Reported Speech
Voronina M.V.

Прямая речь – это речь, переданная дословно, без изменений. На письме выделяется кавычками.
“ I am a student” she says.
Косвенная речь – это передача содержания прямой речи в форме пересказа.
She says that she is a student.

При переводе прямой речи в косвенную применяется согласование:
He says “ I am a student”. – He says that he is a student.
He said “I am very tired”. – He said that he was very tired.
He said “They will go to the theatre next week ”. – He said that they would go to the theatre the following week.

Согласование времён –
это зависимость времени глагола-сказуемого придаточного предложения от времени глагола-сказуемого главного предложения.
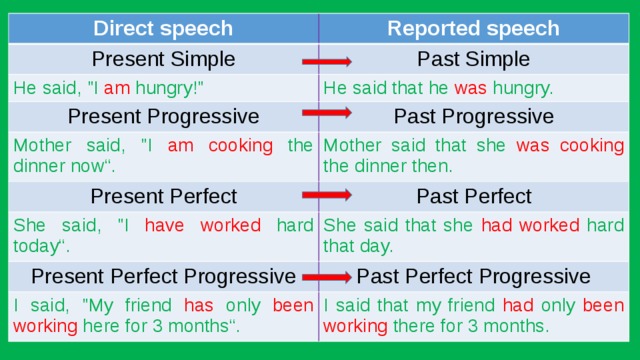
Direct speech
Reported speech
Present Simple
Past Simple
He said, "I am hungry!"
He said that he was hungry.
Present Progressive
Past Progressive
Mother said, "I am cooking the dinner now“.
Mother said that she was cooking the dinner then.
Present Perfect
Past Perfect
She said, "I have worked hard today“.
She said that she had worked hard that day.
Present Perfect Progressive
Past Perfect Progressive
I said, "My friend has only been working here for 3 months“.
I said that my friend had only been working there for 3 months.

NB! Past Simple может оставаться в косвенной речи без изменений (что характерно для разговорной речи и указано время свершения действия).
При употреблении временных обозначений , (the day before, two years before и т.д.) предпочтительнее использовать Past Perfect.
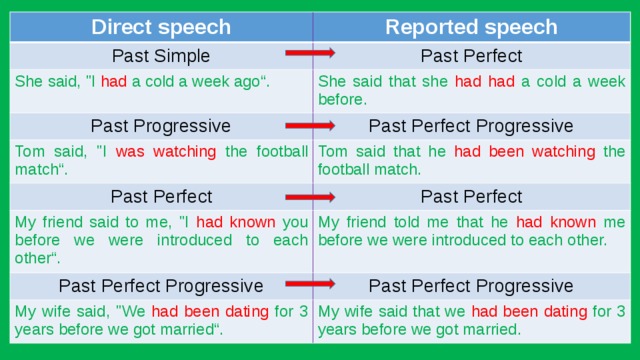
Direct speech
Reported speech
Past Simple
Past Perfect
She said, "I had a cold a week ago“.
She said that she had had a cold a week before.
Past Progressive
Past Perfect Progressive
Tom said, "I was watching the football match“.
Tom said that he had been watching the football match.
Past Perfect
Past Perfect
My friend said to me, "I had known you before we were introduced to each other“.
My friend told me that he had known me before we were introduced to each other.
Past Perfect Progressive
Past Perfect Progressive
My wife said, "We had been dating for 3 years before we got married“.
My wife said that we had been dating for 3 years before we got married.
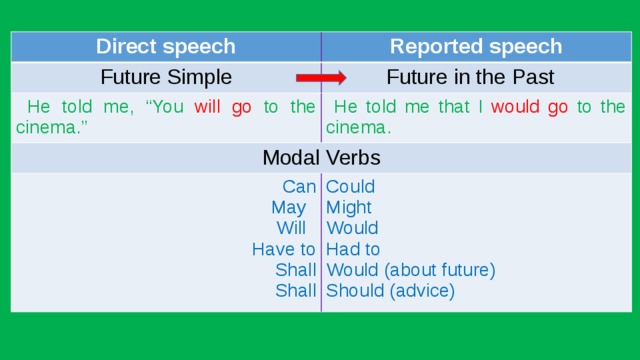
Direct speech
Future Simple
Reported speech
Future in the Past
He told me, “You will go to the cinema.”
He told me that I would go to the cinema.
Modal Verbs
Can
Could
May
Will
Might
Would
Have to
Shall
Had to
Would (about future)
Shall
Should (advice)
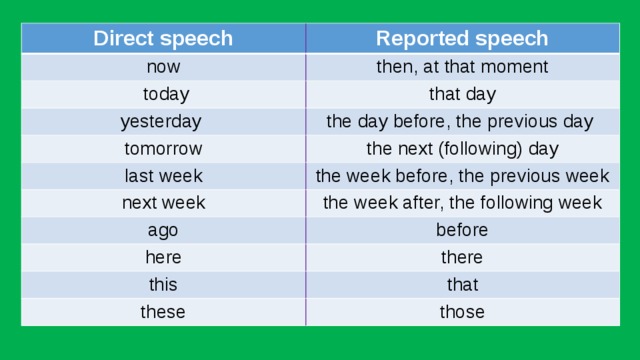
Direct speech
Reported speech
now
then, at that moment
today
that day
yesterday
the day before, the previous day
tomorrow
the next (following) day
last week
the week before, the previous week
next week
the week after, the following week
ago
before
here
there
this
that
these
those

Если в предложении, вводящем прямую речь, употреблен глагол to say без дополнения (указывающего лицо, к которому обращаются с речью), то глагол to say сохраняется . Если же такое дополнение есть , то глагол to say меняется на глагол to tell.
He said , "Our team lost the game“. – He said that their team had lost the game.
She said to me , "I will wait for you outside“. – She told me that she would wait for me outside.

Сообщение (statements)
Direct speech
Reported speech
Tom said, "I am very tired".
Tom said he was very tired.
He said, “I will fly to Moscow tomorrow“.
He said he would fly to Moscow the next day.
При переводе в косвенную речь знаки прямой речи (запятая и кавычки) отсутствуют и действует закон согласования.

Вопрос (Questions)
Direct speech
Reported speech
He asked me, "Do you know Helen?“
He asked me if I knew Helen.
She asked me, "Where are you from?“
She asked me where I was from.
В общем вопросе (без вопросительного слова) используется союз if или whether, прямой порядок слов и закон согласования.
В специальном вопросе – вопросительное слово остаётся, соблюдается прямой порядок слов и закон согласования.

Просьба или приказ (commands)
Direct speech
Reported speech
He said to me, "Wait for me here“.
He asked me to wait for him there .
Peter said to Tom, "Don't do it again".
Peter told Tom not to do it again".
При переводе в косвенную речь употребляется инфинитив (перед глаголом ставится частица to) и закон согласования не действует.

Check Yourself

Задание 1. Переведите предложения из прямой речи в косвенную.
Пример:
She said: “He is my friend” – She said that he was her friend.
- Tom remarked, “I didn’t expect him to be so young.”
- Jane said, “My Dad will be forty next year.”
- Mother answered, “My sons are playing in the yard.”
- Mike noted, “ I called him a few days ago.”
- Sam told me, “I read the books every day.”

Задание 2. Переведите вопросительные предложения из прямой речи в косвенную.
Пример: He said: “Do you know my sister?” – He asked me if I knew his sister.
1. She said: “When are you going to come?”
2. He said: “Who is your favourite actor?”
3. A man said: “Do you have a watch?”
4. My father said: “Where have you been?”
5. Helen said: “Will you be at home?”

Задание 3. Переведите предложения из прямой речи в косвенную.
Пример:
She said: “Open the window!” – She told me to open the window.
1. My mother said: “Put on your coat!”
2. My friend said: “Don’t come tonight.”
3. He said: “Don’t forget to send me an e-mail.”
4. Karrie said: “Call me later.”
5. She said: “Don’t shout at me!”


































