
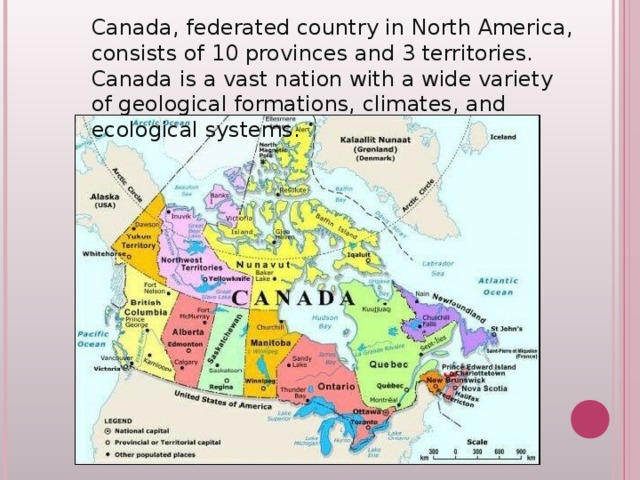
Canada, federated country in North America, consists of 10 provinces and 3 territories. Canada is a vast nation with a wide variety of geological formations, climates, and ecological systems.

Canada stretches from the Pacific Ocean on the west, to the Atlantic Ocean on the east. Northern Canada reaches into the Arctic Circle, while southern Canada stretches below the northern points of the United States.


Much of Canada is still wilderness, cover by forests. The Rocky Mountains cover a major part of western Canada - British Columbia, the Yukon Territory, and the western
part of Alberta.

West-central Canada is mostly prairie, consisting of large grain farms.

The east-central part of Canada are the provinces of Ontario and Quebec. These are major population and industrial areas.

The Maritime provinces on the east coast rely very heavily on the Atlantic Ocean for their way of life.

Most of Canada's northern islands are located inside the Arctic Circle.

The majority of Canada is still wilderness. This makes Canada a popular spot for hunting and fishing.

There are some two million lakes in Canada, covering about 7.6% of the Canadian landmass. The main lakes are Huron, Great Bear, Superior, Great Slave,
Winnipeg, Erie and Ontario.
The largest lake is
Great Bear Lake (31 126 km 2 ).

The St. Lawrence (3058 km long) is Canada’s most important river,
providing a seaway for ships from the Great Lakes to the Atlantic Ocean.
The longest river is The Mackenzie (4241 km long).

Niagara Falls is one of Canada's best known tourist attractions. It is the largest falls in the world, measured in volume of water.
Major cities and population: Toronto, Montreal, Vancouver, Calgary, Edmonton, Winnipeg, Halifax.

Population of Canada is 31,612,897 (2006) .
Canada is the second largest country in the world but has the
same population as the state of California , USA,
which is one-25 th its size.
This is because the north of Canada,
with its harsh Arctic and sub-Arctic
climates, is sparsely inhabited.



The motto of Canada, official since 1921, was suggested as early as 1866 by Sir Samuel Tilley, New Brunswick politico, and a father of Confederation. He drew it from the Old Testament, Psalm 72. In St. Jerome’s Latin version of Holy Writ, called the Vulgate, the passage reads “et dominabitur a mari usque ad mare.” The King James translation is “and he shall have dominion also from sea to sea.”

The maple leaf has been associated with Canada for some
time: in 1868 , it figured in coats of arms
granted to Ontario & Quebec;
and in both world wars, it appeared on
regimental badges. Since the 1965
introduction of the Canadian flag,
the maple leaf has become
the country’s most important symbol.

In 1996 the maple tree was officially recognized as a national emblem.

The flag is red and white, the official colours of Canada as appointed
by King George V in 1921, with a stylized 11-point red leaf in its center.
Several people participated in designing the Canadian flag.
Jacques St. Cyr contributed the stylized maple leaf,
George Bist the proportions, and Dr. Gunter Wyszechi the colouration.
It officially became the national flag on February 15, 1965,
now recognized as Canada’s Flag Day.


The use of the beaver as a Canadian emblem declined in the second half of the 19th century, perhaps because Montréal ceased to be a major fur entrepôt. The animal's emblematic importance was revived by Sir Sandford FLEMING when he designed Canada's first postage stamp, the 1851 3-penny beaver. Today the beaver, noted for its industry and perseverance, qualities considered suitable for a nation to emulate, decorates the reverse of the Canadian 5-cent coin.

It is an Atlantic or "Maritime" province.
It can be found on the East Coast of the country,
near the Atlantic Ocean. It became Canada’s newest province
on March 31, 1949.

- The Newfoundland and Labrador provincial flag was adopted in 1980. The white represents snow and ice, the blue represents the sea; red represents human effort and gold represents our confidence in ourselves.
- The pitcher plant was declared Newfoundland and Labrador's provincial flower in 1954. This amazing plant eats insects - they become trapped and rot inside the pitchers. The plant then soaks up the nutrients.
- The Atlantic Puffin was made Newfoundland and Labrador's provincial bird in 1991. This sea bird lives in the cold ocean waters feeding on small fish such as herring.
They usually mate for life. The female lays one egg each year in an underground burrow.

It is an Atlantic or "Maritime" province. It can be found on the East Coast of the country, near the Atlantic Ocean.
New Brunswick joined the Canadian Confederation in 1867.

- The provincial flag was adopted on February 24, 1965. The top rectangle has a gold lion on a red background. The gold lion is found on many provincial flags. It is a common British symbol. The ship shown on the bottom rectangle is an ancient galley. Shipping and shipbuilding were historically key economic activities in New Brunswick.
- The purple violet was adopted as the official flower of New Brunswick in 1936, at the request of the provincial Women's Institute. It has a delicate flower which people can eat.
- The black-capped chickadee is New Brunswick's official bird. It was adopted as the provincial bird in August 1983.

It is an Atlantic or "Maritime" province. It can be found on the East Coast of the country, near the Atlantic Ocean.
Nova Scotia joined the Canadian Confederation in 1867.

- Blue Saint Andrew's cross with gold and red crest of a lion in the center. In the 1625 it was the first provincial flag in the commonwealth to be authorized.
- The mayflower was declared Nova Scotia's provincial flower in 1901. This beautiful flower blooms in early spring with white blooms and light pink buds.
- The Osprey was made Nova Scotia's provincial bird in 1994. The birds use the same nests each year, hatching 2-3 eggs per year.














































