

СДЕЛАЙТЕ СВОИ УРОКИ ЕЩЁ ЭФФЕКТИВНЕЕ, А ЖИЗНЬ СВОБОДНЕЕ
Благодаря готовым учебным материалам для работы в классе и дистанционно
Скидки до 50 % на комплекты
только до
Готовые ключевые этапы урока всегда будут у вас под рукой
Организационный момент
Проверка знаний
Объяснение материала
Закрепление изученного
Итоги урока

Учебно-методическое пособие по английскому языку "Practice makes perfect"
Цель данного пособия – дать четкое и системное представление о грамматическом строе английского языка, а именно о его видовременных формах глагола. В пособии представлен как теоретический материал, так и комплекс упражнений, направленный на закрепление полученных знаний.
При работе с настоящим учебным пособием, прежде чем приступать к выполнению заданий, следует внимательно ознакомиться с правилами английского языка, изучить таблицы, представленные в данном пособии. Такой подход позволит студентам усвоить аспекты теоретической грамматики и позволит, во-первых, полностью использовать материал, предлагаемый для изучения, во-вторых, систематизировать знания, в-третьих, сопоставлять и использовать материал из отечественных и зарубежных учебных пособий и научных публикаций по грамматике и, в-четвертых, использовать полученные знания в будущем в своей профессиональной деятельности.
Просмотр содержимого документа
«Учебно-методическое пособие по английскому языку "Practice makes perfect"»
PRACTICE MAKES PERFECT
Part I
Dyakova A.A.
Пояснительная записка
Данное учебное пособие предназначается для старшеклассников и студентов первого года обучения, продолжающих изучение английского языка на базе знаний, приобретенных в средней школе (уровень Pre-Intermediate). Оно составлено в соответствии с требованиями программы для студентов неязыковых ВУЗов и имеет практическую профессиональную направленность, готовит студентов к самостоятельному совершенствованию грамматических навыков в дальнейшем, а также к применению полученных знаний в ситуациях реального общения.
Цель данного пособия – дать четкое и системное представление о грамматическом строе английского языка, а именно о его видовременных формах глагола. В пособии представлен как теоретический материал, так и комплекс упражнений, направленный на закрепление полученных знаний.
При работе с настоящим учебным пособием, прежде чем приступать к выполнению заданий, следует внимательно ознакомиться с правилами английского языка, изучить таблицы, представленные в данном пособии. Такой подход позволит студентам усвоить аспекты теоретической грамматики и позволит, во-первых, полностью использовать материал, предлагаемый для изучения, во-вторых, систематизировать знания, в-третьих, сопоставлять и использовать материал из отечественных и зарубежных учебных пособий и научных публикаций по грамматике и, в-четвертых, использовать полученные знания в будущем в своей профессиональной деятельности.
CONTENTS
VERB TENSES 4
THE PRESENT SIMPLE TENSE 4
EXERCISES 5
THE PRESENT PROGRESSIVE TENSE 7
EXERCISES 9
THE PAST SIMPLE TENSE 11
EXERCISES 13
THE PAST PROGRESSIVE TENSE 14
EXERCISES 15
THE PRESENT PERFECT TENSE 17
EXERCISES 19
THE PRESENT PERFECT PROGRESSIVE TENSE 20
EXERCISES 21
THE PAST PERFECT TENSE 23
EXERCISES 24
THE PAST PERFECT PROGRESSIVE TENSE 26
EXERCISES 26
WAYS OF TALKING ABOUT THE FUTURE 28
THE FUTURE SIMPLE TENSE 29
EXERCISES 30
THE FUTURE PROGRESSIVE TENSE 31
EXERCISES 32
THE FUTURE PERFECT TENSE 33
EXERCISES 34
THE FUTURE PERFECT PROGRESSIVE TENSE 36
EXERCISES 37
REPORTED SPEECH / THE SEQUENCE OF TENSES 39
EXERCISES 40
REFERENCE LIST 43
VERB TENSES
THE PRESENT SIMPLE TENSE
1. The Present Simple Tense is used to denote a permanent situation, a regular, habitual action or something that is true in general.
e.g. I visit my granny three times a week.
Water freezes at 00 Celsius.
What do bears eat?
We use the Present Simple tense when we say how often we do things.
e.g. We usually go to the library on Fridays.
They get up at 6 every day.
In winter Helen sometimes skies and skates.
Tom always wears jeans.
2. The formation of the Present Simple Tense:
| Affirmative | Negative | Question |
| I study | I do not (don’t) study | Do I study? |
| You study | You do not (don’t) study | Do you study? |
| We study | We do not (don’t) study | Do we study? |
| They study | They do not (don’t) study | Do they study? |
| He studies | He does not (doesn’t) study | Does he study? |
| She studies | She does not (doesn’t) study | Does she study? |
| It studies | It does not (doesn’t) study | Does it study? |
!!! Spelling rules
| M a |
| V c |
| V a |
| E |
3. Special uses of the Present Simple Tense:
a) to ask for or give instructions.
e.g. “How do I get to the shop?”
“You turn right, then you go straight on to the station, then…”
b) to describe a series of events.
e.g. First I put a lump of butter into a frying pan and light the gas; then I break three eggs into a bowl, like this…”
c) to make a suggestion.
e.g. Why don’t you take a day off tomorrow?
d) to denote a future action when the reference is made to timetables, schedules, programmes, etc.
e.g. His train arrives at 11.00.
e) in adverbial clauses of time and condition instead of will + infinitive ( after conjunctions like if, as soon as, in case, when, before, until, after, on condition that, provided).
e.g. I’ll come to her when I have a free time.
Will you stay here until the plane takes off?
I’ll lend money to you on condition that you bring it back in a month.
I’ll take my umbrella in case it rains.
If I have enough time the day after tomorrow, I’ll help you to do it.
f)with some expressions, like “I hear/see/promise/gather/suppose/advice/ insist/agree/apologise/refuse/It says…/ Here comes… / There goes.”
e.g. I hear you’re getting married.
I gather Peter’s looking for a job.
He promises never to smoke again.
It says in the paper that petrol’s going up again.
Here comes your husband.
There goes our bus – we’ll have to wait for the next one.
g) in formal correspondence. (The Present Simple Tense is more formal than the Present Progressive Tense).
e.g. I enclose my cheque for 200 $.
I look forward to hearing from her.
Exercises
Exercise 1. Put the verb into the correct form.
1. What __________ (title /mean)?
2. What time __________ (the shop/open)?
3. What language __________ (Nick/speak)?
4. Where __________ (Tom/live)?
5. What __________ (she/do)?
6. How long _________ (it/take) you to get to work?
7. How often __________ (you /use) a bicycle?
8. Who (like) ice-cream very much?
9. How __________ (he/get) home?
10. What language __________ (they/speak)?
Exercise 2. Make questions to the following sentences.
Ann speaks English very well.
Who___________________________?
He eats chocolates very seldom.
What__________________________?
The canteen closes at 17.00 every evening.
When__________________________?
Sport competitions take place every year.
What__________________________?
My friends stay at a big hotel every summer.
Where__________________________?
His behavior causes many problems.
What_________________________?
7. My parents like reading adventure books.
What kind of books______________?
8. Helen prefers comedies to soap operas.
What kind of films ______________?
9. His wife teaches English at school.
Who _________________________?
10. Kate goes to the market every Sunday.
Where _______________________?
Exercise 3. Complete using the following.
Here comes I promise I hear I insist I apologise I promise
There goes I recommend take place I suggest I gather
1.The new café in Hill Park is very good. ____________it.
2. _______________ for what I did. It won't happen again.
3. I won't tell anybody what you said. ________________.
4. Mr. Brian is not at work today. ________ you try calling him tomorrow.
5. (in a cafe) You must let me pay for the meal. ________.
6. __________ you’re getting married.
7. __________never to smoke again.
8. ___________ Mary’s looking for a job.
9. __________our bus – we’ll have to wait for the next one.
10. ________ your wife.
Exercise 4. Use the following verbs to complete the sentences.
receive take arrive laugh pay come wear take care grow
1. Nick _____ of his sister every day.
2. Wheat ____________in Russia.
3. They _____ their guests in the hall.
4. He _____ a lot of money for books.
5. He _____ a shower in the morning.
6. She often _____ to see me on Saturday.
7. Tom _____ his slippers at home.
8. My friends _____ at funny films.
9. My train _____ at 11.00.
10. Sport competitions ________every year.
Exercise 5. Translate the following sentences from Russian into English.
Этот студент не всегда выполняет домашние задания.
Моя мама убирает дом два раза в неделю.
На уроках английского мы говорим, читаем, переводим, а дома учим правила.
Он получает много писем от жены и друзей.
Во время урока наш преподаватель обычно ходит по классу или стоит у стола.
Мой друг работает в своей лаборатории.
Многие бизнесмены изучают английский язык.
Моя сестра пишет деловые письма и документы, печатает и отвечает на телефонные звонки.
Подростки смотрят, в основном, комедии и приключенческие фильмы.
В субботу вечером Анна ходит в театр.
THE PRESENT PROGRESSIVE TENSE
1. The Present Progressive Tense is used to denote an action happening at the moment of speaking or the situation around now: before or after the moment of speaking (a temporary situation). The time of the action can be clear from the context or marked by the adverbs: at the moment, now, right now, at present, etc.
e.g. I am reading a book now.
I am looking for Mrs. Smith.
2. The formation of the Present Progressive Tense.
| Affirmative | Negative | Question |
| I am playing | I am not playing | Am I playing? |
| You are playing | You are not playing | Are you playing? |
| We are playing | We are not working | Are we playing? |
| They are playing | They are not playing | Are they working? |
| He is playing | He is not playing | Is he playing? |
| She is playing | She is not playing | Is she playing? |
| It is playing | It is not playing | Is it playing? |
!!! Spelling rules
| M Add – ing |
| V d |
| V d |
| V c |
| T |
| T a |
| T |
3. Some special uses of the Present Progressive Tense:
a) to describe changing or developing situations;
e.g. The climate is getting warmer.
b) to talk about what is going on a particular time that we are thinking of;
e.g. At seven, when the post comes, I’m usually having breakfast.
You look lovely when you’re smiling.
c) to talk about a future action that has been prearranged or planned beforehand;
e.g. What are you doing tomorrow evening?
I’m seeing Paul next week.
d) to talk about an action in the near future with a verb of movement (start, arrive, come, leave, etc.).
e.g. We are leaving for London next week.
e) to talk about repeated actions happening around the time of speaking;
e.g. I am going to a lot of parties these days.
f) to talk about a repeated action in an emphatic context often implying negative emotions;
e.g. You are always losing your keys.
g) the verb to be can also be used in the Present Progressive to give a momentary characteristic of someone’s behavior;
e.g. You’re being selfish, Tom.
h) in informal correspondence or when we are trying to sound less direct.
e.g. I’m looking forward to hearing from you.
I’m wondering if you can lend me 10$.
4. Non – progressive (or stative) verbs.
These verbs are never or hardly ever used in progressive forms. They include:
verbs of mental activity and emotion: to know, to believe, to understand, to doubt, to imagine, to want, to wish, to realize, to think, to suppose, to remember, to recognize, to prefer, to love, to desire, to hate, to like, to dislike, to admire.
verbs of sense perception: to see, to hear, to sound, to smell, to taste, to seem, to appear, to look, to resemble.
verbs of reaction: to agree, to please, to surprise, to astonish, to mean, to promise, to impress, to satisfy, to deny.
verbs of possession: to have, to possess, to belong, to own, to include, to involve, to contain, to consist of, to lack
other: to depend, to concern, to fit, to owe, to measure, to matter, to need, to weigh, to deserve.
e.g. I like this cake.
Do you believe in ghosts?
5. Some of the verbs listed above have both progressive and non-progressive uses.
a) to feel: I feel/am feeling fine. (state)
I feel we shouldn’t do it. (opinion)
b) to think: What are you thinking about? (process)
What do you think of the book? (opinion)
c) to see: I’m seeing Leslie tomorrow. (=meet)
I see what you mean. (=understand)
d) to look: She looks her best today. (characteristic)
Why are you looking at me? (process)
e) to admire: Everybody admires you. (characteristic).
They are admiring the view of the river. (process)
f) to have: He has two younger sisters. (state)
We are having dinner. (set phrase)
g) to smell, to taste, to measure, to weigh, to sound:
Why are you smelling the meat? Is it bad? (process)
Does the meat smell bad? (characteristic)
I’m tasting the cake to see if it’s OK. (process)
The cake tastes wonderful. (characteristic)
Exercises
Exercise 1. Put the verb into the correct form.
1. Listen to her. __________ (She/tell the truth).
2. Take your umbrella.__________ (It/rain) outside.
3. __________ (She/look) for her keys at this moment.
4. Pass me a piece of cake. (I/drink) tea.
5. Let’s take a taxi. __________ (We/get) late.
6. __________ (Susan/wait) for her friend at this moment.
7. _____ (Andrew/learn) Japanese while (we/cook) supper.
8. Tim __________ (work) today, He's taken the day off.
9. Paul and Sally have had an argument. __________ (they/speak)
10. Look at your baby.__________ (He/cry)?
11. It looks awful! What __________ (you/drink)?
Exercise 2. Complete the sentences using the following verbs:
Start try get flow talk become work write change stay improve
1. I must go now. It __________dark.
2. Alex __________in his copybook while David __________ to his friends.
3. Can we stop walking? __________ to feel tired.
4. Please be quiet. They __________to concentrate.
5. Every year products __________ more expensive.
6. She's a doctor, but she not __________at the moment.
7. The weather __________. The wind isn't as strong. The rain has stopped.
8. Today the river__________ faster than usual.
9. I think my German __________ fast?
10. Ann is in London now. She __________at the Park Hotel.
Exercise 3. Correct the underlined verbs where necessary.
Susan is loving her children.
________________________
Are you remembering me?
_______________________
I prefer fish to mea.
_______________________
Does he know what I mean?
_______________________
He's thinking these are her keys.
___________________________
6. He usually enjoy parties.
___________________________
We grows vegetables in our garden.
___________________________
8. Are you believing in God?
___________________________
9. Water is boiling at 100 degrees Celsius.
___________________________
10. He’s seeing his friend the day after tomorrow.
___________________________
Exercise 4. Put the verbs into the correct form (Present Simple or Present Progressive).
What time __________ (your train/arrive) in Moscow?
It __________ (seem) wonderful to have a holiday.
All his family and relatives are there. Everybody _________ (have a wonderful time).
The meat __________ (smell) dreadful.
You can’t believe a word he says. He __________ constantly (lie).
They have changed a lot. __________he (recognize) them now?
We still __________ (listen) to the same text.
I __________ (understand) Spanish well.
__________ (she/ hear) music in the next room?
__________ (you/ know) what I mean?
Exercise 5. Translate the following sentences from Russian into English.
О чем ты задумалась? – Я думаю о своей поездке за границу.
Взгляните на Ника! Он пытается нарисовать картину.
Что ты ешь? Так вкусно пахнет!
Когда ты приезжаешь из Лондона? – Через неделю.
Он все еще ждет, чтобы увидеться с боссом.
Ты постоянно паникуешь. Успокойся!
Говорите громче! Я ничего не слышу!
Я еду к своим родителям на каникулах.
Какие экзамены они сдают сейчас? – Иностранные языки.
Неужели так поздно? Я побежала домой.
THE PAST SIMPLE TENSE
1. The Past Simple Tense is used to denote a finished action in the past. These can be short, single actions, longer situations or repeated actions in the past.
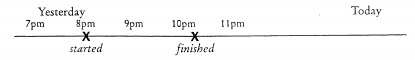
The time of the action can be indicated by an adverbial of the past time, such as yesterday, last week, a year ago, last time, etc.
e.g. I spent my holiday in Spain.
John played football last week.
2. The formation of the Past Simple Tense.
Regular verbs.
| Affirmative | Negative | Question |
| I worked | I did not (didn’t) work | Did I work? |
| You worked | You did not (didn’t) work | Did you work? |
| We worked | We did not (didn’t) work | Did we work? |
| They worked | They did not (didn’t) work | Did they work? |
| He worked | He did not (didn’t) work | Did he work? |
| She worked | She did not (didn’t) work | Did she work? |
| It worked | It did not (didn’t) work | Did it work? |
Irregular verbs
| Affirmative | Negative | Question |
| I began | I did not (didn’t) begin | Did I begin? |
| You began | You did not (didn’t) begin | Did you begin? |
| We began | We did not (didn’t) begin | Did we begin? |
| They began | They did not (didn’t) begin | Did they begin? |
| He began | He did not (didn’t) begin | Did he begin? |
| She began | She did not (didn’t) begin | Did she begin? |
| It began | It did not (didn’t) begin | Did it begin? |
!!! Spelling rules
| M A |
| T |
| T doubled after a short stressed vowel |
| T into “i” after a consonant |
| T an unstressed vowel |
| T a stressed vowel |
3. Some special uses of the Past Simple Tense.
a) in story – telling or when we are telling people about a sequence of past actions.
e.g. One day Mary decided that she didn’t like staying at home all day, so she told her father that she wanted to get a job.
b) when trying to sound more polite and less straightforward:
e.g. Did you want to see me now?
I wondered whether you were free tonight.
c) when the reference is made to a concrete event in the past even though the idea itself may be true in general.
e.g. We were sorry to leave St. Anne. It was such a lovely place.
Exercises
Exercise 1. Complete the sentences using the following verbs in the correct form:
Buy catch teach know enjoy take sleep spend be sell have
We __________ our old car yesterday.
The performance was very interesting. I_________ it very much.
My father __________ me to swim.
Unfortunately, I __________ time to come to see you.
Andrew __________a lot of money last month. He ______________ a new house.
It was cold, so I_________ on my jacket.
Dave __________ the taxi and went to the railway station.
He __________ Sasha was busy.
I __________ well because my uncomfortable bed.
The bags __________very heavy.
Exercise 2. Ask Ann about her holiday. Write your questions.
E.g.: Where/go?
– Where did you go?
How?/by plane?
_______________?
How long/get
_______________?
Go alone?
_______________?
Where/stay
_______________?
How long/stay
_______________?
What…like/the weather?
_______________?
Meet any interesting people?
_______________?
What sightseeing/visit?
_______________?
Which of those places/like most of all?
_______________?
Enjoy?
_______________?
Exercise 3. Correct the underlined verbs where necessary.
Tom get up when it was already light. He looked at his watch and run to the bathroom. He takes a shower and I drank a cup of coffee. He catched the bus and gone to the railway station where he met his friends. They had small backpacks and fishing-rods. They get off the bus at a small station near a forest and founded themselves on the shore of a large river. The boys had spent the whole day there fishing, boating and swimming. They returnt home late at night, tired but happy.
Exercise 4. Put the verb «to be « into the correct form (Past Simple).
... these his shoes? - No, they ... .
I ... late, sorry!
... her dad a designer? Yes, he … .
My brother ... not a police-officer, he… a firefighter
Ann ... a scientist.
... his uncle an engineer? - No, he ... .
... your sister in the university? - Yes, she ... .
... you a doctor? - Yes, I....
...you at work?
... his parents at home? - Yes, they ...
Exercise 5. Translate the following sentences from Russian into English.
1. Мы обсудили эти вопросы в пятницу.
2. Ник опоздал на работу позавчера.
3. Его родители вернулись из Англии вчера утром.
4. В прошлую субботу Том решил остаться дома и помочь родителям.
5. Последний раз я была в театре неделю назад.
6. Вчера я решила отправить письмо своей сестре.
7.В прошлый понедельник я была в университете до 7 вечера.
8. Вчера я ходила на рынок и потеряла там ключи от дома.
9. В 2019 году я окончила школу и поступила в университет.
10. Раньше я не понимала это правило.
PAST PROGRESSIVE TENSE
1. The Past Progressive Tense is used to denote a continuing or developing situation in the past or an action that was in progress around a particular past moment.
The time of the action can be indicated by such adverbial phrases as at 5 o’clock, from 10 till 12, at that time/then or by another past action expressed by a verb in the Past Simple.
e.g. I was watching TV at 7 o’clock yesterday evening.
The snow was falling down slowly.
It was still snowing when I looked out.
2. The formation of the Past Progressive Tense.
| Affirmative | Negative | Question |
| I was working | I was not working | Was I working? |
| You were working | You were not working | Were you working? |
| We were working | We were not working | Were we working? |
| They were working | They were not working | Were they working? |
| He was working | He was not working | Was he working? |
| She was working | She was not working | Was she working? |
| It was working | It was not working | Was it working? |
3. Some special uses of the Past Progressive Tense:
a) to stress that an activity was in progress at every moment during a past period of time.
e.g. I was painting all day yesterday. (Compare: I painted all day yesterday)
b) to describe a temporary action or situation in the past:
e.g. It happened while I was living in Scotland. (Compare: I lived in Boston for 10 years while I was a child)
c) to describe repeated ‘background’ actions (usually with always and continually) or those which happened unexpectedly, in an unplanned way.
e.g. I didn’t like him – he was continually borrowing money.
I was meeting that old lady everywhere I went.
d) to describe an interrupted past action
e.g. When I came home I found that water was running down the kitchen walls.
e) to make something seem less direct or important
e.g. I was talking to the boss yesterday and she said that… ( as if there was nothing special for the speaker)
f) when talking about two simultaneous past actions joined by the conjunction ‘while’ either the Past Simple or the Past Progressive is used.
e.g. While my father was reading/read a newspaper, my mother was cooking/cooked dinner.
Exercises
Exercises 1. What were you doing at this time? Use the Past Progressive.
1. at 9 o'clock yesterday morning ____________________
2. 5 minutes ago __________________________________
3. at 4 o'clock last Tuesday _________________________
4. at 8.15 this morning _____________________________
5. at 5.30 yesterday evening ________________________
6. at 8.45 yesterday evening ________________________
7. two hours ago _________________________________
8. at 11 o'clock last night ___________________________
9. at 12 o'clock last Monday ________________________
10. at 7 o'clock yesterday morning ___________________
Exercise 2. Use the Past Progressive to complete the sentences.
1. When the sun rose, we ___________________________
2. I fell asleep while I _____________________________
3. When the lights went out, our neighbors _____________
4. The telephone rang while I _______________________
5. I _______________________ when you came in.
6. We saw the accident when we _____________________
7. Mary burnt her hand when she ____________________
8. Susan cut her finger when she _____________________
9. When a teacher entered the classroom, the students ____
10. When he opened the door, he ____________________
Exercise 3. Put the verb into the correct form (Past Simple or Past Progressive).
1. While I (read) a story, he _________ (not see) me.
3. My friends____ (argue) about something when I ___ (enter) the room.
4. When I________ (open) the door, I _____________ (see) a surprise.
5. She _________ (study) at the library when I ______ (call) her.
6. I __________ (call) Mary, but she (be/ not) ____________ at work.
7. I ______ (not like) him – he continually ________ (borrow) money.
8. He ______ (talk) to the boss yesterday when he ______ (notice) her.
9. While my father ______ (read) an article, my mother (cook) supper.
10. It _______ (happen) while I (live) in London.
Exercise 4. Make up dialogues using Past Simple and Past Progressive.
E.g.:
- I saw you yesterday, but you didn’t see me.
- Really? When?
- At about 5 o’clock. You were taking a walk in the park.
- That wasn’t me. Yesterday at 5 o’clock I was making supper.
- I guess I made a mistake.
To get on a bus – to watch a football match on TV.
To get out of a car – to get through the park.
To go to the beach – to play volleyball.
To ride a bicycle – to clean the flat.
To walk into the university – to go on a date.
Exercise 5. Translate the following sentences from Russian into English.
Том ехал домой, когда его машина сломалась.
С 5 до 7 вечера я работала в своей лаборатории.
Она накрывала на стол, а ее друзья танцевали.
Она не выходила из дома, потому что шел сильный дождь.
Он пил кофе и слушал музыку целый вечер вчера.
Вчера с утра до вечера шел сильный дождь.
Я делала доклад, когда Вы пришли.
Когда мы проснулись, светило солнце и пели птицы.
Он торопился в университет, когда встретил своего друга.
Я переходила дорогу, когда увидела его.
THE PRESENT PERFECT TENSE
1. The Present Perfect Tense is used to denote an action which happened or started in the past but its effects can still be seen in the present. The exact time of the action isn’t usually mentioned but it always includes the present moment.
e.g. I have repaired your TV set. Now you can watch it.
The time of the action can be specified by one of the following adverbials: just, already, yet, ever, never, all one’s life, recently, lately, of late, so far, this week/month/year, today, in the last/past few days/weeks, for (some period of time), since (a certain moment.
Note: 1) ‘already’ is mostly used in affirmative sentences. It can be used in questions to express some surprise that something happens sooner than expected.
e.g. He has already packed his luggage.
Have you already packed your things?
2) ‘lately’ is mostly used in questions and negatives; in affirmative sentences it is used with only, much, a lot.
e.g. I’ve heard a lot about her lately.
3) ‘yet’ is mostly used in negative and interrogative sentences.
e.g. “Has Ben come yet?”
I haven’t read this book yet.
2. The formation of the Present Perfect Tense.
The Present Perfect Tense is formed with the help of the auxiliary verb to have in Present Simple and Participle II (past participle). The past participle often ends in –ed (finished, decided), but many important verbs are irregular (lost, done/been/written, etc.)
Regular Verbs
| Affirmative | Negative | Question |
| I have worked | I have not (haven’t) worked | Have I worked? |
| You have worked | You have not (haven’t) worked | Have you worked? |
| We have worked | We have not (haven’t) worked | Have we worked? |
| They have worked | They have not (haven’t) worked | Have they worked? |
| He has worked | He has not (hasn’t) worked | Has he worked? |
| She has worked | She has not (hasn’t) worked | Has she worked? |
| It has worked | It has not (hasn’t) worked | Has it worked? |
Irregular verbs
| Affirmative | Negative | Question |
| I have lost | I have not (haven’t) lost | Have I lost…? |
| You have lost | You have not (haven’t) lost | Have you lost…? |
| We have lost | We have not (haven’t) lost | Have we lost…? |
| They have lost | They have not (haven’t) lost | Have they lost…? |
| He has lost | He has not (hasn’t) lost | Has he lost…? |
| She has lost | She has not (hasn’t) lost | Has she lost…? |
| It has lost | It has not (hasn’t) lost | Has it lost…? |
3. Some special uses of the Present Perfect Tense:
a) to stress the present results of a past action.
e.g. I’ve passed my exam!
b) to talk about one’s life experience gained through some past event
e.g. She’s been married four times – and she’s only 31!
c) to give news of recent events.
e.g. The pound has fallen against the dollar.
d) with the expressions It’s the first /second/seventh… time…,It’s the best/the worst …, It’s the only time…
e.g. It’s the first time he’s driven a car.
It’s the best book I’ve ever read.
4. Note: the difference between gone (to) and been (to).
John is on holiday now. He has gone to Spain. (= he is there now or on his way there)
Jack is back home from holiday now. He has been to Spain. (=he has now come back from Spain)
5. There are cases when the Present Perfect Tense can’t be used:
a) when there is no direct link with the present moment and the action is treated as a mere of fact in the past or when the situation has changed.
e.g. I met John today, we talked a bit and then parted.
He got some money from his Uncle but now he’s spent all of it.
b) when talking about some historical events, origin or reasons for certain events, when identifying the person, thing or circumstances responsible for a present situation.
e.g. The Chinese invented paper.
Who let the cat in?
c) in ‘when’-questions the Past Simple Tense is used.
e.g. When did you meet Paul? – Long time ago.
d) when the reference is made to the place of the action.
e.g. Have you found your key? – Yes, I found it in my bag.
Exercises
Exercise 1. Use the Present Perfect to complete the sentences.
E.g.: My parents travelled a lot last year but they haven’t travelled much this year.
Steve wrote a lot of letters to his mother last year but he ________this year.
I read a magazine yesterday but I ___________________today.
It rained a lot last autumn but I ________________this autumn.
The company didn’t make a profit last year but it _____________this year.
Last summer grew a lot of vegetables but this summer ______________.
Last month my brother earned a lot of money but this month __________.
She worked hard last year but _____________this year.
Last season our team _____________.
I didn’t quarrel with my mother last year but I ______________this year.
We saw a lot of films last week but we __________ this week.
Exercise 2. You ask people about things they have done. Write questions with ever.
1. (drive/car?) Have you ever driven a car?
2. (meet/this person?) Have________________________ ?
3. (visit/this sightseeing?) _________________________ ?
4. (go/to this cafe?)______________________________ ?
5. (read/this book) _______________________________ ?
6. (lose/your telephone) __________________________ ?
7. (find/money) _________________________________ ?
8. (see/ this film) ________________________________ ?
9. (buy/ such cakes) _____________________________ ?
10. (think/your future) ___________________________ ?
Exercise 3. Put in gone (to) or been (to).
1. Are you going to the shop?' – No, I've already ___________ there.
2. They aren’t at home. They________ to the railway station to buy a ticket.
3. She's just ______________ to the market. She's bought a lot of things.
4. Ann is on business trip. She's _________to Spain.
5. He has _________________ out. He'll return in a minute.
6. Where is Mark? – He ____________ London for 2 weeks.
7. Where have you been? – I’ve ___________ China.
8. They’ve ________________ to the theatre. They’ve watched a wonderful performance.
9. Where are your parents? – They ____________ America for a month.
10. He's just ______________ to the shop. He's bought a lot of products.
Exercise 4. Complete the sentences using the following verbs:
happen work give up cook appear live part answer quarrel change
1. They ______________ greatly since those days.
2. How long _________ in the city?
3. I can’t understand why they ___________.
4. Tell me why you ___________.
5. She asks what you ____________for supper.
6. She'd like to know why they ___________ her letter.
7. I wonder how long you _______________ at the studio.
8. He can’t say where the cat _______________ from.
9. I’d like to know what ______________ to you.
10. Ann doesn’t say why she __________ sport.
Exercise 5. Translate the following sentences from Russian into English.
1. Мои родители еще не решили, куда поедут на выходных.
2. Он знает английский язык с детства.
3. Я не знаю, почему он не пришел сегодня в институт.
4. В этом году я часто видела их вместе.
5. Мы не виделись целую вечность!
6. Она сильно изменилась с тех пор.
7. Они не были здесь с прошлого года.
8. Я знаю эту семью уже 15 лет.
9. Подожди немного, я еще не собрал свои вещи.
10. Я только что приготовила вкусный пирог.
THE PRESENT PERFECT PROGRESSIVE TENSE
1. The Present Perfect Progressive Tense is used to denote an action which started in the past and is still going on or which has just stopped and has present results.
e.g. Sorry, I’m late. Have you been waiting long?
2. The formation of the Present Perfect Progressive.
| Affirmative | Negative | Question |
| I have been working | I have not (haven’t) been working | Have I been working? |
| You have been working | You have not (haven’t) been working | Have you been working? |
| We have been working | We have not (haven’t) been working | Have we been working? |
| They have been working | They have not (haven’t) been working | Have they been working? |
| He has been working | He has not (hasn’t) been working | Has he been working? |
| She has been working | She has not (hasn’t) been working | Has she been working? |
| It has been working | It has not (hasn’t) been working | Has it been working? |
3. Some special uses of the Present Progressive Tense:
a) with the prepositions/conjunctions for and since and in ‘how long’ - questions.
e.g. How long have you been learning English?
It’s been raining since Christmas.
b) to talk about situations which are coming to an end or may change
e.g. I’ve been thinking about this idea for a long time. Now I’m ready to discuss it.
c) to talk about repeated actions without stating how often they have happened.
e.g. I’ve been watching a lot of films lately.
Compare: I’ve watched 3 films this week.
Exercises
Exercise 1. Write a question for each situation.
1. We __________ (wait) for you for half an hour.
2. He ___________ (swim) since morning.
3. It ___________ (rain) for 3 hours.
4. Paul _________ (work) in the supermarket since July.
5. Ann is a vet._____________ (she/work) for 5years.
6. _______________ (He/think) about you for a long time.
7. Kate is at work today. _____________ (she/work) since morning.
8. _______________ (she/work) very hard recently.
9. I _____________ (watch) a lot of comedies lately.
10. _______ (Sarah think) about her future for a long time.
Exercise 2. Write questions with how long and when.
1. It's snowing.
(how long?) How long has it been snowing?
(when?) When did it start snowing?
2. David works in the bank.
(how long?)______________________________________
(when/start)______________________________________
3. Ann is learning English.
(how long/learn?) ________________________________
(when/start?) ____________________________________
4. His friends are ill.
(how long/be ill?) ________________________________
(when/become?) _________________________________
5. I know John.
(how long/you/know?)_____________________________
(when/you/first/meet?)_____________________________
Sue has a headache.
(how long/have?) _________________________________
(when/start?) ____________________________________
7. Kate and Tom are married.
(how long?)___________ __________________________
(when?)_________________________________________
8. You're watching TV.
(how long?)________________ _____________________
(when?)_________________________________________
9. He knows Mark.
(how long/you/know?)_____________ _______________
(when/you/first/meet?)_____________________________
I have got a bike.
(how long/you/have got?)___________________________
(when/you/buy?)__________________________________
Exercise 3. Fill in for or since.
1. They’ve lived in the town _______ childhood.
2.____ Sarah moved to Paris, I’ve been much happier.
3. Tom’s been waiting for you ______ the morning.
4. We’ve known him _______ 2011.
5. Kevin has been my best friend ________ many years.
6. He hasn't been to abroad ____________________ ages.
7. It has been snowing _____ hours.
8. Jane has been a doctor _______ 15 years.
9. She has been working here _______ 3 years.
10. It has been raining _____ morning.
Exercise 4. Ask your friend about how long…..
E.g.: How long have you been in hospital?
1. (how long/be/in America?)________________________
2. (how long/have/this coat?)________________________
3. (how long/have/piano lessons?)____________________
4. (how long/know/Ann?)___________________________
5. (always/live/in New York?)_______________________
6. (how long/teach/German?)________________________
7. (how long/work/at school?)_______________________
8. how long/play/tennis?)___________________________
9. how long/learn/English?)_________________________
10. how long/be/abroad?)___________________________
Exercise 5. Translate the following sentences from Russian into English.
Сколько времени ты работаешь над этой проблемой? – Уже 5 лет.
Как долго ты ждешь меня? – С 10 утра.
Они изучают английский с тех пор, как поступили в университет.
Она работает в институте уже 3 года.
Он носит очки с детства.
Мальчики играют в теннис уже целый час.
Я ношу это пальто уже 2 года.
Мы готовимся к экзамену уже 2 дня.
Я читаю эту книгу с прошлого месяца.
10.Они ждут телефонного звонка с вечера.
THE PAST PERFECT TENSE
1. The Past Perfect Tense is used to denote an action that happened before another past action and is viewed back from this past moment The time of the prior action can be indicated:
a) with the help of another past action expressed by a verb in the Past Simple.
e.g. When I arrived at the party, Lucy had already gone home.
b) with the help of a by-phrase.
e.g. They had finished their homework by 7 o’clock in the evening.
2. The formation of the Past Perfect Tense.
The Past Perfect Tense is formed with the help of the auxiliary verb to have in Past Simple and Participle II (past participle). The past participle often ends in –ed (finished, decided), but many important verbs are irregular (lost, done/been/written, etc.)
Regular verbs
| Affirmative | Negative | Question |
| I had worked | I had not (hadn’t) worked | Had I worked? |
| You had worked | You had not (hadn’t) worked | Had you worked? |
| We had worked | We had not (hadn’t) worked | Had we worked? |
| They had worked | They had not (hadn’t) worked | Had they worked? |
| He had worked | He had not (hadn’t) worked | Had he worked? |
| She had worked | She had not (hadn’t) worked | Had she worked? |
| It had worked | It had not (hadn’t) worked | Had it worked? |
Irregular verbs
| Affirmative | Negative | Question |
| I had lost | I had not (hadn’t) lost | Had I lost…? |
| You had lost | You had not (hadn’t) lost | Had you lost…? |
| We had lost | We had not (hadn’t) lost | Had we lost…? |
| They had lost | They had not (hadn’t) lost | Had they lost…? |
| He had lost | He had not (hadn’t) lost | Had he lost…? |
| She had lost | She had not (hadn’t) lost | Had she lost…? |
| It had lost | It had not (hadn’t) lost | Had it lost…? |
3. Some special uses of the Past Perfect Tense.
a) to stress the idea of completion.
e.g. I had read all my books, and was beginning to get bored.
b) with the time conjunctions: hardly…when, scarcely…when, no sooner…than.
e.g. I had hardly/scarcely closed my eyes when the mobile phone rang.
c) to talk about unrealized expectations, wishes and hopes.
e.g. He had intended to make a cake but he ran out of time.
There are some cases when the Past Simple can/should be used instead of Past Perfect.
a) The Past Perfect can mark the first action as separate, independent of the second, completed before the second started. In contrast, the Past Simple can suggest that the first action “leads into” the other or that there is a cause-and-effect-link between them.
e.g. When we arrived, the meeting had begun.
When the President arrived the meeting began.
b) to talk about a sequence of events.
e.g. When I entered the room I noticed the difference at once.
c) with the conjunctions: after, before as soon as, etc.
e.g. After he (had) put down the receiver, he looked at me and sighed.
Exercises
Exercise 1. Complete the sentences using Past Perfect:
I went to the post-office after...
She cleaned the room after…
He read a book after...
They went to bed after...
He called me after...
She went to dance after...
I wrote a letter after...
They rebuilt the house after...
We went for a walk after...
I visited my uncle after…
Exercise 2. Complete the sentences using the words in brackets.
1. It was pleasant to see Jane again after many years. (I/not/see/her for 3 years) __________________.
2. I offered Susan something to drink, but (she/just/have/a glass of mineral water)__.
3. I went to Helen’s work, but (she/go out) ____________.
4. John went to his school after such a long time and he saw that (it/change/a lot)___.
5. I (hardly close) my eyes when you called me.
6.I invited Sue to the party, but (she /arrange/to meet with her relatives)_________.
7. When Susan went to the theatre (the performance/already/start)______________.
8. When Lucy arrived at the party, we already (go home) __________________.
9. Nick sang a song. I (hear) it before ________________.
10. We arrived at work in the morning and found that somebody (break) into the office during the night ____________________________________________.
Exercise 3. Make your own sentences ending with never ... before.
E.g.: Helen sang a song. We didn't know it. (hear) We had never heard it before.
_______________________________________________
______________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
Exercise 4.
work miss phone finish see do fall make have sell
Nick was late because he ... the taxi.
She … her homework before her mother returned home.
My friends didn’t want to go to the theatre because they ... already ... this performance.
The baby ... asleep before the nurse came in.
They had no van at that time because they … their old one.
I ... at school before he entered the college.
Ann wasn’t hungry because she … dinner.
After … school, she went to a camp.
I apologized I…not you.
We got a bad mark for the test because we... a lot of mistakes in it.
Exercise 5. Translate the following sentences from Russian into English.
1. Когда я приехал на вокзал, поезд уже ушел.
2. Едва я прилег отдохнуть, как зазвонил телефон.
3. Они закончили готовиться к экзаменам к 9 часам вечера.
4. Когда она вышла из дома, то она вспомнила, что забыла выключить телевизор.
5. Анна была расстроена, потому что никто не пришел на ее день рождение.
6. Когда он пришел, мы уже обсудили наши планы на лето.
7. Он упаковал все свои чемоданы к 3 часам вечера.
8. Ник был счастлив, потому что получил «5» по английскому.
9. Студенты были огорчены, потому что проиграли соревнования.
10. Я закончил писать статью к 6 утра вчера.
THE PAST PERFECT PROGRESSIVE TENSE
1. The Past Perfect Progressive is used to denote an action which had continued up to the past moment and is viewed back from this moment.
e.g. When I met Mary, I could see that she had been crying.
The Past Perfect Tense generally emphasize the continuation of an action while the Past Perfect emphasizes the idea of completion.
e.g. I had been walking for an hour before I met my friend and he gave me a lift
I had walked half the way when I met my friend and he gave me a lift.
2. The formation of the Past Perfect Tense.
| Affirmative | Negative | Question |
| I had been working | I had not (hadn’t) been working | Had I been working? |
| You had been working | You had not (hadn’t) been working | Had you been working? |
| We had been working | We had not (hadn’t) been working | Had we been working? |
| They had been working | They had not (hadn’t) been working | Had they been working? |
| He had been working | He had not (hadn’t) been working | Had he been working? |
| She had been working | She had not (hadn’t) been working | Had she been working? |
| It had been working | It had not (hadn’t) been working | Had it been working? |
Exercises
Exercise 1. Read the situations and make sentences from the words in brackets.
1. My friends were very tired because they (work) hard all day.
2. I was disappointed when you had to cancel my invitation. I (look) forward to our meeting the whole year.
3. When Ann woke up we (to watch) that TV programme for an hour already.
4. When Mark returned home, I (read) a book for 20 minutes already.
5. We (walk) for an hour when it started to rain.
This time make your own sentence:
_______________________________________________
_______________________________________________
_______________________________________________
_______________________________________________
_______________________________________________
_______________________________________________
Exercise 2. Complete the sentences using the following verbs in the correct form:
look drive exercise work play cook do walk write read
He ________ this magazine when we came home.
We ________for about 4 hours when at last we saw the river.
Kevin was in a bad temper because his neighbor _______ the piano all night through and he couldn’t fall asleep.
In the morning I found my sunglasses which I ______ for the whole day yesterday.
She knew that I ______ on my article for 2 months.
My cousin _________ for 3 hours when he stopped for a rest.
Peter looked tired as he _____ the whole day without a rest.
My friend was upset as she ________ supper for the whole evening but we didn’t come to her.
Jason felt tired because he ________ his homework for several hours.
When I entered the classroom, the students ______ a test-paper for half an hour
Exercise 3. Put the verb into the most suitable form, Past Simple, Past Continuous, Past Perfect or Past Perfect Continuous.
He _______ (try) to find her for years but he failed.
I _________ (work) when she came in, and he was very tired because he __ (work) for a long time.
She was never sorry that she _____ (meet) them.
We ______ (visit) them after they had got their new house.
It ________ (rain) hard for a week before our arrival.
Ann ______ (go) to the country before the telegram arrived.
They ______ (learn) the new rule when I phoned them.
The rain began while we ________ (watch) the game.
I phoned you yesterday but you ______ (be) at home.
John was taking a photograph of me while I not (look).
Exercise 4. Make your own sentences using Past Simple and Past Perfect Continuous.
E.g.: We had been working in silence for some time when Nick spoke.
_______________________________________________
_______________________________________________
_______________________________________________
_______________________________________________
_______________________________________________
_______________________________________________
Exercise 5. Translate the following sentences from Russian into English.
1. Они обсуждали эту проблему в течение 2 часов, прежде чем они нашли правильное решение.
2. Он выиграл это соревнование, так как он готовился к нему в течение 3 лет.
3. Кевин выглядел уставшим, так как он работал в саду целый день.
4. Она спала уже в течение получаса, прежде чем ее сестра разбудила ее.
5. Анна гладила одежду в течение часа вчера.
6. Мы плавали в море с самого утра вчера.
7. Дети помогали родителям целый день вчера.
8. Наши перчатки были мокрыми, так как мы играли в снежки и лепили снеговика.
9. Прежде чем я сдала экзамен по биологии, я готовилась к нему целую неделю.
10. Мы ехали 5 часов, как вдруг наша машина сломалась.
WAYS OF TALKING ABOUT THE FUTURE
In modern English there are several ways to talk about the future. In most cases the difference between them is clear-cut, but in many situations two or more structures are possible with similar meanings.
1. The Future Simple Tense
a) prediction;
b) giving or asking for information;
c) statement of a future fact;
d) expression of an immediate intention;
f) offer request threat, promise, etc.
2. The Future Progressive Tense
a) a continuing situation in the future
b) a planned or anticipated event
c) a polite way to ask about one’s plans
3 The Future Perfect Tense
a) an action completed before another future moment
4. The Future Perfect Progressive Tense
a) a continuous action, happening for some time before another future moment
5. The Present Simple Tense
a) a scheduled, programmed or timetabled future
6. The Present Progressive Tense
a) personal arrangements and fixed plans
b) finding out about people’s plans (more pressing for a decision)
c) an action expressed by a verb of movement
7. “To be going to…”
a) future events outside people’s control, when there is some present evidence of a future accomplishment
b) talking about someone’s plans especially a previous decision.
THE FUTURE SIMPLE TENSE
1. The Future Simple Tense is used to denote a future action and have one of the following meanings: a) prediction; b) giving or asking for information; c) statement of a future fact; d) expression of an immediate intention; f) offer request threat, promise, etc.
e.g. I think Liverpool will win
I’ll probably be home late tonight.
I’ll come of age soon.
“The phone is ringing.” “I’ll answer it”
I’ll hit you if you do it again.
Will you help me, please?
The time of a future action can be indicated with the help of such adverbial phrases as tomorrow morning/night, next week//month/year, in 2 days, etc.
2. The formation of the Future Simple
| Affirmative | Negative | Question |
| I will work | I will not (won’t) work | Will I work? |
| You will work | You will not (won’t) work | Will you work? |
| We will work | We will not (won’t) work | Will we work? |
| They will work | They will not (won’t) work | Will they work? |
| He will work | He will not (won’t) work | Will he work? |
| She will work | She will not (won’t) work | Will she work? |
| It will work | It will not (won’t) work | Will it work? |
3 Some special uses of the Future Simple Tense.
a) The Future Simple is not used in the adverbial clauses of time and condition after the conjunctions when, after, before, till, until ,as soon as, while, if, in case unless ,on condition that, etc.
e.g What shall I do if nobody helps me when I come?
I’ll lend you my book if you return it next week.
b) The Present Simple is used instead of the Future Simple in most subordinate clauses introduced by question words, after the verbs to hope, to bet and the phrase “It doesn’t matter”.
e.g. He’ll never do anything that goes against his conscience.
She’ll agree with you whatever you say.
I hope you like the film.
c) The Future Simple is used in object clauses introduced by the same conjunctions as adverbial clauses of time and condition.
e.g. It’s hard to say if we will win the race.
d) The Future Simple Tense is used in adverbial clauses of cause.
e.g. I won’t go to the museum because I’ll get bored there very quickly.
Exercises
Exercise 1. Complete the sentences using will ('ll). Choose from the following:
wait pay become be drop
ask pay lend pass open
His friends think he ____________________
I hope pollution levels _________ soon.
Since it’s your birthday, I _______ for lunch.
______ the door for me, please?
I’ll _______ you my book if you return it next week.
David ______ her to help him with the project.
I’m sure you _______ the exams.
Daniel ___________ 3 years old next week.
I _______ until the rain stops.
When _______ the bills?
Exercise 2. Make one sentence from two.
He will help you. You will ask him politely. (if)
Sam will come soon. We won’t start supper without him. (until)
Things will get worse. I will lose my job. (if)
She will arrive in London next week. I will come and meet her. (when)
Prices will go up again. We won’t buy a new flat. (if)
He will go swimming tomorrow. The water will be cold. (unless)
Jim will ask Mary to marry him. She will say «yes». (if)
They will make their decision. They will let him know. (as soon as)
Nick will join them. Something unexpected will happen. (unless)
I will be there. She will arrive. (when)
Exercise 3. Complete the sentences with I'll + a suitable verb.
If you boil the kettle, ____________ the coffee.
If it rains tomorrow, _____________my umbrella.
If I miss the train, _______________a taxi.
If I have a party, ________________Kate to it.
If Ann phones me, ______________ to her.
If I fail the exam, _______________it again.
If I meet John, _________________ about the football match.
If the letter comes, _____________ you the news.
If she doesn’t come to me, ________to her any more.
If I get salary, __________________a new pair of shoes.
Exercise 4. Put in if, when, until, unless, as soon as, before, after
I’ll stay here _____ she answers me.
We’ll never understand _____ we see our own eyes.
_____ she comes to my birthday party, I will be very pleased.
He’ll go and see New York ______ he reaches America.
They’ll buy new clothes _____ they get wages.
She’ll learn Italian _____ she goes to Italy.
Please, don’t call me _____ it is urgent.
______ she rings me up, I’ll let you know.
______I find somewhere to live, I’ll give you my address.
Visit this theatre _____ you leave.
Exercise 5. Translate the following sentences from Russian into English.
Я надеюсь, тебе понравится поездка за город.
Как только он мне позвонит, я дам тебе знать.
Тому будет 20 лет в следующем году.
После занятий мы пообедаем, отдохнем и выполним домашнее задание.
Я не вызову врача, если температура не поднимется.
Она сдаст свой последний экзамен 23 июня.
Он поможет перевести эту статью с английского на русский.
Ты проспишь, если не заведешь будильник.
Не звони мне вечером. Я буду занята.
Он не опоздает на занятия, если успеет на автобус.
THE FUTURE PROGRESSIVE TENSE
1. The Future Progressive Tense is used to denote an continuing action at a certain moment in the future. It can also be used for planned and anticipated events in the near future.
e.g. This time next week I’ll be lying on a beach in Spain.
The Future Progressive is often used to ask about someone’s plans for the near future in a polite way.
e.g. Will you be passing the post office when you go out?
2. The formation of the Future Progressive Tense.
| Affirmative | Negative | Question |
| I will be working | I will not (won’t) be working | Will I be working? |
| You will be working | You will not (won’t) be working | Will you be working? |
| We will be working | We will not (won’t) be working | Will we be working? |
| They will be working | They will not (won’t) be working | Will they be working? |
| He will be working | He will not (won’t) be working | Will he be working? |
| She will be working | She will not (won’t) be working | Will she be working? |
| It will be working | It will not (won’t) be working | Will it be working? |
Exercises
Exercise 1. Complete the sentences using will be +Ving. Choose from the following:
make stay lie do sleep bloom cross look have help play listen
This time next Sunday, I _______ you with the shopping.
Don’t call me at 7am. I ___________.
Her husband _______ after her children tomorrow evening.
Tomorrow from 4 to 5 she ___________ a report.
My brother _________ on the sofa the whole evening.
This time on Thursday we _________at home.
What you ______ tomorrow morning?
He _________ music while his friends ________ football.
This time tomorrow they ________ the Atlantic Ocean.
It is spring, the trees ___________ soon.
Exercise 2. Make up sentences using the Future Progressive Tense.
She _______ (to drive) to the agency at 8 o’clock tomorrow morning.
The doctor _________ (examine) his patients 8 a.m. till 11 a.m. tomorrow.
He _________ (jog) in the park from 6 a.m. till 7 am. tomorrow.
Molly _______ (decorate) her flat for the birthday party.
We _________ (exercise) in the gym from 5 p.m. till 9 p.m. tomorrow.
My parents _______ (celebrate) their 20th wedding anniversary tomorrow morning.
Henry will be _______ (play) the piano in the hall since 6 o’clock.
Tomorrow at 2 p.m. Brian _______ (drive) towards the Black Sea at that moment.
On Monday at 9 p.m. my dad ________ (take) the cat to the vet.
I _______ (use) the Internet from 4 p.m. till the morning tomorrow.
Exercise 3. Put the verbs in brackets into the Future Simple or the Future Continuous.
I think my father ________ (buy) me a good present.
Helen _______ (pack) her things at this time tomorrow.
I hope he _________ (win) the race tomorrow.
The weather _______ (change) for the worse next week.
George _______ (walk) the dog at 6 o’clock tomorrow morning.
They ______ never (do) it again.
She _______ (be) back late at night.
I _______ (wear) a smart dress at the party tomorrow evening.
My friend _______ (leave) for Krasnodar while I ______ (have) a rest in Sochi at this time tomorrow.
Her family ________ (dine) out tomorrow at 12 o’clock.
Exercise 4. Make your own sentences using the Future Continuous.
E.g.: We will be working in silence while Nick will be preparing for tomorrow’s exam.
_______________________________________________
_______________________________________________
_______________________________________________
_______________________________________________
_______________________________________________
_______________________________________________
Exercise 5. Translate the following sentences from Russian into English.
Твой друг будет ждать тебя после занятий с 4 до 6.
Приходи ко мне сегодня вечером. Мы будем готовиться к экзаменам.
В это время завтра я буду лететь в Нью-Йорк.
На следующих выходных она будет загорать на пляже.
Мы будем плавать в море в это время завтра.
Когда ты будешь проходить аптеку, позвони мне.
В это время на следующей неделе они будут работать над проектом.
Завтра утром моя сестра будет печь праздничный пирог.
Вечером в пятницу мой брат будет ремонтировать велосипед.
Я буду смотреть интересный фильм с 9 до 11 завтра.
THE FUTURE PERFECT TENSE
1 The Future Perfect Tense is used to denote an action which will have happened/finished by a certain moment in the future. The time of the action can be indicated by a by-phrase or by another future action.
e.g. I’m sure you will have arrived by 7 o’clock tomorrow.
2. The formation of the Future Perfect Tense
Regular Verbs
| Affirmative | Negative | Question |
| I will have worked | I will have not worked | Will I have worked? |
| You will have worked | You will have not worked | Will you have worked? |
| We will have worked | We will have not worked | Will we have worked? |
| They will have worked | They will have not worked | Will they have worked? |
| He will have worked | He will have not worked | Will he have worked? |
| She will have worked | She will have not worked | Will she have worked? |
| It will have worked | It will have not worked | Will it have worked? |
Irregular verbs
| Affirmative | Negative | Question |
| I will have done | I will not have done | Will I have done? |
| You will have done | You will not have done | Will you have done? |
| We will have done | We will not have done | Will we have done? |
| They will have done | They will not have done | Will they have done? |
| He will have done | He will not have done | Will he have done? |
| She will have done | She will not have done | Will she have done? |
| It will have done | It will not have done | Will it have done? |
Exercises
Exercise 1. Complete the sentences using will have+Ved/3. Choose from the following:
receive make release look lose open lay publish learn pack
By the time my father arrives, I ________ the gate.
By 5 o’clock tomorrow we __________ our things.
By next year he ________ a lot of letters.
By next year she _________ a new song.
By the time you visit me, I _________ through all the journals.
By 7 o’clock tomorrow my sister _________ all the rules.
By this summer she _______ weight.
By the time I arrive, the author _______ a new novel.
By the time you get up, I _________ the table.
By the end of this year, I _________ a lot of money.
Exercise 2. Correct the underlined verbs where necessary.
If Susan will learn English, she will get a well-paid job.
________________________
The scientists will do the experiment by next year.
________________________
I take some money with me in case I want to buy something.
_________________________
The designer will show his collection next week.
_________________________
She will cleaning the curtains at this time tomorrow.
_________________________
A vet will treat sick animals from 9 a.m. till 11 a.m.
_________________________
They will have find a job soon.
_________________________
Tomorrow at 12 o’clock my friend will be painting a picture.
_________________________
Mary hopes her daughter will become a successful actress by the time she’s 30.
_________________________
On Monday at 9 o’clock he will have met the English ambassador.
________________________
Exercise 3. Put the verbs in brackets into the Future Simple, the Future Continuous or the Future Perfect.
We___________ (wait) Ann at home while she _______ (take) the exams tomorrow morning.
By the end of the week, I __________ (post) the letters.
They ____________ (inform) their boss about this situation tomorrow.
I __________ (get) my exam results in a month.
Jack _________ (make) his bed by the time his mother returns home.
Tomorrow morning, she _______ (iron) the clothes.
If I lose my map, I _______ (ask) for directions.
His son ________ (join) the Army next summer.
By 5 o’clock Paul ___________ (sign) all the documents.
I _________ (spend) all my money by the end of my business trip.
Exercise 4. Write 10 sentences about your family. Use the Future Perfect.
E.g.: My sister will have made a new dress by her birthday.
My uncle will have bought a new car by the end of the year.
_______________________________________________
_______________________________________________
_______________________________________________
_______________________________________________
_______________________________________________
_______________________________________________
_______________________________________________
_______________________________________________
_______________________________________________
_______________________________________________
Exercise 5. Translate the following sentences from Russian into English.
Писатель завершит свой рассказ к концу следующего месяца.
Секретарь закончит эту работу, когда вернется шеф.
Мы опубликуем статьи к концу недели.
Она уже приготовит вкусный ужин к тому времени, когда придут гости.
Анна накроет на стол к 7 вечера.
К концу лета я накоплю достаточно денег для путешествия.
Том сдаст все экзамены к началу августа.
К концу следующего года они выучат грамматику английского языка.
Студенты обсудят этот вопрос, прежде чем учитель войдет в аудиторию.
Если я буду придерживаться диеты, я сброшу 5 кг к концу месяца.
THE FUTURE PERFECT PROGRESSIVE
1. The Future Perfect Progressive Tense is used to denote an action which will have been happening for some time before another future action. It stresses the continuity of a future achievement.
e.g. I’ll have been teaching for 10 years this summer.
2. The formation of the Future Perfect Progressive
| Affirmative | Negative | Question |
| I will have been working | I will not have been working | Will I have been working? |
| You will have been working | You will not have been working | Will you have been working? |
| We will have been working | We will not have been working | Will we have been working? |
| They will have been working | They will not have been working | Will they have been working? |
| He will have been working | He will not have been working | Will he have been working? |
| She will have been working | She will not have been working | Will she have been working? |
| It will have been working | It will not have been working | Will it have been working? |
Exercises
Exercise 1. Complete the sentences using will have been+Ving.
Choose from the following:
work stand explain look try collect build teach learn pack
By the time my father retires, he ________ for the same company for 20 years.
By 3 o’clock we __________ our things for 4 hours.
By next year he ________postcards for 3 years.
By next weekend she _________ to solve her problems for 2 months.
By the time you visit me, I _________ for my keys.
By 7 o’clock my sister _________ me cooking for 6 hours.
By this summer the building _______ here for 10 years.
By the time I arrive, they _______ a country house.
By the time you get up, I _________ this material to her for half an hour.
By the end of this year, I _________ French for 8 months.
Exercise 2. Answer the following questions about yourself.
1. How long will you have been living in your town by the end of this year?
_______________________________________________
2. How long will you have been living in your flat by next summer?
_______________________________________________
3. How long will you have known your English teacher by the end of this year?
_______________________________________________
4. How long will you have driving a car by the end of next month?
_______________________________________________
5. How long will you have known your best friend by next year?
_______________________________________________
6. How long will you have been learning English by next year?
_______________________________________________
7. How long will you have been reading your favourite book by the end of this week?
_______________________________________________
8. How long will you have been attending your university by the end of the next month?
_______________________________________________
9. How long will your parents have been working by the end of the next year?
_______________________________________________
10. How long will you have been watching your favourite TV program by the end of this year?
_______________________________________________
Exercise 3. Put the verbs in brackets into the Future Perfect or the Future Perfect Continuous.
By next weekend, we__________ (move) to a new flat.
By the end of the week, Ann ______ (diet) for 3 weeks.
They ____________ (finish) their meeting by 4 o’clock this afternoon.
By 12 o’clock they __________ (dance) for 5 hours.
Jack _________ (tidy up) by the time we return home.
By tomorrow morning, he _______ (sleep) for 10 hours.
By the time she finishes work, her friend ________ (wait) for more than 2 hours.
His son _______ (buy) a new bike by the next summer.
By 5 o’clock Jane ________ (make) a cake for 5 hours.
I _________ (leave) the house by 7 o’clock tomorrow.
Exercise 4. Write 10 sentences about yourself. Use the Future Simple, the Future Continuous, the Future Perfect or the Future Perfect Continuous.
E.g.: I will go to England next year.
This time next Saturday I will be playing tennis.
By next week I will have finished my report.
By next month I will have been living in Moscow for 2 weeks.
_______________________________________________
_______________________________________________
_______________________________________________
_______________________________________________
_______________________________________________
_______________________________________________
_______________________________________________
_______________________________________________
_______________________________________________
_______________________________________________
Exercise 5. Translate the following sentences from Russian into English.
К концу следующего месяца будет уже 2 года, как мы живем в Москве.
К тому времени, как мы вернемся домой, она уже будет работать над статьей в течение нескольких часов.
К 7 часам Аманда будет за рулем в течение 5 долгих часов.
Когда их сын поступит в университет, они уже будут жить в этой стране 15 лет.
К тому времени, как Мария окончит институт, ее мама проработает в Лондоне 5 лет.
Я буду писать сочинение к тому времени, как моя сестра вернется домой.
К 2025 году Сэлли уже будет жить в Корее в течение 6 лет.
Алекс будет мыть машину до 7 вечера завтра.
Завтра будет 4 года, как мы живем вместе.
К концу следующего месяца будет уже полгода, как Марк путешествует.
REPORTED SPEECH
1. There are two main ways of reporting people’s words ideas thoughts beliefs: direct and indirect speech.
2. Direct speech is used to give exact words that were said by someone.
e.g. And then I thought “Well does he really mean it?”
3. Indirect speech is used to report someone’s words making them a part of a complex sentence.
e.g. So he said that he wanted to go home and just walked out.
The reporting verbs are: to say to think to tell, to ask, to answer, to explain, to wonder, to exclaim, etc.
In reported speech some grammatical changes take place: tenses, pronouns, etc.
e.g. (On Friday evening) John: I don’t like this party. I want to go home now.
(On Saturday morning) Bill: John said that he didn’t like the party and he wanted to go home right away.
4. When reporting a statement the original words become the subordinate clause introduced by the conjunction.
e.g. John said (that) he didn’t like the party.
Note: ‘that” is often dropped, esp. after to say, to think, etc. in informal speech.
“That” can’t be dropped after certain verbs: to reply, to telegraph, to shout, etc. and after nouns.
e.g. I replied that I didn’t want to go to the museum.
He shouted that he was very busy.
5. When reporting someone’s words, some lexical changes take place.
| Direct speech | Indirect speech |
| Next | the next the following |
| last Tuesday | the Tuesday before |
| Last | the … before |
| Today | that day |
| Tonight | that night |
| Yesterday | the day before |
| Tomorrow | the next/following day |
| …ago | … before |
| this… | that |
| These | those |
| Here | there |
| Now | Then, at that time, right away |
6. When reporting actions (orders, requests, offers, suggestions, advice, etc.) infinitives are used.
e.g. I promise to phone you every day. Don’t tell me what to do.
7. When reporting general questions (yes/no-questions), the conjunctions if/whether are used to introduce the clause.
e.g. I don’t know if/whether I can help you.
Я не знаю смогу ли я тебе помочь.
8. When reporting special questions (wh-questions), the question words become conjunctions.
e.g. Everybody wanted to know when the Royal family were arriving.
THE SEQUENCE OF TENSES
1. The sequence of tenses is a certain dependence of the verb in the subordinate clause on the tense of the verb in the principle clause. If it is in one of the past tenses the verb in the subordinate clause is used in one of the past tenses too.
e.g. Bill said that he didn’t like the party.
2. Usually, verbs in subordinate clauses are backshifted (shift one tense back).
a) If the action of the verb in the subordinate clause is simultaneous to the action of the verb in the principle clause, either Past Simple or Past Progressive is used.
e.g. Henry said he wanted to go home.
b) If the action of the verb in the subordinate clause is prior to the action of the verb in the principle clause, either Past Perfect or Past Perfect Progressive is used.
e.g. He said he had forgotten.
c) If the action of the verb in the subordinate clause follows the action of the verb in the principle clause, Future-in-the-Past (shall-should, will-would) is used.
e.g. He said he would phone me the next day.
3. You can use a present tense form in the subordinate clause if you feel that what is said is important in the present or is true in general.
e.g. The teacher asked if New York is (was) bigger than London.
4. The modal verbs could, might, should, ought and modal expressions had better and would rather stay the same in the sequence of tenses and indirect speech.
Exercises
Exercise 1. Imagine that yesterday you met your friend Ann. You hadn't seen her for ages. Ann said to you:
1. I'm living in Moscow.
2. I passed all the exams last month.
3. I am a student now.
4. My parents are very well.
5. I met Andrew at the party last week.
6. I want to buy a bicycle.
7. I'll tell Helen I met you.
8. I haven't seen for a long time.
9. I don't know where Alice is now.
10. I am going abroad next year.
Later that day you tell another friend Jane what Ann said. Use reported speech.
1. Ann said that she was living in Moscow.
2. She said that ___________________________________
_______________________________________________
_______________________________________________
_______________________________________________
_______________________________________________
_______________________________________________
_______________________________________________
_______________________________________________
_______________________________________________
Exercise 2. Complete the sentences with say or tell (in the correct form). Use only one word each time.
Ann said goodbye to me and left.
He _____ me that the cake was delicious.
«If I have a free time, I will help you», he ____.
«You never listen to me», Dave _____ me.
«I don’t think she would ______ a lie», _____ she.
Tom ____ to the class «I’m very happy with your results in the English exams.
He ______Dave that she had met Claire last week.
«To _____ you the truth, it makes me really happy», _____ Jim.
«I _______ good morning to you 2 times but you didn’t answer», _____ Stephen.
Sam ______ that it was a brilliant idea.
Exercise 3. Fill in the gaps with one of the following verbs in the Past Simple:
boast warn promise deny complain ask accuse order beg suggest
Mary ________ about being the best student in the group.
She _______ that her husband bought her flowers very seldom.
John ______ them not to go near the oven.
Helen ______ that she would come to my birthday.
Paul ______ his friend of stealing his wallet.
He ______ taking my money.
She ______ me to help her.
A tourist ______ a taxi-driver to stop.
A woman _______ to call the police.
My sister _______ going for a walk.
Exercise 4. Use any appropriate tense for the verbs in parentheses.
Tom _____ (say) he _______ (get) the results next week.
The teacher _______ (ask) the children if they ______ (be) ready.
Paul _________ (explain) that Tim ______ (be) there because he ______ (play) football the whole evening the whole evening yesterday.
She ______ (tell) her to wait for me her as she ______ (go) shopping.
He ______ (remark) that her friend ______ (have) a party last weekend.
Julie _______ (ask) one of the students what they ______ (do) in the future.
Peter _______ (complain) that he _______ (be) bored.
They ________ (say) they _______ (be) exhausted, explaining that they ________ (work) hard all day.
Ben _______ (ask) if she _______ (want) to go to the cinema with him.
Emma _______ (admit) that she ________ (be) disappointed if she ______ (fail) her entrance exams.
Exercise 5. Translate the following sentences from Russian into English.
Учитель сказал, что он доволен теперь мной.
Том поинтересовался, придет ли Джон к нему на день рождение.
Они не знали, где я жила раньше.
Мой друг поинтересовался, как долго я учу английский.
Она пожаловалась, что у нее болит нога.
Незнакомец спросил меня, говорю ли я по-английски.
Она вдруг вспомнила, что забыла кошелек дома.
Он сказал, что много путешествует.
Я поблагодарила своих родителей за то, что они сделали для меня.
Моя подруга сказала, что подождет меня завтра после занятий.
Reference list
1. Murphy, R. (2012), English Grammar in Use. 4th ed. Cambridge, 380 p.
2. Evans, V. (2011) Round-up 5. Longman, Pearson Education. 208 p.
3. Evans, V. (2011) Round-up 6. Longman, Pearson Education. 210 p.




 ost verbs: get gets
ost verbs: get gets sit sits
sit sits ost verbs: wait waiting
ost verbs: wait waiting ost verbs start started
ost verbs start started









