent and a state – is situated in the Southern Hemisphere, in the southern part of Asia, between the Pacific and Indian oceans. It is about 8 million square kilometres. Australia occupies the Tasmania Island and a number of smaller islands too. It is divided into 8 administrative areas. People of about 200 nationalities live there. The aborigines, the Australian natives, represent about 1.5 percent of the population. The Australian flag is blue. There is the flag of the UK on the Australian banner, a large seven-pointed star beneath it and the Southern Cross constellation.
Another country in the Pacific Ocean where people speak English as an official language is New Zealand. It is located not far from Australia – only the Tasman Sea separates them by a distance of about 1,600 km. New Zealand is a constitutional monarchy with a parliamentary form of government.
New Zealand stays in close association with the United Kingdom as a member of the Commonwealth of Nations. And the formal head of the state is the Queen of the United Kingdom. The New Zealand flag represents the Southern Cross, the stars of it are red with white edgings. The flag of the United Kingdom in the left upper corner shows the recognition to the historical foundations and the fact that New Zealand was once a British colony and dominion. The national emblem of New Zealand is a flightless bird kiwi. And silver fern is a sporting emblem.
Exercise 13.6 Fill in the table with the following information according to the text
|
| The UK | The USA | Canada | Australia | New Zealand |
| Flag |
|
|
|
|
|
| Symbol |
|
|
|
|
|
| Location |
|
|
|
|
|
| Major cities |
|
|
|
|
|
| Population |
|
|
|
|
|
Exercise 13.7 Find in the text English equivalents to the following
Официальный язык; святой покровитель; влажный климат; различные национальности; густонаселённый; левый верхний угол; править страной; семиконечная звезда; парламентская форма правления; официальный глава; символ спорта
Exercise 13.8 Answer the questions
Where is English spoken as an official language?
What English-speaking country has 2 official languages? What are they?
What are emblems of Canada?
What is depicted on Australian flag?
What country is situated between the Pacific and Indian oceans?
How can you prove that New Zealand was once a British colony and dominion?
What is the national emblem of New Zealand?
Exercise 13.9 Compare the English-speaking countries using the information in the table (Exercise 13.6)
Exercise 13.10 Study the new vocabulary
Vocabulary
| to recognize to remain to enable extra payment to negotiate a Trades Union necessarily respectively an anniversary | признавать оставаться давать возможность дополнительная оплата вести переговоры; договариваться профсоюз обязательно соответственно годовщина |
Exercise 13.11 Read the text and match the countries and their holidays in the scheme after the text
Bank Holidays
British bank holidays have been recognized since 1871. The name Bank Holiday comes from the time when Banks were shut and so no trading could take place during this time. Even though Banks are still closed on these days, many shops now remain open.
Traditionally on a Bank Holiday many businesses are closed to enable the workers to have a holiday. This time is often spent with the family. Anyone, who works on Bank Holidays, usually gets extra payment — «time-and-a-half» or even «double time», negotiated for them by the Trades Unions.
In England and Wales there are six bank holidays: New Year's Day, Easter, May Day (not necessarily 1 May), Spring and Late Summer Holidays at the end of May and August respectively, and Boxing Day. There are also two common law holidays on Good Friday and Christmas Day.
Scotland has nine public holidays: New Year's Day, January 2, Good Friday, Easter, May Day (not necessarily 1 May), spring and summer holidays at the end of May and the beginning of August, Christmas Day and Boxing Day.
In Northern Ireland there are seven bank holidays: New Year's Day, St. Patrick's Day (17 March), Easter Monday, May Day (not necessarily 1 May), Spring and Late Summer Holidays at the end of May and August respectively and Boxing Day. There are also two common law holidays on Good Friday and Christmas Day and a public holiday on the anniversary of the Battle of the Boyne that takes place on July, 12.
England Wales
 New Year’s
New Year’s
St. Patrick Day
Easter
May Day
January 2
Good Friday
Spring Holiday
Christmas Day
Late Summer Holiday
Easter Monday
Boxing Day
Battle of the Boyne
Good Friday
Scotland The Northern Ireland
Exercise 13.12 Fill in the logical syntax scheme according to the text (Exercise 13.11)
| Subject | Predicate | Object | Adverbial Modifier |
| British bank holidays | - |
| since 1871. |
| No trading | could take place |
| - |
| Many shops | remain open |
| - |
| Workers | may get | - |
|
| They | - | their time with families. |
|
| - | negotiate | extra payment for anyone who works | - |
| England and Wales | - | ---- Bank holidays. |
|
| People | - | seven Bank holidays | in the Northern Ireland. |
| - | has | nine public holidays. |
|
Exercise 13.13 Tell about the public holidays in the United Kingdom using the scheme from the previous task. Add the words and expressions given below for linking the sentences.
We know that...
Naturally...
But actually....
It was interesting to know that...
It’s very understandable that...
Exercise 13.14 Study the new vocabulary
Vocabulary
| to attach to wear (worn) a ribbon a handkerchief a race an amateur an origin to blow up straw Eisteddfod an ounce to equal a pound a stone a pint a quart a gallon an inch a foot a yard a mile a pound sterling a shilling a half-crown a penny | уделять носить лента носовой платок гонка любитель; дилетант происхождение взорвать; подорвать солома фестиваль бардов унция (= 28б3 г) равняться фунт (=453,6 г) мера веса (равен 14 фунтам, или 6,34 кг) пинта (мера ёмкости; =0,57 – GB; 0,47 – USA) кварта (=1/4 галлона=2 пинтам) галлон (=4,54 л) дюйм (=2,5 см) фут (= 30,48 см) ярд (=3 футам ) миля (= 1609 м) фунт стерлингов (денежная единица) шиллинг (англ. серебряная монета; =1/20 фунта = 12 пенсам) полкроны (монета в 2 шиллинга 6 пенсов) пенни; пенс |
Exercise 13.15 Read the text and find what traditions were mentioned there. Make notes if necessary.
British Traditions and Customs
British nation is considered to be the most conservative in Europe. It is not a secret that every nation and every country has its own customs and traditions. In Great Britain people attach greater importance to traditions and customs than in other European countries. Englishmen are proud of their traditions and carefully keep them up. The best examples are their queen, money system, their weights and measures.
There are many customs and some of them are very old. There is, for example, the Marble Championship, where the team of British Champions is crowned. They win a silver cup known among folk dancers as Morris Dancing. Morris Dancing is an event where people, worn in beautiful clothes with ribbons and bells, dance with handkerchiefs or big sticks in their hands, while traditional music sounds.
Another example is the Boat Race, which takes place on the river Thames, often on Easter Sunday. A boat with a team from Oxford University and one with a team from Cambridge University hold a race.
British people think that the Grand National horse race is the most exciting horse race in the world. It takes place near Liverpool every year. Sometimes it happens the same day as the Boat Race takes place, sometimes a week later. Amateur riders as well as professional jockeys can participate. It is a very famous event.
There are many celebrations in May, especially in the countryside.
Halloween is a day on which many children dress up in unusual costumes. In fact, this holiday has a Celtic origin. The day was originally called All Halloween's Eve, because it happens on October 31, the eve of all Saint's Day. The name was later shortened to Halloween. The Celts celebrated the coming of New Year on that day.
Another tradition is the holiday called Bonfire Night.
On November 5, 1605, a man called Guy Fawkes planned to blow up the Houses of Parliament where the king James 1st was to open Parliament on that day. But Guy Fawkes was unable to realize his plan and was caught and later, hanged. The British still remember that Guy Fawkes' Night. It is another name for this holiday. This day one can see children with figures, made of sacks and straw and dressed in old clothes. On November 5th, children put their figures on the bonfire, burn them, and light their fireworks.
In the end of the year, there is the most famous New Year celebration. In London, many people go to Trafalgar Square on New Year's Eve. There is singing and dancing at 12 o'clock on December 31st.
A popular Scottish event is the Edinburgh Festival of music and drama, which takes place every year. A truly Welsh event is the Eisteddfod, a national festival of traditional poetry and music, with a competition for the best new poem in Welsh.
If we look at English weights and measures, we can be convinced that the British are very conservative people. They do not use the internationally accepted measurements. They have conserved their old measures. There are nine essential measures. For general use, the smallest weight is one ounce, then 16 ounce is equal to a pound. Fourteen pounds is one stone. The English always give people's weight in pounds and stones. Liquids they measure in pints, quarts and gallons. There are two pints in a quart and four quarts or eight pints are in one gallon. For length, they have inches, foot, yards and miles.
If we have always been used to the metric system therefore the English monetary system could be found rather difficult for us. They have a pound sterling, which is divided into twenty shillings, half-crown costs two shillings and sixpence, shilling is worth twelve pennies and one penny could be changed by two halfpennies.
Exercise 13.16 Agree or disagree with the following statements according to the content of the text.
| The best example of English traditions is their queen, money system, their weight and measure systems. | True | False |
|
|
| |
| Morris Dancing is the event when many people go to Trafalgar square on New Year’s Eve. |
|
|
| The Boat race takes place on the river Severn. |
|
|
| The Grand National Horse Race takes place near Liverpool. |
|
|
| Guy Fawkes’ Night holiday began on the 5th of November, 1705. |
|
|
| There are nine essential old everyday measures in Britain. |
|
|
| One English pound sterling contains twenty one shillings. |
|
|
Exercise 13.17 Make up the plan of the text giving a headline for every paragraph in the form of a narrative sentence as if in the Model
Plan
1.British people carefully keep their own customs and traditions such as their queen, money system, weights and measures.
2. …
Exercise 13.18 Make a short report about customs and traditions of Britain using your plan from Exercise 13.17. Add an introductory and final sentences to complete your dialogue. Connect the sentences with the following expressions
I’d like to point out right at the beginning that… - В самом начале хотел бы отметить (обратить внимание), что…;
Now it is going to be my pleasure to explain to you… - Я с удовольствием (с радостью) объясню вам…;
It strikes me that… - Меня поражает, что…;
I’ve got an impression that… - У меня впечатление, что…;
On the other hand… - С другой стороны…;
I have almost no doubt that… - У меня почти нет сомнений, что…;
It looks very unlikely that… - Маловероятно, что…;
Nobody would want to deny the fact that… - Никто не станет отрицать тот факт, что…;
Let me give you a brief example… - Позвольте привести краткий пример…;
What’s more difficult to explain is… - Что еще сложнее объяснить, так это…
To sum it up I’d like to say… - Подытоживая, хочу сказать…
Unit 14 Scientific and Technical Progress
Exercise 14.1 Fill in the table with the words according to the type of their
stressed syllable
Engine; date; device; term; late; man; system; long; wide; force; there; large; pure; mark; vertical; line; human; cord; shape
| I | II | III | IV |
|
|
|
|
|
Exercise 14.2 Translate the words according to the Part of Speech they belong to
Apply – application, applied, applying; invent – invention, inventor, invented, inventing; know – knowledge, known, knowing; history – historian, historic, historically; design – designer, designing, designed; build – builder, building (2); engine – engineer, engineering; origin – original, originate; long – length, lengthen; wide – width, widen; high – height; science – scientist, scientific; develop – developer, development, developed, developing
Exercise 14.3 Find the international words in the text and translate them into Russian without a dictionary
Exercise 14.4 Make sure that you know the following Proper Nouns and abbreviations
BC, AD, Latin, the Ancient Era, the Egyptians, the Greeks, the Romans, the Great Pyramid of Giza, Cheops, Snefro, Ptolemaic temple,
Exercise 14.5 Make up Adverbs with –ly suffix using the following Adjectives. Translate the Adverbs into Russian
pure, main, scientific, original, vertical, successful, great, perfect
Exercise 14.6 Study the new words
Vocabulary
| ancient to acquire to apply design to design implement to devise to exist to cover to consider to require enormous a tool a builder’s thread a measuring arm a straight edge to impress to erect to lay grounds to influence to explain a cord seesaws scissors a fishing rod to employ lever | древний получать применять конструкция, разработка проектировать, конструировать воплощать в жизнь разрабатывать, придумывать существовать охватывать, покрывать считать, рассматривать требовать огромный, громадный инструмент отвес (строительный) измерительная линейка (древний инструмент длиной 52 см) правило (древний инструмент) производить впечатление возводить заложить основы оказывать влияние объяснять шнур, провод качели ножницы удочка использовать, нанимать на работу рычаг |
Exercise 14.7 Read and translate the text
Engineering in Ancient Era
Engineering is the discipline, art and profession that acquires and applies technical, scientific and mathematical knowledge to design and implement materials, structures, machines, devices, systems and processes. The concept of engineering has existed since ancient times when humans devised fundamental inventions such as pulley, lever and wheel. The term engineering is of late origin. It dates back to the 13th century and comes from Latin word ingenium which means “a clever invention”.
The Ancient Era covers three famous ancient civilizations – the Egyptians, the Greeks and the Romans. The ancient Egyptians are considered the first builders ever known to a man. According to the historians, they constructed the Egyptian pyramids, the greatest and the most famous structures in the human history during 2800 – 2400 BC. The extraordinary great pyramid, the Great Pyramid of Giza, was built by Cheops, son of Snefro. Its original height was 146 metres, but later 9 metres at the top were lost. The Egyptians also built temples and statues. Ptolemaic temple is still one of the most famous religious monuments in Egypt. It is 137 metres long, 79 metres wide and 36 metres high. To build such structures ancient Egyptians required knowledge of theoretical and applied sciences and great skill in architecture and engineering. They also had to have a large work force in order to construct their enormous structures. However, their knowledge was purely experimental and their tools were very primitive. They mainly consisted of a builder’s thread to mark vertical lines, an angle, a measuring arm (52 cm long) and a straight edge. With these primitive tools the Egyptians could make plans for their colossal but very beautiful structures that still impress the world. The ancient Egyptians taught humanity how to design and erect buildings and so they laid grounds for human civilization.
Ancient Greek technology developed especially successfully during the 5th century BC. The ancient Greeks made discoveries that have influenced many aspects of modern life. Many of our everyday items use scientific principles that Greek scholars first explained. For example, the cord mechanism that we use to open and close curtains applies principles that Greeks discovered about the operation of a pulley. Seesaws, scissors and fishing rods are examples of common objects that employ principle of the lever, which was also first explained by the Greeks. Indeed, the world has benefited greatly from the scientific discoveries that were made by the ancient Greeks.
Ancient Romans are famous for their engineering achievements, although some of their own inventions were improvements of older ideas, concepts and inventions. For example, roads were common at that time, but the Romans improved their design and perfected the construction to the extent that many of their roads are still in use today. By the 1st century AD the Romans had become the best engineers and architects in the world. One of the greatest Roman engineering achievements was the use of the arch. The arch shape is very strong; it is able to support great amounts of weight. The Romans’ two greatest uses of the arch are the aqueduct and the bridge. Roman bridges were among the first large and lasting bridges that a man had ever built. And aqueducts (bridges and tunnels for the water) were used by the Romans to provide water to towns.
The Romans also invented concrete and it allowed them to build very large structures (buildings and bridges) that have survived many centuries. The engineering discoveries of ancient Rome have played a key role in the history of architecture and engineering. Many of Rome’s roads, bridges and aqueducts have been in use from the 1st century until the 21st century. Several major structures from early Rome, for example the Coliseum, still stand.
Exercise 14.8 Match the words in the both columns to form true expressions
| 1. to acquire and apply
2. to design and implement
3. to devise
4. to construct 5. to build 6. to require 7. to have 8. to impress 9. to make 10. to influence 11. to be famous for 12. to be able to support | knowledge and great skills fundamental inventions modern life temples and statues discoveries a large work force
technical, scientific and mathematical knowledge the world materials, structures, machines, devices, systems and processes the extraordinary great pyramid great amount of weight engineering achievements |
Exercise 14.9 Translate from Russian into English
Научные знания; разрабатывать системы и устройства; блок и рычаг; быть более позднего происхождения; охватывать три древние цивилизации; считаться первыми строителями; первоначальная высота; прикладные науки; большое мастерство; рабочая сила; развиваться успешно; многие стороны жизни; предметы быта; работа шкива; применять принцип; получить значительную выгоду; улучшение изобретения; прочный мост; пережить много веков.
Exercise 14.10 Fill in the table with the missed forms of Adjectives from the text
| Положительная | Сравнительная | Превосходная |
| ancient | … | … |
| … | … | the most famous |
|
| later | … |
| … | … | the greatest |
| long | … | … |
| wide | … | … |
| high | … | … |
| primitive |
|
|
|
|
| the best |
Exercise 14.11 Fill in the gaps with the necessary prepositions where they are necessary
The concept … engineering has existed since ancient times. (-, of, for)
They constructed the Egyptian pyramids … 2800 – 2400 BC. (in, since, during)
The extraordinary great pyramid, the Great Pyramid of Giza, was built … Cheops. (by, with, to)
Its original height was 146 metres, but later 9 metres … the top were lost. (at, on, -)
The Egyptians could make plans for their colossal but very beautiful structures … these primitive tools. (by, with, in)
The ancient Egyptians laid grounds … human civilization. (for, to, with)
The Greeks made discoveries that have influenced … many aspects of modern life. (on, to, -)
The world has benefited greatly … the scientific discoveries. (from, of, - )
Exercise 14.12 Transform the Passive construction into Active ones and vice versa
Model 1: Engineering acquires and applies technical, scientific and mathematical knowledge to design and implement materials, structures, machines, devices, systems and processes. (Active Voice) – Technical, scientific and mathematical knowledge is acquired and applied by engineering to design and implement materials, structures, machines, devices, systems and processes. (Passive Voice)
Model 2: The ancient Egyptians are considered the first builders. (Passive Voice) – We consider the ancient Egyptians the first builders. (Active Voice)
Humans devised fundamental inventions such as pulley, lever and wheel.
The Ancient Era covers three famous ancient civilizations.
They constructed the Egyptian pyramids during 2800 – 2400 BC.
The Egyptians also built temples and statues.
The ancient Greeks discoveries have influenced many aspects of modern life.
Many scientific principles were first explained by Greek scholars.
Roman engineers used the arch.
And aqueducts were used by the Romans to provide water to towns.
Exercise 14.13 Answer the questions
What does engineering acquire and apply?
What does engineering acquire and apply technical, scientific and mathematical knowledge for?
Does the term engineering date back to the 13 century or ancient times when such inventions as pulley, lever and wheel were devised?
What three famous civilizations does the Ancient Era cover?
Who are known as the first builders?
When were the Egyptian pyramids constructed?
What are the dimensions of the Great Pyramid of Giza, was built by Cheops, son of Snefro?
What are the dimensions of the Ptolemaic temple, one of the most famous religious monuments in Egypt?
What did ancient Egyptians require to build such structures?
What were their primitive tools?
What was a builder’s thread used for?
When did Ancient Greek technology develop especially successfully?
What our everyday items use scientific principles that Greek scholars first explained?
Exercise 14.14 Read the text and try to understand it without a dictionary
Isaac Newton
Newton, one of the greatest scientists of all times was born in 1642 in the little village in Lincolnshire, England. His father was a farmer and died before Newton was born. His mother was a clever woman whom he always loved.
After school, Newton studied mathematics at Cambridge university and received his degree in 1665. Then the university was closed because of the danger of plague and Newton went home for eighteen months. It was most important period in his life when he made his three great discoveries – the discoveries of the differential calculuses, of the nature of white light, and of the law of gravitation.
These discoveries are still important for the modern science. Newton had always been interested in the problems of light. Many people saw colours of a rainbow but only Newton showed, by his experiments, that white light consists of these colours.
It is interesting how he discovered the law of gravitation. Once, as he sat at the garden, his attention was drawn by the fall of an apple. Many people saw such a usual thing before. But it was Newton who asked himself a question: «Why does that apple fall perpendicularly to the ground? Why doesn't it go sideward or upward? » The answer to this question was the theory of gravitation, discovered by Newton.
Newton died at the age of 84, and was buried in Westminster Abbey, where his monument stands today.
Vocabulary
| danger plague discovery the differential calculuses the law of gravitation a rainbow to consists of to draw attention
| опасность чума открытие дифференциальное исчисление закон гравитации радуга состоять из привлекать внимание |
Exercise 14.15 Organize the sentences in the right logical order to have a short story about I. Newton
He made three great discoveries – the discoveries of the differential calculuses, of the nature of white light, and of the law of gravitation.
Once, as he sat at the garden, his attention was drawn by the fall of an apple.
Newton died at the age of 84.
After school, Newton studied mathematics at Cambridge university and received his degree in 1665.
Newton was born in 1642 in the little village in Lincolnshire, England.
It was Newton who asked himself a question: “Why does that apple fall perpendicularly to the ground?”
These discoveries are still important for the modern science.
Exercise 14.16 Match the groups of words and the items of the plan given below
A B
mathematics a) garden
danger b) fall
the differential calculuses c) question
degree d) ground
law of gravitation e) theory of gravitation
discovery f) sideward
g) upward
C D
was born a) rainbow
village b) experiment
farmer c) colour
clever d) to consist of
Plan
Newton and his family.
The period of study and research.
The problems of light.
The fundamental law of Physics.
Exercise 14.17 Make necessary changes (shortages or additions) using the material of Exercise 14.15 and Exercise 14.16 and retell the text “I. Newton”
Exercise 14.18 Answer the questions
1. Do you know the name of Mikhail Lomonosov?
2. Was he a scientist, a writer, or a businessman?
3. Was he born in the south or north of Russia?
Exercise 14.19 Study the new words
| province to strive (strove, striven) for to complete to return to engage research to conduct works at the request to create mosaics | область стремиться завершать возвращаться заниматься исследование проводить работы по просьбе создавать мозаика |
Exercise 14.20 Listen to the text and fill in the gaps with missing words. Check your work according to the key
Mikhail Lomonosov
Mikhail Lomonosov was born in 1711 in Archangelsk _________. His father was __________ and young Mikhail liked to help him. He always strove for knowledge and liked reading ________. As he was 19 years old, he decided to study in Moscow. He went there on foot. In Moscow he entered the Slavic- Greek-Latin __________. After his graduation from Academy he was sent abroad to complete his knowledge in _____________ and mining. After he had returned from abroad, he became the first Russian _____________ of chemistry in 1745.
At first he was engaged in research in physics and chemistry. Since _______ he had conducted works in the first Russian chemical research laboratory, which was built at his request. Since 1753 he was engaged in research in many fields of natural and applied sciences. He wrote works on physics, _____________, geography, history. Besides scientific works, he wrote ___________ as well. He is the author of the first scientifical grammar of the _______________________.
He founded the factory producing coloured glass. He created some mosaics using the ________ produced at the factory.
Lomonosov was the founder of the first Russian ____________. This university is situated in Moscow and still carries his name.
Mikhail Lomonosov died in 1765. But he is still known as the __________ of the Russian science, an outstanding poet, the founder of Russian literature.
Exercise 14.21 Answer the questions
Where was Mikhail Lomonosov born?
How did he get to Moscow?
What Academy did M. Lomonosov study at?
What did he study abroad?
What fields was he engaged in?
What language work did he carry out?
Can Lomonosov be called a businessman?
What did he found in Moscow?
Exercise 14.22 Read the text and give the headline for each paragraph in Declarative sentences. Write them down as a plan of the text
Sergei Pavlovich Korolyov – the Founder of Practical Cosmonautics
Academician S. P. Korolyov is a famous scientist and founder of practical cosmonautics. He was the chief constructor of the first Earth sputniks and spaceships.
S. P. Korolyov was born in 1906 in the small Ukrainian town of Zhitomir in a family of teachers. He spent his childhood with his grandparents in the town of Nezhin where he studied at home with a teacher. In 1922, at the age of 15, Sergei Korolyov began to study at a vocational building school in Odessa, where he received his secondary education and became a builder. He was interested in mathematics, literature and he read a great deal. All his life he loved music.
In 1923 Sergei Korolyov joined a Glider Pilots' Club, where he learned to construct gliders and to fly them. In 1925 Korolyov entered Kiev Polytechnical Institute where he studied aviation and mathematics, but in the evening he had to work for money: he was a building worker, he worked at the post-office and he played very small roles in films.
After two years in Kiev Korolyov came to Moscow. In the day-time he worked at an aeroplane factory and in the evening he studied at Moscow Higher Technical School. After lectures he worked at home on the design of a new glider. At Moscow Higher Technical School Korolyov learned about K. E. Tsiolkovsky's ideas on space travel and about his rocket. In 1930 S. P. Korolyov graduated from Moscow Higher Technical School and became an aviation engineer. At the same time he finished Moscow Pilot School.
During the Great Patriotic War S. P. Korolyov constructed a jet engine for aeroplanes and rockets.
On October 4,1957 the first man-made satellite of the Earth was launched into space. It was the result of thirty years hard work and Chief Constructor was S. P. Korolyov. Then dogs were sent into space. And only after a lot of experiments the first cosmonaut in the world — Y. A. Gagarin was launched into space in the spaceship «Vostok» on April 12, 1961. After this there were many other longer and more difficult flights. Then followed rockets to the Moon, Mars and Venus.
S. P. Korolyov died in 1966. For his brilliant work in the name of science and progress he was awarded two Gold Stars of the Hero of Socialist Labour. People will always remember the names of those who opened a new era in the conquest of outer space, and the name of S. P. Korolyov is one of them.
Vocabulary
| a glider to graduate from at the same time a jet engine man-made satellite to launch to follow to award labour 10. conquest | планер заканчивать высшее учебное заведение в то же время реактивный двигатель искусственный спутник запускать следовать; идти за награждать труд завоевание |
Exercise 14.23 Read the text once more and write out additional 7 -10 sentences giving the important information to complete your plan
Exercise 14.124 Make your own reasoning in writing to prove that S. P. Korolyov devoted his life to science and progress. Use the expressions given below
I have high opinion of him. – Я о нём высокого мнения.
It seems to me… - Мне кажется…
I think… - Я думаю…
I consider that… - Я считаю, что
I agree that… - Я согласен с тем, что
That’s very likely. - Вполне вероятно
It looks like… - Похоже, что это так
In all respects… - Во всех отношениях
Unit 15 Human Activity and the Nature
Exercise 15.1 Answer the introductory questions
Do you know when people of the Earth celebrate the Earth’s Day?
How do you think in what country did a tradition of planting trees on that day appear?
How do people of the world show their concern about our mutual Mother – the Earth and call everybody to actions?
Exercise 15.2 Write down the new words and learn them by heart
Vocabulary
| source environment interference to increase enterprise by-products to pollute dust harmful to suffer to upset rare species disaster befell consequences for the sake of | источник окружающая среда вмешательство увеличивать предприятие побочные продукты загрязнять пыль вредный страдать нарушать редкий род, вид катастрофа пасть (на) последствия ради |
Exercise 15.3 Read and translate the text
Ecological Problems
Since ancient times Nature has served Man, being the source of his life. For thousands of years people lived in harmony with environment and it seemed to them that natural riches were unlimited. But with the development of civilization man's interference in nature began to increase.
Large cities with thousands of smoky industrial enterprises appear all over the world today. The by-products of their activity pollute the air we breathe, the water we drink, the land we grow grain and vegetables on.
Every year world industry pollutes the atmosphere with about 1000 million tons of dust and other harmful substances. Many cities suffer from smog. Vast forests are cut and burn in fire. Their disappearance upsets the oxygen balance. As a result some rare species of animals, birds, fish and plants disappear forever, a number of rivers and lakes dry up.
The pollution of air and the world's ocean, destruction of the ozone layer is the result of man's careless interaction with nature, a sign of the ecological crises.
The most horrible ecological disaster befell Russia, Ukraine and Belarus and their people after the Chernobyl tragedy in April 1986. Bryansk, Orel and Tula regions in Russia, Kiev and Zhitomir regions in Ukraine and about 23 percent of the territory of Belarus, were polluted with radioactive substances. Chernobyl accident caused a great damage to the agriculture, forests and people's health of these countries. The consequences of this explosion at the atomic power station are tragic for the Russian, Ukrainian, Belarussian and other nations of Europe.
One more terrible disaster was an energy accident at the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant in Japan initiated primarily by the tsunami following the earthquake on 11 March 2011. It had hard impact on the environment too.
Environmental protection is of a universal concern. That is why serious measures to create a system of ecological security should be taken.
Some progress has been already made in this direction. As many as 159 countries — members of the UNO — have set up environmental protection agencies. Numerous conferences have been held by these agencies to discuss problems facing ecologically poor regions including the Aral Sea, the South Urals, Kuzbass, Donbass, Semipalatinsk and Chernobyl. An international environmental research centre has been set up on Lake Baikal. The international organisation Greenpeace is also doing much to preserve the environment.
But these are only the initial steps and they must be carried onward to protect nature, to save life on the planet not only for the sake of the present but also for the future generation
Exercise 15.4 Answer the questions
How did people live for thousands years?
What cities appear all over the world today?
What pollutes the air we breathe?
What is the result of the pollution the atmosphere?
Why is environmental protection a problem of a universal concern?
What are the initial steps in this direction?
Exercise 15.5 Organize the items of the plan to the text in the right order and write it down
The oxygen balance upset.
Environmental protection measures.
For the sake of the future.
The development of civilization.
A matter of a universal concern.
Dangerous air, water and land.
Ecological disasters.
Exercise 15.6 Write out the key words for each item of the plan
Exercise 15.7 Tell what you know about the ecological problems. Use the plan, key words and necessary information of the text and your own information
Exercise 15.8 Think and say if you change your own environment for the better or for the worse
What did you use water for last week?
Did you waste any?
Do you often take hot baths or showers?
Do you often wash clothes?
How much water do you spend on washing?
Exercise 15.9 Point out the methods of building of the following words
Newspaper, pollution, importance, scientists, replanted, re-use.
Exercise 15.10 Learn and remember some new words and word combinations. Guess their meanings from the explanations and give their Russian equivalents
| Words and word combinations | Explanations |
| Environment | To tell or show something |
| To pollute | To keep somebody or something safe |
| Stuff | Everything around us |
| To point out | To make something little |
| To deal with | To look after something and do what is necessary |
| Relation | To do something to the material like paper or glass so that they can be used again |
| To protect | To make air, rivers, soil dirty and dangerous |
| Considerable | 1)To take somebody or something away from danger; 2)to keep smth., especially money, to use later; 3)to use less of smth. |
| Pure | Great or large |
| To lessen | Any material, substance or group of things |
| To recycle | Not mix with anything else, clean |
| To save | To take action on; to do business with |
Exercise 15.11 Read the text and give the title to each paragraph
The Environmental Protection
People all over the world are worried about what is happening to the environment. Newspapers and magazines write about air, land and water pollution. They write that the Earth is our home and all people must take care of it. We must do everything possible to save the nature, to make our rivers and air clean. The importance of this task is pointed out by scientists. The branch of science that deals with the relations of living things to their environment is called ecology. From the point of view of ecology the mankind should first of all lessen pollution.
Forest areas and nature parks are of great importance for people’s health. It’s necessary to create nature parks. There are a lot of such parks in Ukraine. We have not only to protect them but to see that they multiply.
Considerable progress was made during the second half of the 20th century: forest areas have been planted and replanted, millions of hectares of new forests are planted every year.
The closed cycle use of water by industry was put into practice. Each factory purifies and re-uses the same water, instead of taking more from a river or lake.
Most of the factories in the gas, iron, and steel industries now operate closed cycle water systems.
Nature has its rights, and it is the duty of man to respect and defend these rights.
Vocabulary
| to happen to take care a branch the point of view to create to multiply to plant a plant closed cycle use | случаться заботиться отрасль точка зрения создавать умножать сажать завод; 2.растение замкнутый цикл использования
|
Exercise 15.12 Point out what the text is about in one sentence. Write it down
Exercise 15.13 Make a plan of the text using simple Declarative sentences. Leave some space between the phrases to write some details
Exercise 15.14 Give detailed information for the items of the plan
Exercise 15.15 Formulate the main idea of the text. Write it down. Now you have made a Summary
Exercise 15.16 Write down and remember the following words
| 1.to save safe 2. rare 3. species 4.CFC (Сhloro-fluoro-carbons)
5.lead 6.to be unleaded 7.to insulate 8.to throw away 9.rubbish | беречь, спасать безопасный редкий виды опасные для воздуха газы, содержащиеся в аэрозолях, холодильниках, пластиковых упаковках. Разрушая воздух, уменьшают озоновый слой атмосферы свинец не содержать свинец изолировать выбрасывать мусор |
Exercise 15.16 Listen to the text comprising the items of practical ideas of nature protection marked with numbers. Write the numbers 1 to 19 in your notebooks. Listen to them and put (+) if you do this way and (-) if you never do it
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10… |
| +/ - |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
To save nature and to keep the Earth safe, alive and beautiful for future generations is the duty of mankind and of each person on the planet. You will listen to some practical ideas. All of them can help the environment. Here they are:
Buy fresh food that does not need a lot of packaging.
Look for and buy “organic fruit and vegetables from farmers who don’t use chemicals.
Save as much waste as possible.
Use products that will not stay forever in the earth or sea when you throw them away.
Use bottles more than once.
Try to save paper.
Don’t buy products made from rare or protected species.
Try to eat a healthier diet. Avoid too much fat or sugar.
Don’t buy hamburgers or pizzas in plastic boxes which contain CFCs.
Use public transport.
Make sure that your family and friends use unleaded petrol in their cars.
Look for aerosols which have not got any CFC in them.
Use batteries as little as little as possible. It takes 50 times more energy to make them than they produce.
Don’t leave on electric lights, TV, if you are not using them.
Help old people in your area to insulate their homes (to protect against cold and wet weather). This saves energy.
Find out more about Green organizations in your area.
Write letters to the government in your country about Green problems which worry you.
Try to throw away at last 25% less rubbish.
Find out more about nature in your area. Are there any woods, fields, etc. in danger?
Exercise 15.17 Listen to the text once more and write down the items marked with + sign in your table (Exercise 15.16)
Exercise 15.18 Make a conclusion about your personal contribution in environment preservation
МОДУЛЬ: ПРОФЕССИОНАЛЬНЫЙ
Unit 16 ACHIEVEMENTS AND INNOVATIONS IN SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
Exercise 16.1 Form adjectives with the following suffixes
| -ful power – powerful harm – help - | al technology – technological memory – digit – universe – dimension – industry – politic -
|
| -able consider- considerable predict – sustain – manage - |
Exercise 16.2 Explain how the following words are built. Translate the words into Russian
Semiconductor; megabyte; microprocessor; network; three-dimensional; high-precision; knowbots; software; life-support; breakdown; air-traffic
Exercise 16.3 Look through the text and find international words
Exercise 16.4 Write down the new words in your notebooks and learn them by heart
| to predict to consider considerable to measure measurement source search artificial to penetrate wire responsive to increase possibility to perform access to appear to improve dependence software vulnerable violation opportunity to commit fraud theft to punish fortunately | предсказывать считать, полагать, рассматривать значительный измерять измерение источник поиск искусственный проникать провод, проволока отзывчивый, ответный, чуткий увеличить возможность выполнять, совершать доступ появляться улучшать(ся) зависимость программное обеспечение уязвимый, ранимый нарушение, насилие возможность совершать мошенничество, обман кража, воровство наказывать к счастью |
Exercise 16.5 Read and translate the text
Technologies of the 21st Century
One way to predict technological change over time is to consider measurements of speed, size or cost. From this perspective, progress is easy to calculate. Twenty-five years ago a megabyte of semiconductor memory cost around $ 550,000; today it costs around $4. Microprocessors in 1997 were 100,000 times faster than the 1950 originals. If these trends go on to continue – and there are many experts who think they will – by 2030 one computer will be as powerful as all modern computers in Silicon Valley*.
“Faster”, “cheaper”, “smaller” are the slogans for future technology sector. Network technology will continue to move forward. Considerable progress will be made in the computer industry. All audio, video and text information sources will be in digital form and available for universal search. Most current problems of computer security and privacy will have been solved. Many analysts predict slow progress in the area of “artificial intelligence” in the future. Considerable progress is expected in the development of VRML** (Virtual Reality Modeling Language), a three-dimensional version of the text-based HTML (Hyper Markup Language)*** that currently dominates Web pages on the Internet.
Twenty-five years from now, after more than fifty years of development, the microprocessor, information technologies in general and networks will probably penetrate into every aspect of human activity. Many parts of the world will be wired, responsive and interactive. The use of computers will allow us to choose where and how to live and work. The computers will also greatly increase possibilities of production, transportation, energy, commerce, education, and health. For example, industrial robots will perform dangerous, high-precision tasks in many sectors of the economy. They will also be employed in deep sea and outer space operations. In the field of energy production and conservation , new horizons will open up. Powerful computers will make design of environmentally sustainable products easier.
Computer will develop electronic commerce. Anyone with a computer and Internet access will be able to sell and buy goods and services from around the world. As a result, new products and services and new markets will appear. Computer technologies will improve our capacity to communicate. In order not to get lost in the ocean of information, people will probably use “knowbots” (knowledge robots) to navigate effectively. A person will transfer his/ her wishes to a computer, a special programme will decode them and do different tasks, for example check e-mail or search for necessary information on its own. Still, with all these advantages, there are a lot of risks that could be provoked by tomorrow’s technological innovations. Firstly, tomorrow’s technologies contain destructive potential that mankind won’t be able to control.
Dependence on computers, networks and the software makes society’s life-support systems (from nuclear power plants to security systems) vulnerable to attack of different people, terrorists, for example. The spread of information technology also make violation of basic privacy or civil rights easier. People also have more opportunities to commit crime such as fraud or theft and will not be punished for it.
Secondly, purely technological risks involve vulnerability to system breakdowns, for example in the air-traffic control infrastructure. Some people are afraid that as the world becomes more dependent on technology, there will be a risk of unmanageable mistakes that can cause social or economic catastrophe.
Thirdly, innovative technologies such as human cloning or artificial intelligence always raise ethic problems.
Fortunately, these risks will depend not only on new technologies but also on social and political choices. That is why all people should realize technology’s potential and be ready to make a choice.
Notes to the text
*Silicon Valley – Кремниевая долина (мировой центр компьютерной и электронной индустрии, Калифорния США)
**VRML – язык конструирования виртуальной реальности, язык VRML (произносится «вермул»)
***HTML - язык гипертекстовой разметки HTM
Exercise 16.6 Match the English words and phrases on the left with their Russian equivalents on the right
| over time slogan network technology artificial intelligence wired, responsive, interactive commit crime high-precision
outer space life-support system unmanageable | искусственный интеллект высокоточный с течением времени сетевые технологии совершать преступление космическое пространство соединённый проводами, быстрореагирующий, взаимодействующий лозунг, девиз неконтролируемый система жизнеобеспечения |
Exercise 16.7 Find in the text the equivalents of the following words or phrases
В этом ракурсе; двигаться вперёд; цифровая форма; всемирный поиск; безопасность и конфиденциальность; текущие проблемы; трехмерный; намного увеличить возможности; доступ к интернету; подделка или кража; наказывать за; клонирование
Exercise 16.8 Find antonyms in the both columns
| easy fast cheap security privacy artificial increase allow dangerous fortunately improve advantage punish | danger decrease disadvantage hard expensive unfortunately natural prohibit safe reward deteriorate publicity slow |
Exercise 16.9 Fill in the table with the missed forms of adjectives
| Положительная | Сравнительная | Превосходная |
| - | faster | - |
| powerful | - | - |
| - | cheaper | - |
| - | smaller | - |
| - | - | the most harmful |
| - | easier | - |
| - | more | - |
| - | more dependent | - |
Exercise 16.10 Find appropriate prepositions for the following verbs according to the text
| to move to penetrate to open to depend to go to search | into for on on forward up |
Exercise 16.11 Fill in the gaps with the necessary phrasal verbs in the appropriate form and necessary preposition. Translate the sentences
| to open to depend to search to go to move to penetrate |
The technology never stands still, it always … … .
I do not like … … other’s people help.
The new course in engineering … … opportunities for better understanding of engineers’ work.
Are you planning … … your studies?
The light … … every room of the house.
I’m preparing for my seminar and going … the Internet … necessary information.
Exercise 16.12 Choose the right answer
One way to predict technological change over time is to consider measurements of speed, size or … .
shape b) cost c) effectiveness
By 2030 one computer will be as powerful as all modern computers in … .
Death Valley b) Silicon Valley c) Valley Forge
The slogans for future technology sector are … .
farther, more, better b) newer, larger, taller c) faster, cheaper, smaller
Considerable progress will be made in … .
the computer industry b) the medicine c) the artificial intelligence
Computer will develop electronic … .
industry b) commerce c) communication
Tomorrow’s technologies contain destructive potential that mankind won’t be able … .
to control b) to eliminate c) to decrease
Unit 17 MACHINES AND MECHANISMS
Exercise 17.1 Build nouns with suffixes using the following verbs
| to supply to fit to build to produce to provide | + -er |
| to handle to drill to dig to cut to rivet | + -ing |
Exercise 17.2 Fill in the table with the words given below according to the Parts of Speech they belong to
Apply, application, applying; move, movement; link; at least; machine, machinery; entirely; manufacture, manufacturing; industry, industrial, agricultural, agriculture; construct, construction; grow, growth, growing; furthermore; reliable
| Noun | Verb | Adjective | Adverb | Participle I |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Exercise 17.3 Match the words in English and Russian in the both columns
| produce product producer production productive productivity | производитель производительность производить, добывать продуктивный продукт продукция производство |
Exercise 17.4 Look through the text and find appropriate sentences for the following interpretations
1. Машинное оборудование можно описать как агрегат, оснащенный или предназначенный для оснащения системой привода, отличной от непосредственно прилагаемых усилий человека или животного, состоящий из связанных частей или компонентов, по крайней мере один из которых движется и которые соединены для конкретного применения.
2. К ним относятся машины и оборудование для сельского хозяйства, горнодобывающей промышленности и строительства, а также станки и запасные части, и различные подразделения, которые производят оборудование для различных промышленных и коммерческих секторов.
3. Технические характеристики могут включать грузоподъёмность для перевозки больших масс и объемов, обработку конкретных материалов и необходимые условия при бурении или копке.
Machinery and Equipment
Machinery can be described as an assembly, fitted with or intended to be fitted with a drive system other than directly applied human or animal effort, consisting of linked parts or components, at least one of which moves, and which are joined for a specific application.
The machinery and equipment in manufacturing sector is almost entirely focused on supplying capital goods or their components to other sectors of the economy, such as the industrial, agricultural or construction sectors, with a view to improving their productivity growth and quality. It provides equipment for use in many mining, manufacturing, energy and construction sectors, as well as producing domestic appliances. Furthermore, the machinery and equipment manufacturing sector covers arms and ammunition, whether for military or sporting uses, including some military vehicles such as tanks, but not military aircraft or warships (which are classified under the manufacture of transport equipment).
Key subsectors of machinery are:
Specialized machinery and equipment for specific industry. These are machinery and equipment for agricultural, mining and construction and the machine tools and parts sectors, and a miscellaneous division, which manufactures equipment for a variety of industrial and commercial sectors.
Specialized machinery production is a complex process including machine operation, design and engineering, parts assembly and manufacturing supervision. Due to the specific and precise nature of the particular machinery and equipment manufactured, production and assembly processes must be followed closely so that variation in component construction is minimized. Products manufactured for use by the agricultural, mining, machinery or other industrial sectors must be practical, easy to maintain and reliable, as well as being designed and engineered with expertise. Design specifications may involve carriage capacity for large masses and volumes, the handling of specific materials and drilling or digging requirements. Production of machinery and equipment is mostly in metals and alloys; however, some specific products may also involve plastics, rubber or glass.
Power generating machinery and equipment, which comprises machinery for the production and use of mechanical power. This includes internal combustion engines, as well as steam, gas, wind and hydraulic turbines, pumps and compressors, taps and valves, bearings, gears, driving elements and transmission equipment, but excludes the manufacture of propulsion engines for aircrafts, vehicles or cycles (зд. мотоциклы).
Metalworking machinery, which comprises the manufacture of mechanical power transmission equipment, parts for industrial machinery, electric and gas welding and soldering equipment, rolling mill equipment, machine tools, dies, hand tools of all types (such as axes, spanners, screw-drivers, wrenches, hammers, pincers, riveting tools and other hand tools) cutting tools.
General industrial machinery and equipment. This category covers establishments primarily engaged in manufacturing machinery, equipment, and components for general industrial use, and for which no special classification is provided. It includes furnaces and burners, lifting and handling equipment and non-domestic cooling and ventilation equipment. The general industrial machinery and equipment industry is heavily dependent upon sales to other manufacturing businesses and to construction industries.
Nowadays machinery and equipment manufacturing sector is an important part of efficient industry and economy. Hydraulic cranes, earthmovers, generators, construction equipment, oilfields pieces, transport and other related accessories are very important because they enable people to complete their targeted tasks in an easy way, to reduce the manual labour and also the risk factor.
Exercise 17.5 Write down the new words and learn them by heart
Vocabulary
| to describe an assembly to fit with
to intend to apply (effort)
at least manufacture to improve furthermore mining a vehicle miscellaneous division precise to maintain reliable engineer to engineer capacity
volume to handle to require requirement alloy steam a tap a valve a bearing a gear rolling mill
a die an axe a spanner (Br.) wrench (US)
screw-driver hammer a pincer a riveting tool accesories | описывать агрегат, сборочный узел оснащать, устанавливать монтировать намереваться, предназначать применять, прикладывать (силу, усилие) по крайней мере производить улучшать кроме того, более того добыча полезных ископаемых автомобиль, транспортное средство разнообразный, разносторонний отдел, раздел, категория, участок точный, высокоточный обслуживать надёжный инженер, механик, проектировщик проектировать мощность, производительность, вместимость, объем, емкость, грузоподъемность объём обрабатывать, управлять, справляться требовать, нуждаться, предписывать требование, потребность, необходимое условие сплав пар кран клапан подшипник передача, механизм, шестерня прокатный стан, металлопрокатный завод штамп, пуансон, пресс-форма, волочильная доска топор гаечный ключ (в США – регулируемый) гаечный ключ (в Британии – регулируемый) отвертка молоток клещи, тиски, щипчики клепальный инструмент принадлежности, вспомогательное оборудование, комплектующие |
Exercise17.6 Read and translate text from Exercise 17.4
Exercise17.7 Find in the text the equivalents for the following Russian words and word combinations
Система привода; соединять детали; с целью; способность транспортировать (переносить); передающее устройство; промышленное оборудование; отвёртка; ручной инструмент; оборудование для металлопроката; клепальный инструмент; режущий инструмент; гидравлический кран; экскаватор; строительное оборудование; месторождение нефти; ручной труд
Exercise17.8 Match the English and Russian words and word combinations in the both columns
| capital goods ventilation equipment welding equipment quality handling equipment internal combustion engine lifting equipment cooling equipment propulsion engine domestic appliances soldering equipment | бытовая техника двигатель внутреннего сгорания средства производства паяльное оборудование подъёмное оборудование главный, тяговый двигатель сварочное оборудование погрузочно-разгрузочное оборудование вентиляционное оборудование холодильное оборудование качество |
Exercise17.9 Find synonyms in the both columns
| link part apply manufacture intend build improve miscellaneous precise engineer require | produce accurate tie need various wish use enhance design component construct |
Exercise 17.10 Define the functions of the words with –ed in the end in the following sentence
1. Machinery can be described as an assembly, fitted with or intended to be fitted with a drive system other than directly applied human or animal effort, consisting of linked parts or components, at least one of which moves, and which are joined for a specific application.
2. Due to the specific and precise nature of the particular machinery and equipment manufactured, production and assembly processes must be followed closely so that variation in component construction is minimized.
Part of the verb in Passive
Participle II
Part of the Passive Infinitive
Exercise 17.11 Define the Tense and Voice form of the verbs in the following sentences
1. The machinery and equipment in manufacturing sector is almost entirely focused on supplying capital goods. 2. It provides equipment for use in many mining, manufacturing, energy and construction sectors. 3. Our new design has involved carriage capacity for large masses and volumes, the handling of specific materials and drilling or digging requirements. 4. This category covered establishments primarily engaged in manufacturing machinery. 5. People have been enabled to complete their targeted tasks in an easy way with the new equipment.
Exercise 17.12 Fill in the gaps with the appropriate preposition
1. The machinery and equipment in manufacturing sector is almost entirely focused … supplying capital goods or their components … other sectors of the economy. (at, for; on, to; in from)
2. Production and assembly processes must be followed closely … the specific and precise nature of the particular machinery and equipment manufactured. ( for; to ;due to)
3. Production … machinery and equipment is mostly … metals and alloys. (of, in; in of; to, for)
4. This category covers establishments primarily engaged … manufacturing machinery, equipment, and components … general industrial use. (for, in; at, to; in, for)
Exercise17.13 Put Special questions to the following sentences
1. Machinery is usually fitted with a drive system. (3)
2. The manufacturing sector provides equipment for use in many fields of industry. (4)
3. The machinery and equipment manufacturing sector covers arms and ammunition for military or sporting uses. (3)
Exercise17.14 Answer the questions
1. How can machinery be described?
2. What is the focus of machinery and equipment sector?
3. What are the spheres of machinery and equipment manufacturing sector application?
4. What are key subsectors of machinery?
5. What does power generating machinery and equipment comprise?
6. What does metalworking machinery comprise?
7. What does general industrial machinery and equipment cover?
Unit 18 Modern Computer Technologies
Exercise 18.1 Translate the following international words without a dictionary
Computer, combination, electronic, electromechanical, component, information, system, element, instruction, programme, mathematical, logical, operation
Exercise 18.2 Find the corresponding words and expressions in the Russian and English sentences given below. Mark them with necessary numbers
| 1. Computer has no intelligence by itself* and is referred to* as hardware*. | 1. Сам по себе1 компьютер не имеет разума2 и его называют оборудованием («железом»)3. |
| 2. When one computer system is set up* to communicate with another computer system, connectivity* becomes the sixth system element. | 2. Когда одна компьютерная система устанавливается1 для связи с другой компьютерной системой, связь2 становится шестым элементом системы. |
| 3. Software* is the term used to describe* the instructions that tell the hardware how to perform* a task. | 3. Программное обеспечение1 это термин, используемый для описания2 инструкций, которые указывают оборудованию, как выполнить3 задачу. |
| 4. Computers accept* information in the form of instruction called* a programme and characters* called data*. | 4. Компьютеры воспринимают1 информацию в форме инструкций, называемых2 программой и символов3, называемых данными4. |
| | |
Exercise 18.3 Read the text and find the paragraphs which are translated below
Когда одна компьютерная система устанавливается для связи с другой компьютерной системой, связь становится шестым элементом системы. Другими словами, способ, которым различные отдельные системы, связаны – например, телефонная линия, микроволновая передача или спутник – является элементом всей компьютерной системы.
Основной работой компьютера является обработка информации. Компьютер воспринимает информацию в форме инструкций, называемых программой, и символов, называемых данными для выполнения математических и логических операций, а затем выдает результаты. Данные являются сырьем, в то время как информация является организованной, обработанной, очищенной и пригодной для принятия решений. Компьютеры используются для преобразования данных в информацию.
What Is a Computer?
The term computer is used to describe a device made up of a combination of electronic and electromechanical (part electronic and part mechanical) components. Computer has no intelligence1 by itself and is referred to as hardware2. A computer system is a combination of five elements:
• Hardware
• Software3
• People
• Procedures
• Data/information
When one computer system is set up to communicate with another computer system, connectivity4 becomes the sixth system element. In other words, the manner5 in which the various individual systems are connected — for example, by phone lines, microwave6 transmission7, or satellite — is an element of the total computer system.
Software is the term used to describe the instructions that tell the hardware how to perform a task. Without software instructions, the hardware doesn't know what to do. People, however, are the most important component of the computer system: they create the computer software instructions and respond to the procedures8 that those instructions present.
The basic job of a computer is processing information. Computers accept information in the form of instruction called a programme and characters called data to perform mathematical and logical operations, and then give the results. The data is raw9 material while information is organized, processed, refined10 and useful for decision making11. Computer is used to convert12 data into information.
Exercise 18.4 Write down new words and learn them by heart
| 1 | intelligence | [in′telidʒәns] | разум |
| 2 | hardware | [ha:dwεә] | оборудование |
| 3 | software | [softwεә] | программное обеспечение |
| 4 | to connect | [kә′nekt] | соединять |
| 5 | manner | [′mænә] | манера, способ |
| 6 | microwave | [′maikrouweiv] | микроволновая |
| 7 | transmission | [trænz′miʃәn] | передача |
| 8 | procedures | [prә'si:dʒәz] | процедуры, операции |
| 9 | raw | [гɔ:] | необработанный, сырой |
| 10 | to refine | [ri′fain] | очищать |
| 11 | decision making | [di′siʒәnmeikiη] | принятие решений |
| 12 | to convert | [kәn′vә:t] | превращать, преобразовывать |
Exercise 18.5 Organize the items of the plan below in right order
Software
The sixth computer system element.
Computer’s basic job.
Computer system description.
Exercise 18.6 Choose an appropriate Tense form in Passive Voice for the Infinitives in brackets in the following sentences
1. These two individual systems (to connect) by the satellite at that time.
A – is connected; В – are connected; С – were connected
2. Computer (to use) to convert data into information.
A - is used; В - was used; С - has been used
3. A new sophisticated computer system (to set up) at our plant in the nearest future.
A - is set up; В - will be set up; С - are set up
Exercise 18.7 Complete the sentences with the necessary words or expressions given below
1. Computer is often referred to as ... .
2. The instructions that tell the hardware how to perform a task is known as ... .
3. The basic job of a computer is ... .
A - processing information; В - software; С - hardware
Exercise 18.8 Define the function of the Infinitives in the following sentences
1. The term computer is used to describe a device made up of a combination of electronic and electromechanical parts.
2. To perform mathematical and logical operations becomes possible due to instructions called programs.
3. Computer was the first device to convert data into information.
A - Subject; В - Attribute; С - Adverbial Modifier of Purpose
Exercise 18.9 Find English and Russian equivalents in the both columns
| 1. to refine | а) передавать |
| 2. to connect | b) цифровые данные |
| 3. to create | с) очищать |
| 4. a device | d)соединять |
| 5. procedure | е) осуществлять |
| 6. to transmit | f) создавать |
| 7. software | g) устройство |
| 8. to perform | h) отвечать |
| 9. to respond | i) программное обеспечение |
| 10. data | j) операция |
Exercise 18.10 Insert prepositions into the gaps choosing from those given in brackets
1. A computer has no intelligence ... itself. (with; by; in)
2. A computer system is a combination ... five elements. (to; from; of)
3. The hardware can't work ... software instructions. (with; in; without)
Exercise 18.11 Define the Part of Speech of the ing-forms in the following sentences
1. Information is organized, processed, refined and useful for decision making.
2. Describing a device made up of electronic and electromechanical components use the term "computer"
3. The processing of information is the basic job of a computer.
A - Verbal Noun; В - Participle I Active; С - Gerund
Exercise 18.12 Point out which conjunction should be used to connect the parts of the sentences
1. The hardware must be provided with software to know ... to do.
2. Data is raw material ... information is useful for decision making.
3. People respond to the procedures ... software instructions present.
A - while; В - that; С - what
Exercise 18.13 Find right equivalents to translate the following words into Russian
1. Connectivity - соединять; соединённый; соединение.
2. Various - различаться; различный; различие.
3. Acceptance - принимать; принятие; принятый.
Exercise 18.14 Answer the questions
What does the term computer describe?
How is computer electronic and electromechanical parts refered to?
What five elements does a computer system include?
In what case does the sixth element appearin a computer system?
How can computer be connected?
What do they call software?
What is the most important component of a computer system?
What is raw material for a computer?
What is information?
Exercise 18.15 Use the following verbs to describe the performance of a computer system
to process → to accept → to perform → to give → to convert
Exercise 18.16 Learn new words by heart
| 1 | to require | [rikwaiә] | требовать |
| 2 | to direct | [dai′rekt] | управлять, руководить |
| 3 | general-purpose | [dʒenerәl ′pә:pәs] | общего назначения |
| 4 | control | [kәn′troul] | управление |
| 5 | internal | [in′tә:nәl] | внутренний |
| 6 | regardless regard | [rigadlәs] [riga:d] | несмотря на, безотносительно; отношение |
| 7 | to boot | [bu:t] | загружать |
| 8 | memory capacity | [′memәri kә′pæsiti] | вместимость памяти |
| 9 | specific | [spesifik] | конкретный, определенный |
| 10 | peripheral | [pe′riferәl] | периферийный |
| 11 | mainboard | [meinbɔ:d] | материнская плата |
| 12 | to attach | [ә′tætʃ] | присоединять |
| 13 | developer | [di′velәpә] | разработчик |
| 14 | to handle | [hændl] | управлять, обращаться с |
| 15 | to transfer | [træns′fә:] | переводить, переносить |
| 16 | to provide with | [prә′vaidwið] | обеспечивать чем-либо |
| 17 | security to secure | [sikjuriti] [si′kjuә] | безопасность обеспечивать безопасность |
| 18 | to check | [tʃek] | проверять |
| 19 | Web-browser | [web brauzә] | «браузер» (программа, позволяющая пользователю искать и считывать информацию с глобальной электронной сети Internet) |
Exercise 18.17 While reading the text find the paragraphs which are translated below
Системные программы создаются для определенного оборудования. Эти программы называются носителями (драйверами) и согласовывают деятельность периферийного оборудования и самого компьютера. Пользователю необходимо установить определенный носитель (драйвер) для того, чтобы активировать периферийное оборудование. Например, если вы намереваетесь купить принтер или сканер, вам нужно побеспокоиться заблаговременно о программе носителе, которая, впрочем, обычно идет вместе с оборудованием. Путем установления драйвера вы «учите» материнскую плату «понимать» новую установленную деталь (оборудование).
Обмен данными внутри и между компьютерными системами осуществляется системным программным обеспечением. Коммуникационное программное обеспечение переводит данные из одной компьютерной системы в другую. Эти программы обычно обеспечивают пользователя безопасностью данных и проверкой ошибок вместе с физическим переводом данных между памятью двух компьютеров. В течение последних пяти лет развивающаяся электронная коммуникационная сеть стимулировала все больше компаний производить различное коммуникационное программное обеспечение, такое как Веб-браузера для Интернета.
Software
A computer to complete a job requires1 more than just the actual equipment or hardware we see and touch. It requires Software — programs for directing2 the operation of a computer or electronic data.
Software is the final computer system component. These computer programs instruct the hardware how to conduct processing. The computer is merely a general-purpose3 machine which requires specific software to perform a given task. Computers can input, calculate, compare, and output data as information. Software determines the order in which these operations are performed.
Programs usually fall in one of two categories: system software and applications software.
System software controls4 standard internal5 computer activities. An operating system, for example, is a collection of system programs that aid in the operation of a computer regardless6 of the application software being used. When a computer is first turned on, one of the system programmes is booted7 or loaded into the computers memory. This software contains information about memory capacity8, the model of the processor, the disk drives to be used, and more. Once the system software is loaded, the applications software can be brought in.
System programmes are designed for the specific9 pieces of hardware. These programmes are called drivers and coordinate peripheral10 hardware and computer activities. User needs to install a specific driver in order to activate a peripheral device. For example, if you intend to buy a printer or a scanner you need to worry in advance about the driver programme which, though, commonly goes along with your device. By installing the driver you «teach» your mainboard11 to «understand» the newly attached12 part. However, in modern computer systems the drivers are usually installed in the operating system.
Applications software satisfies your specific need. The developers13 of application software rely mostly on marketing research strategies trying to do their best to attract more users (buyers) to their software. As the productivity of the hardware has increased greatly in recent years, the programmers nowadays tend to include as much as possible in one programme to make software interface look more attractive to the user. These class of programmes is the most numerous and perspective from the marketing point of view.
Data communication within and between computers systems is handled14 by system software. Communications software transfers15 data from one computer system to another. These programmes usually provide16 users with data security17 and error checking18 along with physically transferring data between the two computer's memories. During the past five years the developing electronic network communication has stimulated more and more companies to produce various communication software, such as Web-Browsers19 for Internet.
Exercise 18.18 Read the text given in Exercise 18.17 and translate it into Russian
Exercise 18.19 Choose the most suitable translation for the following English expressions
1. the final computer system component a) конечная система компьютерного
компонента;
b) конечный компонент
компьютерной системы;
c) финальный системный компонент
компьютера;
2. standard internal computer activities a) обычная внутренняя работа
компьютера;
b) внутренняя деятельность обычного
компьютера;
c) стандартная работа внутреннего
компьютера;
3. system programs collection. a) набор системных программ;
b) системная программа набора;
c) программа системного набора.
Exercise 18.20 Match English and Russian equivalents in the both columns
1. system software
2. a peripheral device
3. to worry in advance
4. to install drivers
5. application software
6. the hardware productivity
7. error checking
8. data security
9. network communication
10. specific pieces
a) прикладные программы
b) конкретные устройства
c) безопасность данных
d) системные программы
e) побеспокоиться заблаговременно
f) сетевая связь
g) периферийное устройство
h) устанавливать дисководы
i) производительность компьютерного устройства
j) проверка ошибок
Exercise 18.21 Organize the items of the plan below in right order
Drivers.
Communications software.
The final computer system component.
Applications software.
Systems software.
Exercise 18.22 Choose an appropriate end for each of the sentences given below
1. Data communication within and between computers is handled by ... .
2. A user needs to install a specific driver in order to activate ....
3. The drivers are usually installed in ... .
a) a peripheral device;
b) system software;
c) the operating system
Exercise 18.23 Insert necessary prepositions into the gaps choosing from those given in the brackets
1. A computer requires Software ... directing its operation or electronic data, (to; for; on)
2. One of the system programs was booted ... the computer's memory, (in; to; into)
3. The developers ... application software rely mostly on marketing research strategies. (to; from; of)
Exercise 18.24 Choose an appropriate form of the infinitives in the brackets for the following sentences
1. Software determines the order in which all operations (to perform).
A - is performed; В - has performed; С - are performed
2. The driver program commonly (to go) along with your device.
A - goes; В - go; С - is going
3. The productivity of the hardware (to increase) greatly in the recent years.
A - had increased; В - increases; С - has increased
Exercise 18.25 Determine the Part of Speech the ing-forms in the sentences belong to
1.By installing the driver you "teach" your mainboard to "understand" the newly attached part.
2. The developers rely mostly on marketing research strategies trying to do their best to attract more buyers to their software.
3. The error checking is usually made during the computer working.
A - the Participle I Active; В - the Gerund; С - the Verbal Noun
Exercise 18.26 Define the function of the Infinitives in the following sentences
1. This software contains information about the disk drivers to be used.
2. If you intend to buy a printer you need to worry in advance about the driver program.
3. The programmers nowadays tend to include as much as possible in one program to make software interface look more attractive to the users.
A - Adverbial Modifier of Purpose; В - Attribute; С - Part of the verbal Predicate; D - Object
Exercise 18.27 Connect the parts of the compound sentences with the necessary conjunctions
1. The computer is merely a general-purpose machine ... requires specific software to perform a given task.
2. An operating system is a collection of system programs ... aid in the operation of a computer.
3. ... a computer is first turned on, one of the system programs is loaded into the its memory.
A - that; В - when; С – which
Exercise 18.28 Answer the questions
What is software?
In what two basic groups software (programs) could be divided?
What is system software for?
What is an operating system – a system software or application software?
What is a “driver”?
What is application software?
What is application software used for?
What is the tendency in application software market in the recent years?
What is application of the communication software?
Exercise 18.29 Which of the listed below statements are true / false. Specify your answer using the text
| № | Statements | True | False |
| 1. | Computer programs only instruct hardware how to handle data storage. |
|
|
| 2. | System software controls internal computer activities. |
|
|
| 3. | System software is very dependable on the type of application software being used. |
|
|
| 4. | The information about memory capacity, the model of the processor and disk drives are unavailable for system software. |
|
|
| 5. | The driver is a special device usually used by car drivers for Floppy-disk driving. |
|
|
| 6. | It is very reasonable to ask for a driver when you buy a new piece of hardware. |
|
|
| 7. | Software developers tend to make their products very small and with poor interface to save computer resources. |
|
|
| 8. | Communication software is in great demand now because of the new advances in communication technologies. |
|
|
| 9. | Application software is merely a general-purpose instrument. |
|
|
| 10. | Web-browsers is the class of software for electronic communication through the network. |
|
|
Exercise 18.30 Find English equivalents in the text
Программное обеспечение определяет порядок выполнения операций.
Прикладные программы выполняют поставленную вами конкретную задачу (удовлетворяют вашу потребность).
Этот класс программ — самый многочисленный и перспективный с точки зрения маркетинга.
Системные программы предназначены для конкретных устройств компьютерной системы.
Устанавливая драйвер, вы «учите» систему «понимать» вновь присоединенное устройство.
Exercise 18.31 Read and translate international words without a dictionary
Computer, planet, start, user, interface, program, account, address, browser, e-mail
Exercise 18.32 Explain the method of the building of the words below and translate them
Network, downloading, user, helpful, database, knowledge, communication, information, beginning, connection, finally, simply
Exercise 18.33 Form Participles I Active and Participles II Passive of the verbs below. Translate them into Russian
Model: to inform (сообщать) – informing (сообщающий); informed (информированный)
To span, to start, to use, to call, to deploy
Exercise 18.34 Write down the new words and learn them by heart
| huge network to span surrounding to share data (мн. oт datum) to surf to download interface obsolete to deploy email accounts quantum mechanics instantaneous browser broadband connection dial-up to type search program site to solve to match query to provide | большой, гигантский, громадный сеть обхватывать, охватывать окружающий делить, распределять данные, факты, сведения зд. находиться в сети загружать, пересылать по линии связи интерфейс, адаптер ненужный, старый, вышедший из употребления пользоваться, употреблять; развёртывать учётные записи электронной почты квантовая механика мгновенный; немедленный, незамедлительный браузер, окно просмотра, программа просмотра выделенное подключение удалённый доступ к сети печатать программа-поисковик сайт решать; находить выход подходить, соответствовать запрос, вопрос снабжать, доставлять, обеспечивать |
Exercise 18.35 Read the text and find the paragraph about the ways of searching for necessary information
The Internet
The Internet is a huge network of computers spanning this planet and is now started to bring in the surrounding area like space. Some computers like servers share data, others just surf the web as clients downloading the data. Public Internet began in the late 70-s. At that time web users used an interface called telnet, but now that program is mainly obsolete. Telnet is most widely deployed in accessing college email accounts. The Internet is very helpful, because it’s a huge database of knowledge, from the pictures of family trips to an analysis of quantum mechanics. Everyone should have the Internet because of its near instantaneous communication and huge wealth of knowledge. But how to go on the Internet and do a search for information we need. There are two ways of doing it.
The first is when you know an internet address of data you need and the second one is when you try to find information you need by searching program. In the beginning we have to enter any browser you like. It could be an Internet Explorer, Netscape Navigator, Opera, etc. If we have a broad-band connection, we connect to our dial-up service. Finally, if we want to find some information in the Internet, we are to type an address of this data in the browser we use or simply use the existing search-programs such as the Google, Rambler, Yandex or Yahoo search programs. They are very simple and popular networks of sites. In these programs we can just type the word or name of a thing, we would like to find and then press “enter”. A search program solves this problem. We get our results in the same window. After this we simply choose whatever site best matches our query or keep searching.
Besides data, one can get from the Internet, we can also send and receive e-mail (electronic mail). This internet service is cheaper than ordinary mail and much quicker. It is becoming popular day by day. We can get some news from the internet, because there are many information services in the web.
Exercise 18.36
Match the beginnings and the ends to make true sentences
| In the 70s web users used an interface … If we have a broadband connection, … We simply choose … We can also send and receive … This Internet service is … There are many information servers … | whatever site best matches our query. cheaper and quicker. called telnet. in the web. e-mail or electronic mail. we connect to the Internet at once. |
Exercise 18.37 Fill in the gaps with appropriate prepositions
1. The Internet is a huge network … computers. (in; of; at)
2. Everyone should have the Internet … of its near instantaneous communication. (because of; thanked to; due to)
3. How to do a search … information we need. (about: of; for)
4. We can connect … our dial-up service. (in; to; through)
5. It is becoming popular day … day. (by; in; after)
Exercise 18.38 Answer the questions
What is Internet?
What are servers?
When did public Internet appear?
What was the most popular mail interface used in 70s?
What kind of browsers do you know?
How can we get information in the Internet?
Is it cheaper to use the Internet mail service instead of ordinary post office?
What search programs do you know?
Unit 19 At an Industrial Exhibition
Exercise 19.1 Read and translate the text
Exhibitions and Fairs
Every year a lot of international, national and specialized exhibitions and fairs are held in different countries of the world. The number of countries and companies who take part in them is growing from year to year and the scope of fairs and exhibitions is becoming larger. 400 international exhibitions are held annually. The world’s largest, busiest and most attractive exhibition centers are located in Western Europe (Germany, France, Italy, the UK) and the USA.
Exhibitions and fairs are classified according to certain features:
Location (national and international exhibitions);
Sphere of activity (reginal, interregional, world exhibitions). An example of the World Exhibition is “Expo - 2000” (Hannover, Germany). 200 countries and organizations took part in it;
Exhibits characteristics: universal and specialized exhibitions;
Terms of holding (Consumer goods exhibitions are held 2 – 4 times a year, new high-tech exhibitions are held every 2 – 5 years and permanent exhibitions and fairs for demonstration of export goods abroad.)
The display during these exhibitions includes a wide range of exhibits, which shows the latest achievements in different fields of industry, science and agriculture of many countries.
Usually fairs and exhibitions are crowded with visitors, who show much interest in the exhibits on display.
At international and national exhibitions commercial centres are established where participants can negotiate the sale and the purchase of different goods.
Every exhibition is an eye-opening experience and also a method to advertise products. Fairs and exhibitions are usually held under various mottoes: people and progress, peace and progress through economic cooperation and so on. International fairs and exhibitions pave the way for the consolidation of friendship among countries and nations.
Exercise 19.2 Find the equivalents for the following Russian expressions in the text
Проводить выставку; количеств стран растёт; масштаб ярмарок; ежегодно; в соответствии с определёнными особенностями; характер выставочных экспонатов; сроки проведения; постоянная выставка; широкий спектр экспонатов; последние достижения; быть заполненным посетителями; вести переговоры; покупка товаров; поучительный опыт; способ рекламировать; проложить путь
Exercise 19.3
Exercise 19.4 Define the Tense and Voice form of the verbs in the following sentences
1. The number of countries and companies is growing from year to year and the scope of fairs and exhibitions is becoming larger. 2. The world’s largest exhibition centers are located in Western Europe and the USA. 3. The display during these exhibitions includes a wide range of exhibit. 4. They have settled all the problems connected with the purchasing of goods. 5.Usually fairs and exhibitions are crowded with visitors.
Exercise 19.5 Transform Passive constructions into Active ones. Begin them with the words in the brackets
1. Exhibitions and fairs are classified according to certain features. (They …)
2. Consumer goods exhibitions are held 2 – 4 times a year. (This centre …)
3. At international and national exhibitions commercial centres are established. (We …)
4. Fairs and exhibitions are usually held under various mottoes. (Providers …)
5. The exhibition was visited by thousands of people yesterday.
Exercise 19.6 Answer the questions
1. What is held in different countries of the world every year?
2. How many international exhibitions are held annually?
3. Where are the world’s largest, busiest and most attractive exhibition centers located?
4. How are exhibitions and fairs classified?
5. What exhibitions and fairs do you know as to their location?
6. What kind of exhibitions and fairs do you know according to their sphere of activity?
7. What example of the World Exhibition do you know?
8. How often are new high-tech exhibitions held?
9. What does the display during these exhibitions include?
10. Are fairs and exhibitions usually crowded with visitors?
11. What is established at international and national exhibitions?
12. What are commercial centres established for?
13. What mottoes are usually fairs and exhibitions held under?
14. What way do international fairs and exhibitions pave for?
Exercise 19.7 Write out the key words and expressions from the text
Exercise 19.8 Make a plan of the text
Exercise 19.9 Give your own point of view on the theme “Exhibitions and fairs are important factors for humanity progress”. Use the key words (ex. 19.6) and your plan (ex. 19.7)
Exercise 19.10 Read an introductory text and translate it without a dictionary
At the Exhibition
Last month Ivan Smirnov, an engineer from Soyuzimport had instructions to visit an exhibition of electronic equipment which was held at Olympia in London.
Soyuzimport was interested in purchasing computers of the latest model. The Model R 800 computer of Witson & Co attracted Smirnov's attention. After he had seen the computer in operation he got in touch with Mr. Adams, the Sales Manager of the company, to start talks for the purchase of computers.
Exercise19.11 Translate the following speech patterns and memorize them
Have you been to our pavilion?
We've just seen your display.
The latest models of equipment.
Does the equipment go for export?
Your equipment meets our requirements.
The demand for the equipment.
You are interested in the equipment to set up a joint venture.
It'll be mutually beneficial.
Let's discuss the matter in detail.
We'd like to establish business relations with you.
We'll be glad to cooperate with you.
Exercise19.12 Read and translate the dialogue into Russian
Mr. Smirnov (S) has come to London to continue talks with Mr. Adams (A). He contacts Mr. Adams and at 10 o'clock he is in Mr. Adams's office.
A: Good morning, Mr. Smirnov.
S: Good morning, Mr. Adams.
A: How are you?
S: Just fine, thank you. And how are you?
A: Very well, thank you. Are you enjoying your stay in London?
S: Yes, my stay here is very pleasant. The weather is fine.
A: We have a few problems to discuss. First comes the problem of delivery terms. As far as I remember you prefer f.o.b. terms.
S: You're quite right.
A: These terms are acceptable to us.
S: What's your idea of an f.o.b. price?
A: It's & 1 200 per unit. If you buy on f.o.b. loaded and stowed terms, then the price will be & 1300.
S: Pardon?
A: 1300 Pounds.
S: Well, I suppose f.o.b. loaded and stowed terms suit us. But will you give us a discount if we buy, say, 50 machines?
A: In this case we can give you a 10% discount.
S: So, the problem has been settled. When can you deliver the machines?
A: Well, we can dispatch the machines in two equal lots of 25 machines each. We can promise to deliver the first lot in April.
S: And can the second lot be delivered in July?
A: Yes, I think we can meet these delivery dates.
S: Fine. It seems to me we have settled all the problems and we can sign the contract now.
A: We'll do so as soon as the secretary has typed it... You'll have to wait a little.
(Mr. Adams buzzes on the intercom and gives the necessary instructions to his secretary). Mr. Petrov would you like to go to the theatre tonight? We can go and see a very good modern ballet at the Royal Opera House.
S: That's a wonderful idea. Thank you very much.
A: The performance starts at 7 p.m. I'll be in the lobby of your hotel at 6.30.
S: Well, I'll be there on time.
Notes
1. f.o.b. terms = free on board – франко-борт (Термин “Франко борт” означает, что продавец выполнил поставку, когда товар перешел через поручни судна в названном порту отгрузки. Это означает, что с этого момента все расходы и риски потери или повреждения товара должен нести покупатель)
2. & - pound sterling – фунт стерлингов
Exercise 19.13 Act out the dialogue
Exercise 19.14 Make a similar dialogue. Use the expressions from ex. 19.10
Exercise 11.9 (аудирование)
On Board an Airplane
- Excuse me. Is it possible to have another blanket (1), please? I am a little cold.
- Sure. Would you like just one or two?
- One will be enough I think.
- OK. I’ll be right back with your blanket. Would you like anything else?
- Yes. Can I get something to drink (2) too?
- Sure. We should avoid (3) dehydration during these long flights. What would you like to drink?
- I’d like some orange juice (4), please. And no ice (5) in it, of course.
- Oh yes. I’ll bring it to you in a minute (6). By the way you can unfasten (7) your seat belts. It is safe to do so now. And why did you put this bag (8) under your seat? I think it is very uncomfortable (9) for you. You should put it on the shelf above your seat, into the locker.
- OK, thanks. I will do that. Could you tell me how long it’ll take to reach New-York?
- Well, you know it’s a long (10) journey. We still have 6 more hours before landing.
- Will there be any food before we land (11)?
- Sure. We’ll serve another meal in 3 hours. But if you are hungry I can bring you a little snack (12) if you want.
- Yes, that would be great.
- No problem. … Here you are, sir. And here is an arrival card (13) for the immigration service. Please, fill in this form before we land. Use black (14) pen, please
- Thank you. But I need a black pen. Could you lend me one?
- One moment, please. Another flight attendant (15) will be bringing pens around shortly.
- Thanks a lot.
- Enjoy your flight.
Exercise 14.15 (аудирование)
MIKHAIL LOMONOSOV
Mikhail Lomonosov was born in 1711 in Archangelsk province. His father was a fisher and young Mikhail liked to help him. He always strove for knowledge and liked reading books. As he was 19 years old, he decided to study in Moscow. He went there on foot. In Moscow he entered the Slavic- Greek-Latin Academy. After his graduation from Academy he was sent abroad to complete his knowledge in chemistry and mining. After he had returned from abroad, he became the first Russian professor of chemistry in 1745.
At first he was engaged in research in physics and chemistry. Since 1748 he had conducted works in the first Russian chemical research laboratory, which was built at his request. Since 1753 he was engaged in research in many fields of natural and applied sciences. He wrote works on physics, astronomy, geography, history. Besides scientific works, he wrote poems as well. He is the author of the first scientifical grammar of the Russian language.
He founded the factory producing coloured glass. He created some mosaics using the glass produced at the factory.
Lomonosov was the founder of the first Russian university. This university is situated in Moscow and still carries his name.
Mikhail Lomonosov died in 1765. But he is still known as the father of the Russian science, an outstanding poet, the founder of Russian literature.
СПИСОК ЛИТЕРАТУРЫ
Агабекян И. П., Английский для ссузов : учебное пособие / И. П. Агабекян. – М. : Проспект, 2015. – 288 с.
Афанасьева О. В., Дули Д., Михеева И. В. и др. [Текст] : учеб.для общеобразоват. Организаций с прил. на электрон.носителе: базовый уровень 10 кл./ О. В. Афанасьева, Д. Дули, И. В. Михеева. – М.:ExpressPublishing: Просвещение, 2014. – 248с.: ил. – (Английский в фокусе)
Афанасьева О. В., Дули Д., Михеева И. В. и др. [Текст] : учеб.для общеобразоват. Организаций с прил. на электрон.носителе: базовый уровень 11 кл./ О. В. Афанасьева, Д. Дули, И. В. Михеева. – М.:ExpressPublishing: Просвещение, 2014. – 248с.: ил. – (Английский в фокусе)
КарповаТ.А. English for Colleges. Английский язык для колледжей / Т.А. Карпова - Кнорус, 2015.
Нарочная Е. Б. Английский язык для технических направлений: учебник / Е. Б. Нарочная, Г. В. Шевцова, Л. Е. Москалец. – М. : КНОРУС, 2015. – 400 с.
Электронные ресурсы
Сайт для изучающих английский язык, студентов и преподавателей вузов – Режим доступа: http://study-english.info
Изучение английского языка онлайн – Режим доступа: http://www.lovelylanguage.ru
Learning English – BBC – Режим доступа: https://www.bbc.co.uk/learningenglish/
Сайт для изучающих английский язык, студентов и преподавателей вузов – Режим доступа: https://www.fluentu.com/
Наталья Владимировна Сухарева
ИНОСТРАННЫЙ ЯЗЫК
Практикум
для студентов 1 курса
профиля: технического
очной формы обучения
Судомеханический техникум ФГБОУ ВО «Керченский государственный морской технологический университет»
298309 г. Керчь, Орджоникидзе, 123
© 2020, Сухарева Наталья Владимировна 506 7
Рекомендуем курсы ПК и ППК для учителей
Похожие файлы
Полезное для учителя






















