
Causes and consequences of natural disasters

LESSON OBJECTIVES
- Learn new words for discussing natural disasters, their causes and their consequences.
- Read the text and do multiple-choice and fill-in-the gap tasks.


What is a natural disaster?

SYNONYMS you should know
natural disaster (n) something that happens in nature and causes a lot of damage or kills a lot of people, for example a flood or an earthquake
catastrophe (n) an event that causes a lot of damage or makes a lot of people suffer
calamity (n) an event that causes serious damage, or causes a lot of people to suffer, for example a flood or fire
state of emergency (n) a situation in which a government takes action to deal with an event such as a flood or a fire that is putting a lot of people in danger
cataclysm (n) a sudden natural event that causes a lot of damage, for example a flood or an earthquake

What disasters of the natural world do you know ?

Words you should know
volcanic eruption - earthquake - sinkholes - heatwaves
(non) renewable resources - to prevent - climate change
pollutant - deforestation - ecosystem - hurricane
tornado - wildfire - flood - drought - tsunami
landslide - avalanche - blizzard - invasive species
to deplete - pollution - ecosystem - lightning – soil erosion

New Vocabulary

Katrina was initially labeled as the most destructive hurricane when it hit the Mississippi Gulf Coast and Louisiana in 2005.
Hurricane
a large, circular storm with strong winds

The most "extreme" tornado recorded is Tri-State Tornado, which spread through parts of Missouri, Illinois, and Indiana on March 18, 1925.
TORNADO
extremely strong winds concentrated in one area

The earth experiences 8 to 9 million lightning strikes every single day. When the lightning touches a building, tree, car, or person, we say they have been “struck” by lightning.
LIGHTNING
the occurrence of a natural electrical discharge of very short duration and high voltage between a cloud and the ground or within a cloud, accompanied by a bright flash and typically also thunder

During the 1997, Indonesian forest fires destroyed 97,000 km 2 of rainforest.
FOREST FIRE / Wildfire
a large, destructive fire that spreads over a forest or area of woodland

March 11, 2011, Japan's 8.9-magnitude earthquake is one of the strongest in history.
EARTHQUAKE
a sudden violent shaking of the ground, typically causing great destruction, as a result of movements within the earth's crust or volcanic action.

August 30, 2017, more than 1,200 people died across India, Bangladesh and Nepal as a result of flooding.
FLOOD
an overflow of a large amount of water beyond its normal limits, especially over what is normally dry land

In September 2018, Indonesia experienced many earthquakes, but the scale of the quake and tsunami which hit Palu took local people and scientists by surprise.
TSUNAMI
a long, high sea wave caused by an earthquake or other disturbance

DROUGHT
In the 150 years prior, Spain never witnessed such a long and intense drought as it suffered in 2014.
a prolonged period of abnormally low rainfall, leading to a shortage of water

More than 400 people in the Northeast died during the Great Blizzard, the worst death toll in United States history for a winter storm.
BLIZZARD
a large, circular storm with strong winds

May 31, 1970, in Peru, the earthquake triggered an avalanche that alone claimed the lives of almost 20,000 people, making it the deadliest avalanche in the recorded history of humankind.
AVALANCHE
a large, circular storm with strong winds

In December, 1999, in the highlands of Venezuela, excessive rainfall resulted in deadly mudslides which ravaged the country.
LANDSLIDE / MUDSLIDE
when soil, rocks, and/or mud falls down the side of a hill or mountain

Mt. Vesuvius, the active volcano that looms over the Bay of Naples in southern Italy, has erupted more than 50 times. Its most famous eruption took place in the year 79 A.D., when the volcano buried the ancient Roman city of Pompeii under a thick carpet of volcanic ash.
VOLCANIC ERUPTION
occurs when hot materials from the earth's interior are thrown out of a volcano

In 1859, an English farmer introduced just 24 grey rabbits to his plot of land in Australia to remind him of home. Within ten years the plague of them invaded the territory, and now rabbits impact on 304 species of Australian plant and animal.
Invasive species
species that are not native to a specific location, and that has a tendency to spread to a degree believed to cause damage to the environment, human economy or human health

Deforestation is a crucial problem in Amazonia. Since 1970, over 700,000 square kilometers of the rainforest have been destroyed. In 2012, it was approximately 5.4 million square kilometers, which is only 87% of the Amazon's original state.
Deforestation
the action of clearing a wide area of trees

Soil erosion
Almost 100 million people in south-west China will lose the land they live on within 35 years if soil erosion continues at its current rate.
displacement of the upper layer of soil, one form of soil degradation

In addition to air and water pollution, fracking also increases the potential for oil spills, which can harm the soil and surrounding vegetation. Fracking may cause earthquakes due to the high pressure used to extract oil and gas from rock and the storage of excess wastewater on site.
fracking
a method of getting oil or gas from the rock below the surface of the ground by making large cracks in it
Fracking is short for “hydraulic fracturing".

A giant sinkhole measuring about 650 feet long and up to 100 feet wide opened up on New Zealand’s north island.
sinkhole
a cavity in the ground, especially in a limestone formation, caused by water erosion and providing a route for surface water to disappear underground

The people of Nauru depleted all the minerals from the soil in Nauru, which led to erosion and landslides.
To deplete
use up the supply or resources

An ecosystem is a community made up of living organisms and nonliving components such as air, water, and mineral soil.
ecosystem
a biological community of interacting organisms and their physical environment

pollutant
Air pollution could be responsible for 3.2 million new cases of type 2 diabetes every year globally.
a substance that pollutes something, especially water or the atmosphere

An example is carbon-based, organically-derived fuel. The original organic material, with the aid of heat and pressure, becomes a fuel such as oil or gas.
(non) renewable resources
a resource that does not renew itself at a sufficient rate for sustainable economic extraction in meaningful human time-frames

reading: The end of life on Earth?
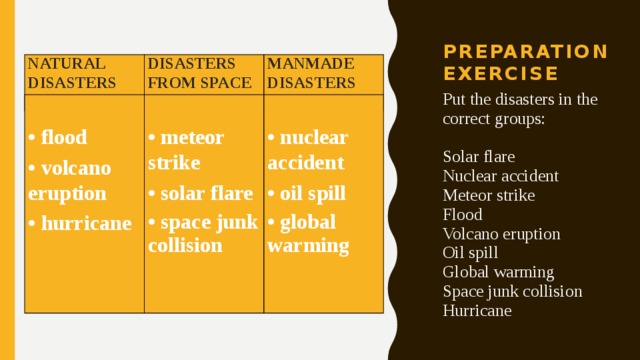
Preparation exercise
NATURAL DISASTERS
DISASTERS FROM SPACE
MANMADE DISASTERS
Put the disasters in the correct groups:
Solar flare
Nuclear accident
Meteor strike
Flood
Volcano eruption
Oil spill
Global warming
Space junk collision
Hurricane
• flood
• meteor strike
• volcano eruption
• hurricane
• solar flare
• nuclear accident
• space junk collision
• oil spill
• global warming

Reflection & reminder
- What do you think are the biggest problems in the natural world? Do you think humans have caused these problems or made them worse in any way? How?
- H/W – Learn new vocab & finish the reading tasks.
















































