
Past Simple (простое прошедшее)

УПОТРЕБЛЕНИЕ PAST SIMPLE
- слова, указывающие на время действия:
yesterday (вчера),
two weeks ago (две недели назад),
the other day (на днях),
a long time ago (давно),
last month (в прошлом месяце),
in 2010 (в 2010 году),
on Monday (в понедельник)
Эти слова обязательно должны обозначать законченный период времени.
- когда рассказываем историю или перечисляем несколько событий, которые происходили одно за другим в прошлом.

Study this example:
Wolfgang Amadeus Mozart was an Austrian musician and composer. He lived from 1756 to 1791. He started composing at the age of 5 and wrote more than 600 pieces of music. He was only 35 years old when he died .
Lived, started, wrote, was, died – are all past simple.

Very often the past simple ends in -ed ( regular verbs):
We invited them to our party, but they decided not to come.
Laura passed her exam because she studied very hard.
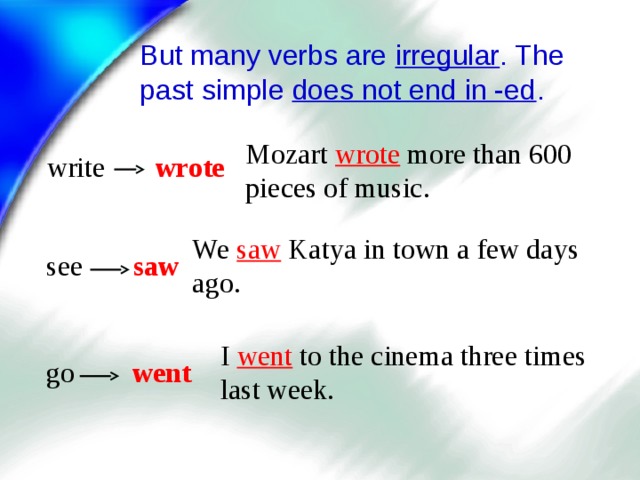
But many verbs are irregular . The past simple does not end in -ed .
Mozart wrote more than 600 pieces of music.
write wrote
We saw Katya in town a few days ago.
see saw
I went to the cinema three times last week.
go went

In questions and negatives we use did/didn't+ infinitive (enjoy/see/go etc.):
I
She
enjoy ed
I
She
you
Did
saw
They
didn’t
she
enjoy?
went
enjoy?
They
see?
see?
they
go?
go?
A: Did you go out last night?
B: Yes, I went to the cinema, but I didn't enjoy the film much.
They didn't invite us to the party, so we didn't go .
'Did you have time to do the shopping?' 'No, I didn't .'

In the following examples, do is the main verb in the sentence:
What did you do at the weekend?
( not What did you at the weekend?)
I didn't do anything. ( not I didn't anything)

The past of be is was/were :
I/he/she/it
Was
was/wasn't
we/you/they
I/he/she/it?
Were
were/weren't
we/you/they?
Note that we do not use did in negatives and questions with was/were :
I was angry because they were late.
Was the weather good when you were on holiday?
They weren't able to come because they were so busy.

Complete the sentences using the following verbs in the correct form:
buy fall hurt spend teach write cost
- Mozart wrote more than 600 pieces of music.
- 'How did you learn to drive?' 'My father ........... me.'
- Dave........down the stairs this morning and ........his leg.
- Ann ........a lot of money yesterday. She........... a dress which ……100 $.
taught
fell
hurt
spent
bought
cost

Complete the sentences. Put the verb into the correct form, positive or negative:
- It was warm, so I …….. off my coat. (take)
- The film wasn't very good. I ………….... it much. (enjoy)
- We were very tired, so we ............... the party early. (leave)
- The bed was very uncomfortable. I ........................ well. (sleep)
- The window was open and a bird.... .. .. . into the room. (fly)
- The hotel wasn't very expensive. It ... ... . ......... much. (cost)
- I was in a hurry, so I ... .... ... .. .... time to phone you. (have)
took
didn’t enjoy
left
didn’t sleep
flew
didn’t cost
didn’t have

Present Perfect (простое завершенное)

Study this example situation:
Tom is looking for his key. He can't find it. He has lost his key.
He has lost his key = He lost it recently , and he still doesn't have it.
Have/has lost is the present perfect :
I/we/they/you have
he/she/it has
finished
lost
done
been
The present perfect simple is have/has+ past participle . The past participle often ends in -ed ( finish ed /decid ed etc.), but many important verbs are irregular ( lost/done/written etc.).

- When we say that “something has happened”, this is usually new information :
Oh! I've cut my finger.
- When we use the present perfect, there is a connection with now . The action in the past has a result now :
“ Where's your key?”
“ I don't know. I've lost it.” (= I don't have it now)

You can use the present perfect with just, already and yet
“ Are you hungry?” “No, I've just had lunch.”
- We use already to say that something happened sooner than expected:
“ What time is Mark leaving?” “He's already left.”
- Yet shows that the speaker is expecting something to happen. Use yet only in questions and negative sentences:
I've written the e-mail, but I haven't sent it yet .

Complete B's sentences. Make sentences from the words in brackets.
A
B
I’ve just had lunch
1. No, thanks………………..
to eat?
(I / just / have / lunch)
2. Yes, ……………………..
2. Do you know where Julia is?
(I / just / see / her)
3. ....................................
3. What time is David leaving?
(he / already / leave)
4. What's in the newspaper
4. I don't know.
today?
………………………… ..
(I / not / read / it / yet)
I’ve just saw her
He has already left.
I have not read it yet.
































