
Прямая и косвенная речь Direct and Reported speech
подготовила учитель английского языка
МБОУ «СШ №32» г. Норильска
Мишина Ирина Васильевна

Прямая речь – это чьи-либо цитируемые, точные слова. Прямая речь заключается в кавычки
He said: " I can speak three foreign languages“.
Косвенная речь передает точное содержание чьего-либо высказывания, но не точные слова. В косвенной реки кавычки не используются. После глаголов (say, tell) используется или может быть опущено that
He said ( that) he could speak two foreign languages

Say или Tell
* SAY – при отсутствии личного дополнения
Jack said (that) he felt tired
* SAY+ to + дополнение, обозначающее адресата
Jack said to us (that) he felt tired.
* TELL + косвенное дополнение (кому)
Jack told us (that) he felt tired

Remember!!!

Высказывания в косвенной речи
В косвенной речи личные/притяжательные местоимения изменяются соответственно значению предложения.
Mary said, “ I ’ve lost my wallet.”
Mary said (that) she had lost her wallet.

- Если в главном предложении глагол употреблен в настоящем времени ( says, answers, asks ) в придаточном предложении глагол не изменяется :
She says : “I phone my friends every day”. She says that she phones her friends every day.

* Если же глагол в главном предложений употреблен в прошедшем времени ( said, asked, answered ) в придаточном предложении глагол употребляется обязательно в одном из прошедших времен. She said : “I phone my friends every day”. She said that she phoned her friends every day.

Если глагол в главном предложении стоит в Past Indefinite, Past Continuous или Past Perfect, то
Present Indefinite
Past Indefinite
Present Perfect
Past Perfect
Present Perfect Continuous
Past Perfect Continuous
Present Continuous
Past Continuous
Past Simple
Past Perfect
Past Continuous
Past Perfect Continuous
Future
Future in the Past
Past Perfect|Past Perfect Continuous
Past Perfect|Past Perfect Continuous

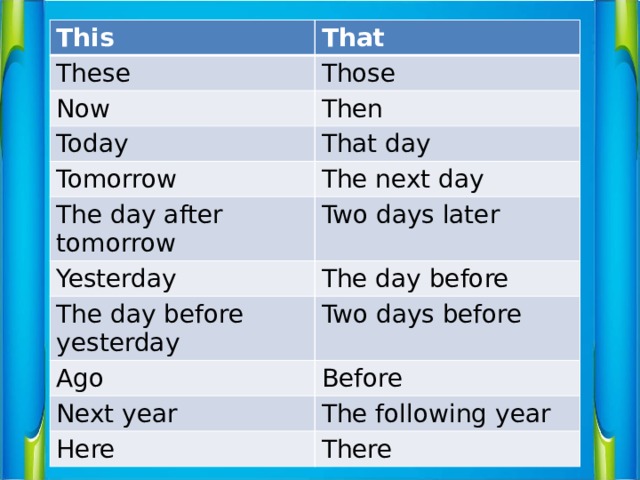
При переводе прямой и косвенной речи меняются так же слова, обозначающие место и время действия
- today – that day
- tonight – that night
- yesterday – the day before
- tomorrow – the next day
- (a week) ago – (a week) before
- last year – the year before
- next year – the following year
- this evening – that evening
- now – then
- this – that
- these – those
- here - there
This
That
These
Those
Now
Then
Today
That day
Tomorrow
The next day
The day after tomorrow
Two days later
Yesterday
The day before
The day before yesterday
Two days before
Ago
Before
Next year
The following year
Here
There

Модальные глаголы
в придаточном предложении так же изменяются
Shall - Should
Will - Would
Can - Could
May - Might
Must - Had to

Для передачи в косвенной речи вопросов чаще всего используются следующие глаголы:
asked, wanted to know, wondered
В косвенной речи вопросы имеют прямой порядок слов, а вопросительный знак в конце предложения заменяется на точку.
Краткий ответ на общий вопрос косвенной речи вводится союзом that без слов yes / no :
She answered, “Yes, I do.”
She answered that she did.

Общие вопросы вводятся союзами
if и whether :
● I asked, “Have you seen my pencil?” I asked him whether / if he had seen my pencil.
● Are you a good sportsman?
She asked me if I was a good sportsman.
● “ Do you like play football?”
She wanted to know if I liked play football.
● “ Will you come party?”
She wondered if I would come to the party.
● “ Have you met before?”
She asked if we had met before.

Для передачи в косвенной речи специальных вопросов союз if не используется, порядок слов в вопросе становится прямым
● How did you know about my birthday?
He wondered how I had known about his birthday.
● Why are you sad today?
He asked why my cousin was sad that day.

Повелительные предложения
Приказание: глагол say заменяется на tell (велеть) или order (приказать).
Просьба: глагол say заменяется на ask (просить).
Повелительное наклонение заменяется инфинитивом. Отрицательная форма повелительного наклонения заменяется инфинитивом с частицей not.
● Mom told me, “Clear your room.” Mom told me to clear my room.
● He said, “Don’t run in the corridor.” He said not to run in the corridor.

Report the sentences
1. He said, "I am drawing."
2. We said, "We are busy."
3. They said, “We know a better hotel."
4. She said, "I went to bed late."
5. He said, “She won’t ring me."
6. They said, "We have just married."
7. He said, “Mary will clean the dishes."
8. Tom said, "I did not say that."

































