Degrees of Comparison of Adjectives

What is the Adjective
An adjective is a part of speech that describes a person, an object, a place or an animal.
Example : tall , smart , hot , long , old , big .
A comparative adjective compares two things .

Adjective change in form when they show comparison.
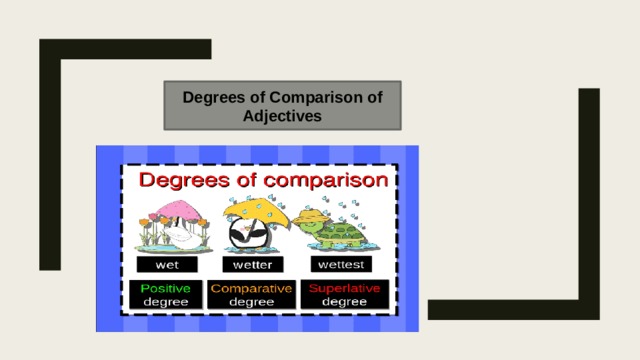
Positive Degree: An adjective is said to be in the positive degree when there is no comparison.
Comparative Degree: An adjective is said to be in the comparitive degree when it is used to compare two nouns/pronouns.
Superlative Degree: An adjective is in superlative degree when it is used to compare more than two nouns/pronouns. We use the article 'the' before the superlative degrees.
Formation of Comparative & Superlative Degrees of Adjectives
Adjectives usually form their comparative and superlative degrees:

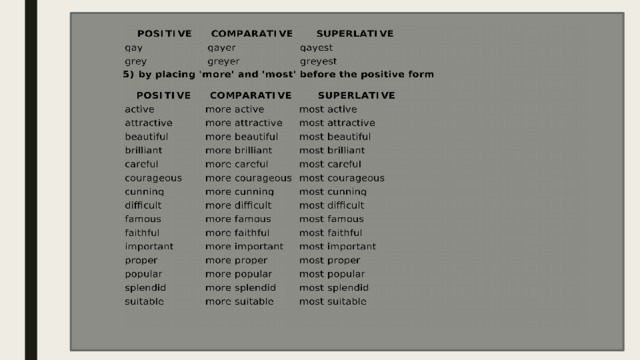
For the formation of a comparative degree, the word more is placed before the adjective, and before the superlative degree-the most.
Example:
Honest – more honest – the most honest
Difficult – more difficult – the most difficult
Russian is difficult to learn. – Arabic is more difficult . – What is the most difficult language to learn?
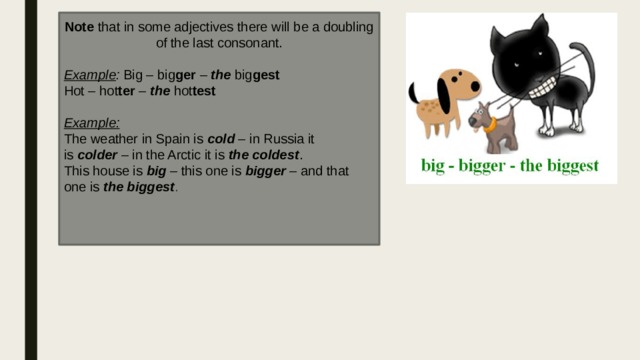
Note that in some adjectives there will be a doubling of the last consonant.
Example : Big – big ger – the big gest
Hot – hot ter – the hot test
Example:
The weather in Spain is cold – in Russia it is colder – in the Arctic it is the coldest .
This house is big – this one is bigger – and that one is the biggest .

Example :
Ice-cream is better than cakes.
Buses are cheaper than planes.
A superlative form compares more than two things .
Example :
Peter is the tallest in his family.
You are the smartest in your class.
Let’s see the next example: Jane is a smart girl.

Note : we use than , when we compare two things.
Comparative : Jane is smarter than her sister.
Superlative : Jane is the smartest in her class.

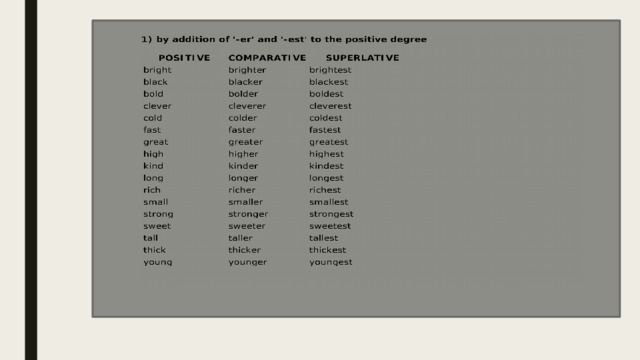
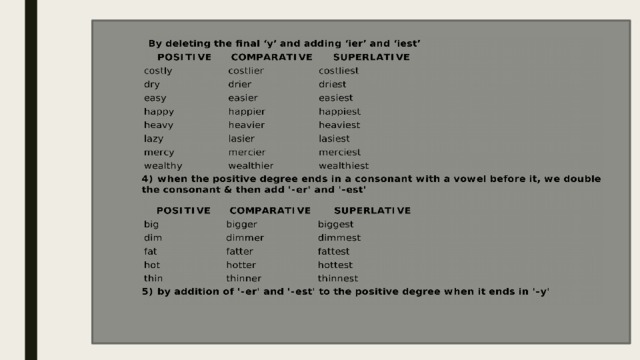
Depending on the number of syllables in a word, the comparative and superlative adjectives are formed in two different ways.
Thus, monosyllabic adjectives form degrees of comparison using the endings-er (for the comparative degree) and-est (for the superlative degree).
Don't forget the article the before the superlative of adjectives.
Example : Tall – tall er – the tall est
Hard – hard er – the hard est
Cold – cold er – the cold est



Practice

Set Expressions
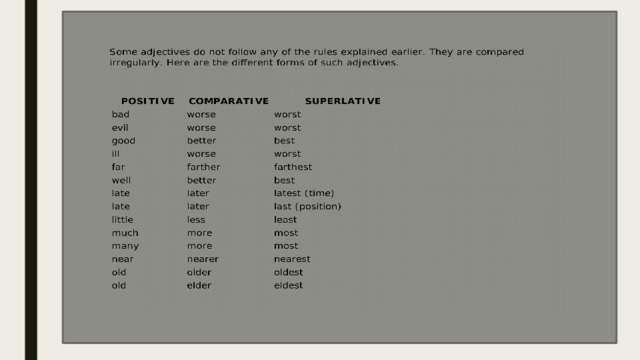
There are quite a few set expressions containing the comparative or superlative forms of irregular adjectives.
For example:
a change for the better; a change for the worse;
at best / at the best;
at most / at the most;
at worst / at the worst;
get the worst of it;
go from bad to worse;
if worst comes to worst / if the worst comes to the worst;
last but not least;
more or less; none the less;
not in the least;
prepare for the worst;
so much the better;
so much the worse.
If he leaves, so much the better. If he doesn't want to obey the rules,
so much the worse for him.
Many companies sustained losses during that period, but small companies got the worst of it.









































