
DIODS AND RESISTORS
Resistor Color Code

DIODE
A diode is an electronic component with two electrodes (connectors) that allows electricity to go through it in one direction and not the other direction.
Diodes turn alternating current into direct current.
Today, the most common diodes are made from semiconductor materials such as silicon or sometimes germanium.
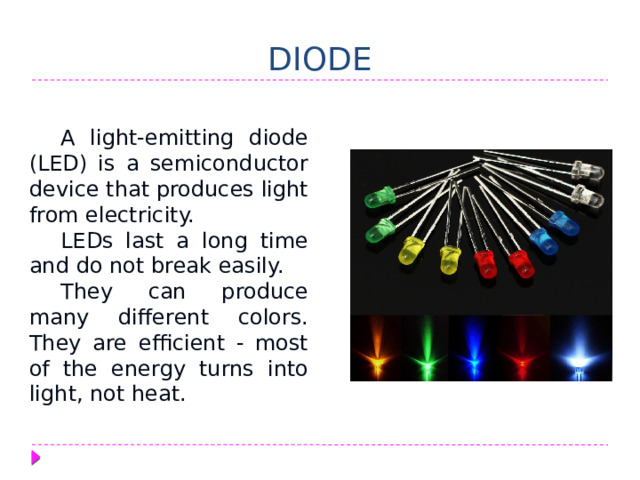
DIODE
A light-emitting diode (LED) is a semiconductor device that produces light from electricity.
LEDs last a long time and do not break easily.
They can produce many different colors. They are efficient - most of the energy turns into light, not heat.

DIODE
Sir John Ambrose Fleming (1849 - 1945)
English electrical engineer and physicist
The first types of diodes were called Fleming valves. They were vacuum tubes much like a light bulb. Inside the glass bulb there was a small metal wire and a large metal plate.
The metal wire would heat up and emit electricity, which was captured by the plate.

DIODE
The large metal plate was not heated, so electricity could go in one direction through the tube but not in the other direction.
Thomas Edison also discovered this property when working on his light bulbs.
Fleming valves are not used much anymore because they have been replaced by semiconductor diodes.
Thomas Alva Edison
(1847 –1931)
an American inventor

RESISTOR
A resistor is one of the most common elements of any circuit. It limits the electric current that flows through a circuit. The energy of the electrons passing through the resistor is changed to heat and/or light.

RESISTOR
Two resistors in serial circuit
Two resistors in parallel circuit
Series and parallel resistors can be linked in various combinations to help make a circuit.
Connecting two resistors in series results in a higher resistance, and connecting them in parallel makes a lower resistance.

RESISTOR COLOR CODE
Resistor’s values are rated by the colors that are painted on the resistor. The colored bands on the sides of a resistor are black, brown, red, orange, yellow, green, blue, violet, grey, and white.
Each color represents a different number. The black band represents the number 0, brown band represents the number 1, red is 2 and so on all the way to white which is the number 9. These numbers are very important in the electronic field.

RESISTOR COLOR CODE
The color-coding technique makes it easy to print on small components, such as resistors. This standard was formed in 1920 by the Radio Manufacturers Association. With these color bands, we can identify the resistive value and its percentage tolerance of a resistor.

RESISTOR COLOR CODE
This technique of “color coding” has 2 disadvantages. The first one is when it becomes difficult to distinguish between colors (for example “Red” and “Brown” ) when the component is overheated.
The second color blind people can not identify the device using color codes. But it can be easily do with a help of a multimeter.

4-Band Resistor Color Code Identification
Let us consider the resistor with the bands BROWN-BLACK-RED-GOLD.
Brown is ‘1’. Black represents ‘0’ and Red represents the multiplier ‘100’.
The value of the resistance is 10x100 = 1000 ohms or 1 kilo ohm.
Gold represents a tolerance of +/- 5%. Thus, the actual value of the 1 kilo ohm can be between 950 ohms and 1050 ohms.

5-Band Resistor Color Code Identification
Let us consider the resistor with the bands YELLOW-VIOLET-BLACK-BROWN-GREY.
Yellow is ‘4’, Violet ‘7’ and Black is ‘0’. Brown represents the multiplier ‘10’.
Thus the value of the resistance to the corresponding color code is 470x10 = 4700 ohms or 4.7-kilo ohm with the tolerance band being Grey which represents a tolerance of +/- 0.05%.

6-Band Resistor Color Code Identification
6 band resistor has 4 color bands on the left side and 2 color bands on the right side.
Here the first 3 color bands represent significant digits, the 4th one represents multiplier, the 5th one represents tolerance and the 6th one represents the temperature coefficient of the resistor.

6-Band Resistor Color Code Identification
470 X10 =4700 4700 ohms or 4.7-kilo ohm
The resistor has a value of 4.7 kilo ohms, with tolerance +/- 0.05% and with a temperature coefficient of 10 ppm/K (parts per million/Kelvin).

RESISTOR
Color coding is also used in other electronic components like inductors, capacitors, and others as well. Nowadays, with advances in printing technology, it is possible to print numeric values on small components as well, like the one you see on an SMD resistor (surface mount resistor) where the resistance values are printed using a three-digit code.

На корпусе 5 колец
RESISTOR
Here the first two digits indicate its resistance value and the third digit its multiplier. However, color coding still holds on to its popularity.
Online calculators are available to calculate color codes. When the color codes are put into the calculator, it will automatically calculate the value of the resistor, along with the tolerance.
https://www.chipdip.ru/calc/resistor

RESISTOR COLOR CODE
Black Big
Brown Boys
Red Race
Orange Our
Yellow Young
Green Girls
Blue But
Violet Violet
Grey Generally
White Wins
Since it is quite difficult to remember such a code, many mnemonics have been created to memorize the order of the colors.
Большие Мальчики Соревнуются С Нашими Юными Девочками, Но Виолетта Обычно Побеждает

1. Do diodes turn alternating current into direct current?
2. What can LEDs produce?
3. What is the difference between a diode and a resistor?
4. Which colors do the numbers 2 and 7 represent?
5. What disadvantages has Resistor Color Coding?
6. Are online calculators available to calculate color codes?

COUNT THE VALUE AND TOLERANCE OF THIS RESISTOR
The value of resistance is calculated as 50 × 10 2 ± 2 % = 5KΩ± 2%.

COUNT THE VALUE AND TOLERANCE OF THIS RESISTOR
The value of resistance is calculated as 260×1000± 0.05 = 260 KΩ ± 0.05%

COUNT THE VALUE, TOLERANCE AND A TEMPERATURE COEFFICIENT OF THIS RESISTOR
The resistance is calculated as 359 × 10 6 ± 5% 100 ppm/K = 359MΩ± 5% 100 ppm/K.

THANK YOU FOR YOUR WORK!







































