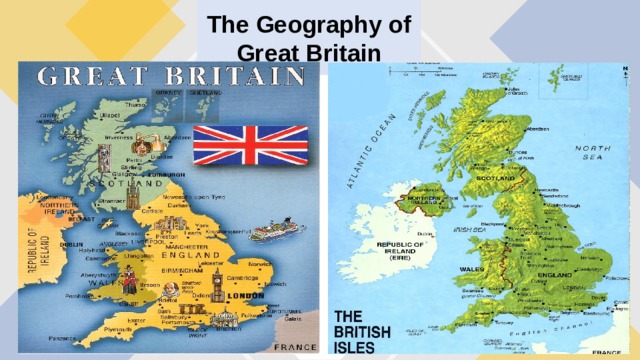
The Geography of Great Britain
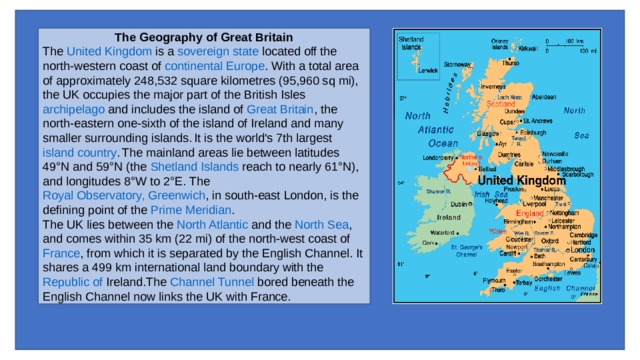
The Geography of Great Britain
The United Kingdom is a sovereign state located off the north-western coast of continental Europe . With a total area of approximately 248,532 square kilometres (95,960 sq mi), the UK occupies the major part of the British Isles archipelago and includes the island of Great Britain , the north-eastern one-sixth of the island of Ireland and many smaller surrounding islands. It is the world's 7th largest island country . The mainland areas lie between latitudes 49°N and 59°N (the Shetland Islands reach to nearly 61°N), and longitudes 8°W to 2°E. The Royal Observatory, Greenwich , in south-east London, is the defining point of the Prime Meridian .
The UK lies between the North Atlantic and the North Sea , and comes within 35 km (22 mi) of the north-west coast of France , from which it is separated by the English Channel . It shares a 499 km international land boundary with the Republic of Ireland .The Channel Tunnel bored beneath the English Channel now links the UK with France.

Nature
Great Britain is situated in the temperate zone of Europe. The nature of Great Britain is greatly affected by the sea: there is no place situated more than 100-120 km from the seashore, in the northern parts only 40-60 km.
The territory of Great Britain can be divided into three natural regions:
1) Scotland with highland and upland relief and coniferous and mixed forests;
2) Wales and mountainous England with upland considerably cut by ravines and valleys and covered with meadows, moorland and cultivated farmland, with patches of broadleaf forest;
3) South-east England with plain landscape, fertile soils, the predominance of cultivated farmland, with patches of broadleaf forest.

Coasts
The coastline of Great Britain is greatly indented, especially in the west and north-west where the mountains come close to the coast.
The coasts of Scotland, as well as the coasts of the Hebrides, the Orkney Islands and the Shetland Islands, are cut by numerous fiords.
In the south and east the land gradually slopes down towards the sea, and the coasts are sandy aid gentle, here and there interrupted by the ends of hill-ranges, which form low cliffs.

Climate
Great Britain enjoys the humid and mild marine West-Coast climate with warm winters and cool summers and a lot of rainfall throughout the year.
The prevailing winds blow from the south-west. As these winds blow from the ocean, they are mild in winter and cool in summer, and are heavily charged with moisture at all times. As they approach the mountainous areas near the west coasts, they rise up the mountain slopes. Their temperature drops, which causes condensation of moisture in the form of rain. Therefore the wettest parts of Britain are those areas where high mountains lie near the west coast: the western Highlands of Scotland, the Lake District and North Wales. The eastern part of Britain is said to be in the rain-shadow, as the winds lose most of their moisture in their passage over the highlands of the west.
All parts of the British Isles receive rain at any time of the year. Still autumn and winter are the wettest seasons, except in the Thames District, where most rain falls in the summer half of the year. Oxford, for example, has 29 per cent of its rain in summer and only 22 per cent in winter.
As to temperature, Great Britain has warmer winters than any other district in the same latitude. It is due in large measure to the prevalence of mild southwest winds. Another factor is the Gulf Stream1, which flows from the Gulf of Mexico and brings much warmth from the equatorial regions to north-western Europe.
![Area The total area of the United Kingdom according to the Office for National Statistics is 248,532 square kilometres (95,960 sq mi), comprising the island of Great Britain , the northeastern one-sixth of the island of Ireland (Northern Ireland) and many smaller islands. This makes it the 7th largest island country in the world. [2] England is the largest country of the United Kingdom , at 132,938 square kilometres (51,330 sq mi) accounting for just over half the total area of the UK. Scotland at 80,239 square kilometres (30,980 sq mi), is second largest, accounting for about a third of the area of the UK. Wales and Northern Ireland are much smaller, covering 21,225 and 14,130 square kilometres (8,200 and 5,460 sq mi) respectively. [5] The British Antarctic Territory , which covers an area of 1,709,400 km 2 is geographically the largest of the British Overseas Territories followed by the Falkland Islands which covers an area of 12,173 km 2 . The remaining twelve overseas territories cover an area 5,997 km 2 . Other countries with very similar land areas to the United Kingdom include Guinea (slightly larger), Uganda , Ghana and Romania (all slightly smaller). The UK is the world's 80th largest country by land area and the 10th largest in Europe (if European Russia is included).](https://fsd.multiurok.ru/html/2021/01/08/s_5ff8664eb8d93/img5.jpg)
Area
The total area of the United Kingdom according to the Office for National Statistics is 248,532 square kilometres (95,960 sq mi), comprising the island of Great Britain , the northeastern one-sixth of the island of Ireland (Northern Ireland) and many smaller islands. This makes it the 7th largest island country in the world. [2] England is the largest country of the United Kingdom , at 132,938 square kilometres (51,330 sq mi) accounting for just over half the total area of the UK. Scotland at 80,239 square kilometres (30,980 sq mi), is second largest, accounting for about a third of the area of the UK. Wales and Northern Ireland are much smaller, covering 21,225 and 14,130 square kilometres (8,200 and 5,460 sq mi) respectively. [5] The British Antarctic Territory , which covers an area of 1,709,400 km 2 is geographically the largest of the British Overseas Territories followed by the Falkland Islands which covers an area of 12,173 km 2 . The remaining twelve overseas territories cover an area 5,997 km 2 .
Other countries with very similar land areas to the United Kingdom include Guinea (slightly larger), Uganda , Ghana and Romania (all slightly smaller). The UK is the world's 80th largest country by land area and the 10th largest in Europe (if European Russia is included).
![Physical Geography The physical geography of the UK varies greatly. England consists of mostly lowland terrain, with upland or mountainous terrain only found north-west of the Tees-Exe line . The upland areas include the Lake District , the Pennines , North York Moors , Exmoor and Dartmoor . The lowland areas are typically traversed by ranges of low hills, frequently composed of chalk , and flat plains. Scotland is the most mountainous country in the UK and its physical geography is distinguished by the Highland Boundary Fault which traverses the Scottish mainland from Helensburgh to Stonehaven . The faultline separates the two distinctively different regions of the Highlands to the north and west, and the Lowlands to the south and east. The Highlands are predominantly mountainous, containing the majority of Scotland's mountainous landscape, while the Lowlands contain flatter land, especially across the Central Lowlands , with upland and mountainous terrain located at the Southern Uplands . Wales is mostly mountainous, though south Wales is less mountainous than north and mid Wales . Northern Ireland consists of mostly hilly landscape and its geography includes the Mourne Mountains as well as Lough Neagh , at 388 square kilometres (150 sq mi), the largest body of water in the UK. [12] The overall geomorphology of the UK was shaped by a combination of forces including tectonics and climate change , in particular glaciation in northern and western areas. The tallest mountain in the UK (and British Isles) is Ben Nevis , in the Grampian Mountains , Scotland. The longest river is the River Severn which flows from Wales into England. The largest lake by surface area is Lough Neagh in Northern Ireland, though Scotland's Loch Ness has the largest volume.](https://fsd.multiurok.ru/html/2021/01/08/s_5ff8664eb8d93/img6.jpg)
Physical Geography
The physical geography of the UK varies greatly. England consists of mostly lowland terrain, with upland or mountainous terrain only found north-west of the Tees-Exe line . The upland areas include the Lake District , the Pennines , North York Moors , Exmoor and Dartmoor . The lowland areas are typically traversed by ranges of low hills, frequently composed of chalk , and flat plains. Scotland is the most mountainous country in the UK and its physical geography is distinguished by the Highland Boundary Fault which traverses the Scottish mainland from Helensburgh to Stonehaven . The faultline separates the two distinctively different regions of the Highlands to the north and west, and the Lowlands to the south and east. The Highlands are predominantly mountainous, containing the majority of Scotland's mountainous landscape, while the Lowlands contain flatter land, especially across the Central Lowlands , with upland and mountainous terrain located at the Southern Uplands . Wales is mostly mountainous, though south Wales is less mountainous than north and mid Wales . Northern Ireland consists of mostly hilly landscape and its geography includes the Mourne Mountains as well as Lough Neagh , at 388 square kilometres (150 sq mi), the largest body of water in the UK. [12]
The overall geomorphology of the UK was shaped by a combination of forces including tectonics and climate change , in particular glaciation in northern and western areas.
The tallest mountain in the UK (and British Isles) is Ben Nevis , in the Grampian Mountains , Scotland. The longest river is the River Severn which flows from Wales into England. The largest lake by surface area is Lough Neagh in Northern Ireland, though Scotland's Loch Ness has the largest volume.
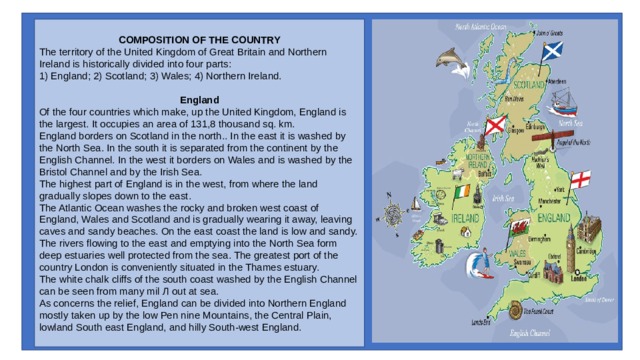
COMPOSITION OF THE COUNTRY
The territory of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland is historically divided into four parts:
1) England; 2) Scotland; 3) Wales; 4) Northern Ireland.
England
Of the four countries which make, up the United Kingdom, England is the largest. It occupies an area of 131,8 thousand sq. km.
England borders on Scotland in the north.. In the east it is washed by the North Sea. In the south it is separated from the continent by the English Channel. In the west it borders on Wales and is washed by the Bristol Channel and by the Irish Sea.
The highest part of England is in the west, from where the land gradually slopes down to the east.
The Atlantic Ocean washes the rocky and broken west coast of England, Wales and Scotland and is gradually wearing it away, leaving caves and sandy beaches. On the east coast the land is low and sandy.
The rivers flowing to the east and emptying into the North Sea form deep estuaries well protected from the sea. The greatest port of the country London is conveniently situated in the Thames estuary.
The white chalk cliffs of the south coast washed by the English Channel can be seen from many mil Л out at sea.
As concerns the relief, England can be divided into Northern England mostly taken up by the low Pen nine Mountains, the Central Plain, lowland South east England, and hilly South-west England.

Scotland
Scotland is the most northern of the countries that constitute the United Kingdom. It occupies an are! of 78,8 thousand sq. km.
Scotland is washed by the Atlantic Ocean in the north and west and by the North Sea in the east.
The coastline of Scotland is greatly indented. Ь many places deep fiords penetrate very far inland. I Geographically the territory of Scotland can be divided into three regions: the Northern Highlands! the Central Lowlands and the Southern Uplands.
The Highlands are the highest mountains in the British Isles.
Their average height does not exceed 157 m above sea level, though some peaks are much heftier, rising over a thousand meters. Ben Nevis, the highest peak in the British Isles, reaches the height of 1343 m.
The Lowlands are the cradle of the Scottish nation. They are densely populated.
The Southern Uplands seldom rise over 579 m above sea level.
It is one of the most sparsely populated districts in Great Britain.

Wales
Wales is a peninsula washed by the sea on three sides: the Bristol Channel in the south, the St. George's Channel in the west, and the Irish Sea in the north. Its territory is 20,8 thousand sq. km.
Geographically Wales may be considered part of highland Britain, the Cumbrian Mountains occupying most of the land. It is an area of high mountains, deep valleys, waterfalls and lakes.
Wales is a region of heavy rainfall brought by the prevailing west winds from the Atlantic Ocean. The valleys are sheltered by the high mountains from cold east winds. The climate is rather mild. Wales has never been densely populated. The Welsh have kept their own language, but English is spoken in town as well.

Northern Ireland
Northern Ireland occupies the north-eastern part of Ireland, which is separated from the island of Great! Britain by the North Channel. In the south-west Northern Ireland borders on the Irish Republic) (Eire).
Almost all the area of Northern Ireland is a plain of volcanic origin, deepening in the centre to form! the largest lake of the British Isles, Lough Neagh.
The greatly indented coastline of Northern Ireland is abundant in rocks and cliffs.
Northern Ireland has a typical oceanic climate with mild damp winters (the mean temperature in January is +4, +5) and cool rainy summers (the mean temperature in July is +14, +15).
Forests are rather scarce, moors and meadows prevail.
Northern Ireland is mostly an agrarian district. On small farms they grow crops, especially oats, vegetables and potatoes. Large areas are taken up by meadows, where cattle graze. On the river banks and n the coasts the population is engaged in fishing.
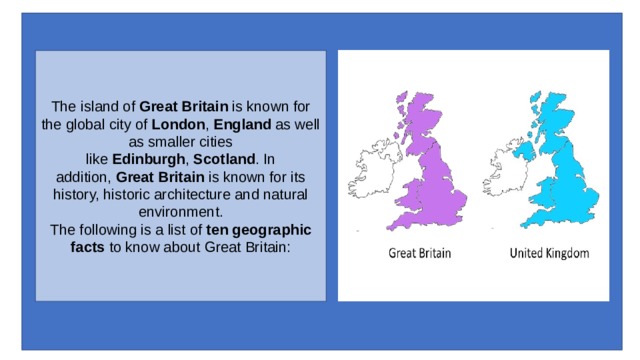
The island of Great Britain is known for the global city of London , England as well as smaller cities like Edinburgh , Scotland . In addition, Great Britain is known for its history, historic architecture and natural environment. The following is a list of ten geographic facts to know about Great Britain:
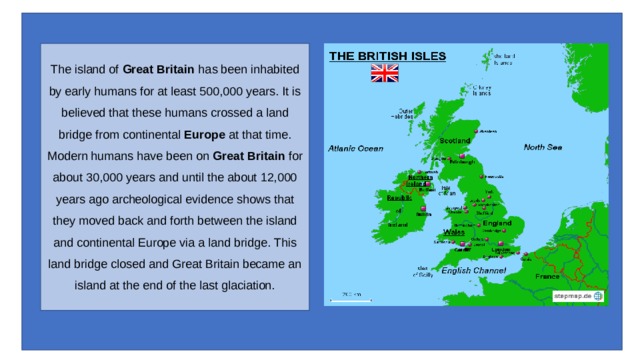
The island of Great Britain has been inhabited by early humans for at least 500,000 years. It is believed that these humans crossed a land bridge from continental Europe at that time. Modern humans have been on Great Britain for about 30,000 years and until the about 12,000 years ago archeological evidence shows that they moved back and forth between the island and continental Europe via a land bridge. This land bridge closed and Great Britain became an island at the end of the last glaciation.

Throughout its modern human history, Great Britain was invaded several times. For example in 55 B.C.E., the Romans invaded the region and it became a part of the Roman Empire . The island was also controlled by various tribes and was invaded several times. In 1066 the island was a part of the Norman Conquest and this began the cultural and political development of the area. Throughout the decades following the Norman Conquest, Great Britain was ruled by several different kings and queens and it was also a part of several different treaties between the countries on the island.

The use of the name Britain dates back to the time of Aristotle, however the term Great Britain was not officially used until 1474 when a marriage proposal between Edward IV of England's daughter, Cecily, and James IV of Scotland was written. Today the term is used to specifically refer to the largest island within the United Kingdom or to the unit of England, Scotland and Wales.
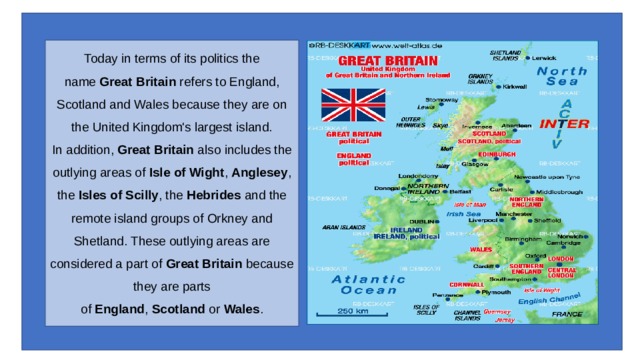
Today in terms of its politics the name Great Britain refers to England, Scotland and Wales because they are on the United Kingdom's largest island. In addition, Great Britain also includes the outlying areas of Isle of Wight , Anglesey , the Isles of Scilly , the Hebrides and the remote island groups of Orkney and Shetland. These outlying areas are considered a part of Great Britain because they are parts of England , Scotland or Wales .

Great Britain is located to the northwest of continental Europe and east of Ireland . The North Sea and the English Channel separate it from Europe, however the Channel Tunnel, the longest undersea
rail tunnel in the world,
connects it with continental Europe. The topography of Great Britain consists mainly of low gently rolling hills in the eastern and southern portions of the island and hills and low mountains in the western and northern regions.
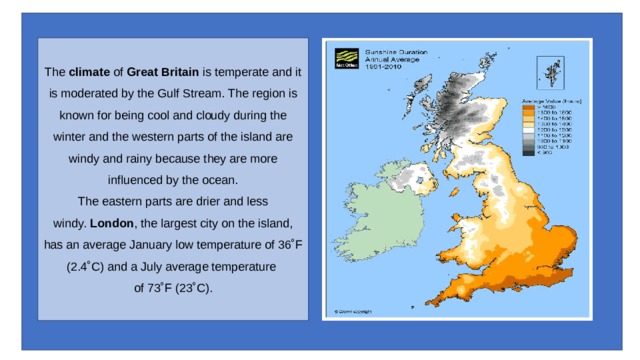
The climate of Great Britain is temperate and it is moderated by the Gulf Stream. The region is known for being cool and cloudy during the winter and the western parts of the island are windy and rainy because they are more influenced by the ocean. The eastern parts are drier and less windy. London , the largest city on the island, has an average January low temperature of 36˚F (2.4˚C) and a July average temperature
of 73˚F (23˚C).

Despite its large size the island of Great Britain has a small amount of fauna. This is because it has been rapidly industrialized in recent decades and this has caused habitat destruction across the island. As a result there are very few large mammal species in Great Britain and rodents like squirrels, mice and beaver make up 40% of the mammal species there. In terms of Great Britain's flora, there is a large variety of trees and 1,500 species of wildflower.
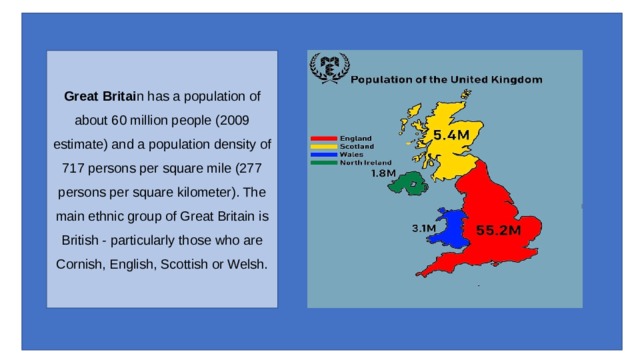
Great Britai n has a population of about 60 million people (2009 estimate) and a population density of 717 persons per square mile (277 persons per square kilometer). The main ethnic group of Great Britain is British - particularly those who are Cornish, English, Scottish or Welsh.
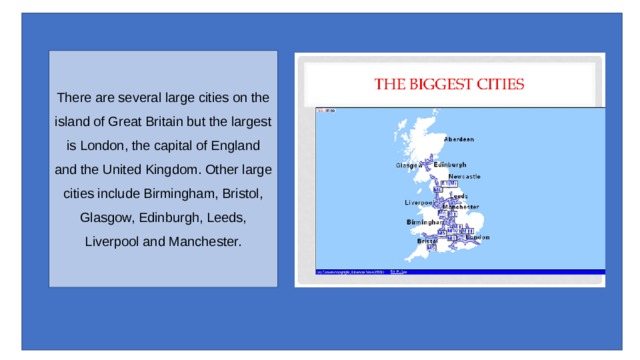
There are several large cities on the island of Great Britain but the largest is London, the capital of England and the United Kingdom. Other large cities include Birmingham, Bristol, Glasgow, Edinburgh, Leeds, Liverpool and Manchester.

Great Britain's United Kingdom has the third largest economy in Europe.

The majority of the UK 's and Great Britain 's economy is within the service and industrial sectors but there is also small amount of agriculture. The main industries are machine tools, electric power equipment, automation equipment, railroad equipment, shipbuilding, aircraft, motor vehicles, electronics and communications equipment, metals, chemicals, coal, petroleum, paper products, food processing, textiles and clothing. Agricultural products include are cereals, oilseed, potatoes, vegetables cattle, sheep, poultry and fish.












![Area The total area of the United Kingdom according to the Office for National Statistics is 248,532 square kilometres (95,960 sq mi), comprising the island of Great Britain , the northeastern one-sixth of the island of Ireland (Northern Ireland) and many smaller islands. This makes it the 7th largest island country in the world. [2] England is the largest country of the United Kingdom , at 132,938 square kilometres (51,330 sq mi) accounting for just over half the total area of the UK. Scotland at 80,239 square kilometres (30,980 sq mi), is second largest, accounting for about a third of the area of the UK. Wales and Northern Ireland are much smaller, covering 21,225 and 14,130 square kilometres (8,200 and 5,460 sq mi) respectively. [5] The British Antarctic Territory , which covers an area of 1,709,400 km 2 is geographically the largest of the British Overseas Territories followed by the Falkland Islands which covers an area of 12,173 km 2 . The remaining twelve overseas territories cover an area 5,997 km 2 . Other countries with very similar land areas to the United Kingdom include Guinea (slightly larger), Uganda , Ghana and Romania (all slightly smaller). The UK is the world's 80th largest country by land area and the 10th largest in Europe (if European Russia is included).](https://fsd.multiurok.ru/html/2021/01/08/s_5ff8664eb8d93/img5.jpg)
![Physical Geography The physical geography of the UK varies greatly. England consists of mostly lowland terrain, with upland or mountainous terrain only found north-west of the Tees-Exe line . The upland areas include the Lake District , the Pennines , North York Moors , Exmoor and Dartmoor . The lowland areas are typically traversed by ranges of low hills, frequently composed of chalk , and flat plains. Scotland is the most mountainous country in the UK and its physical geography is distinguished by the Highland Boundary Fault which traverses the Scottish mainland from Helensburgh to Stonehaven . The faultline separates the two distinctively different regions of the Highlands to the north and west, and the Lowlands to the south and east. The Highlands are predominantly mountainous, containing the majority of Scotland's mountainous landscape, while the Lowlands contain flatter land, especially across the Central Lowlands , with upland and mountainous terrain located at the Southern Uplands . Wales is mostly mountainous, though south Wales is less mountainous than north and mid Wales . Northern Ireland consists of mostly hilly landscape and its geography includes the Mourne Mountains as well as Lough Neagh , at 388 square kilometres (150 sq mi), the largest body of water in the UK. [12] The overall geomorphology of the UK was shaped by a combination of forces including tectonics and climate change , in particular glaciation in northern and western areas. The tallest mountain in the UK (and British Isles) is Ben Nevis , in the Grampian Mountains , Scotland. The longest river is the River Severn which flows from Wales into England. The largest lake by surface area is Lough Neagh in Northern Ireland, though Scotland's Loch Ness has the largest volume.](https://fsd.multiurok.ru/html/2021/01/08/s_5ff8664eb8d93/img6.jpg)






































