
Domestic garbage- Residential waste
Deforestation-The process of destroying a forest and replacing it with something else, especially by an agricultural system.
Air pollution- The contamination of the atmosphere by noxious gases and particulates
Acid rain - Rain mixed with acids formed by gases released into the atmosphere when fossil fuels are burned.

water pollution - pollution of the water in rivers and lakes
pollution - the introduction of contaminants into an environment that causes instability, disorder, harm or discomfort to the ecosystem
Pesticides- a chemical used to kill pests (as rodents or insects a chemical used to kill pests (as rodents or insects)
garbage- waste

nuclear waste- The radioactive products formed by fission and neutron transmutation of materials in a reactor
ozone hole- a region of the stratosphere over Antarctica (and a smaller one over the Arctic) that is depleted of ozone .
landfill- a location for the disposal of human waste be it domestic, commercial or industrial
oil spill- the release of a liquid petroleum hydrocarbon into the environment due to human activity


industrial waste- Wastes from any factory, transportation apparatus, from scientific research, dredging, sewage and scrap metal.
greenhouse effect- increase in temperature caused when incoming solar radiation is passed but outgoing thermal radiation is blocked by the atmosphere
hurricane- an intense, rotating oceanic weather system that possesses maximum sustained winds exceeding 119 km/hr (74 mph)
global warming- warming that results when solar radiation is trapped by the atmosphere
Environmental Pollution
There are three types of environmental pollution: air, ground, and water pollution.
Air pollution
Acid rain
Historically, air pollution comes from industries and transport. Factories, power stations and cars burn oil and coal. This rises into the air as different forms of sulphur and nitrogen. The sulphur and nitrogen combine with water in the air to make sulphuric or nitric acid. This falls to the ground as acid rain.
We burn large quantities of coal and oil, and this creates millions of tonnes of acid rain. The wind carries the rain long distances, and this creates problems. One country makes acid rain, and it falls to the ground in another country, for example, Canada gets a lot of acid rain from the USA, and Norway gets a lot of acid rain from Britain.
The greenhouse effect
Industrial countries also cause the greenhouse effect (also called “global warming” or “climate change”). Burning coal and oil produces carbon dioxide (CO2). The (CO2) increases in the Earth’s atmosphere, and retains heat from the sun (it works like the glass in a greenhouse- it lets heat in, but doesn’t let the heat out).
The Earth is getting hotter. Weather patterns are changing: some places have no water for years, and some places have floods. When a country has no water, the effects are very hard- in Chile in 1999, the result was electricity cuts around the country. There was no water for the hydro-electric power stations.
Ozone layer depletion
The ozone layer is a band of gas around the Earth. It protects us from dangerous ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun. It is vital to human and animal survival.
Unfortunately, we are producing chemicals which destroy the ozone layer. The damage starts in the Antarctic and spreads. Sheep in the Magallanes are becoming blind because the ozone layer is thinner. In Australia, a lot of people are getting skin cancer from the sun.
Pre-reading
Think of three environmental problems. Write:
the name of the problems
any information you have about the problems
Reading
Read the texts quickly. Which problems are described here? Is the writer worried or not worried about them?
Find these words in the text. Match them with their meanings.
a) pollution …. a factory which produces electricity
b) climate …. world’s weather patterns
c) power station …. energy from the sun
d) acid rain …. rising temperatures around the world
e) greenhouse effect …. rain containing chemicals which pollute the
environment.
f) radiation …. Something that makes the earth, air or water
dirty and dangerous.
Are the statements True or False?
….. The page is from a magazine
….. The text describes different types of air pollution
….. Canada sends acid rain to the USA
….. Global warming is also called climate change
….. Industrial countries cause the “greenhouse effect”
….. You can see the effects of ozone layer depletion in Chile
ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION QUIZ
Which of the following is NOT usually included in the three "R's" of recycling?
a. Reduce
b. Reuse
c. Recycle
d. Reclaim
2. Commercial whaling is outlawed around the world. True or False.
a. True
b. False
3. Which of the following endangered birds is the United States' national symbol?
a. Bald Eagle
b. California Condor
c. Northern Spotted Owl
4. Which of the following types of energy produces the least pollution?
a. Coal
b. Natural Gas
c. Oil
d. Wind
5. When is the concentration of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere expected to double from pre-industrial levels?
a. It already has doubled
b. Mid to late 21st century
c. The early 22nd century
d None of the above
6. By approximately how much did the world warm during the 20th century?
3 degrees Fahrenheite (ca 1.6 Celcius)
1 degrees Fahrenheit (ca 0.6 Celcius)
5 degrees Fahrenheite (ca 2.7 Celcius)
2.5 degrees Fahrenheit (ca 1.25 Celcius)
7. For the world as a whole, has precipitation increased, decreased, or stayed the same during the past century?
Increased
Decreased
Stayed the Same
Trick Question
8. Where do greenhouse gases trap energy?
In the atmosphere
In the mountains
In outer space
In the soil.
9. At what time in history did humans start to add lots of greenhouse gases to the atmosphere?
The little Ice Age
The Great Depression
The Industrial Revolution
The Jurassic Period
10. Which one of these is a greenhouse gas?
Oxygen
Platinum
Methane
Helium
11. Where is global warming expected to have the largest impact?
High latitudes like the Arctic
Mid latitudes like the Great Plains
Low latitudes like the Southwest
The Equator
12. Which continent is likely to be the most vulnerable to climate change?
North America
South America
Africa
Europe
13. Which of the following is not a significant source of methane?
Cattle
Landfills
Rice paddies
Nitrogen fertilizers
14. The elimination of a species from an island, local area, or region.
Extirpation
Extinction
Feral
All of the above
15. The movement of animals, fish and birds in search of food or shelter, often on an annual basis according to the seasons.
Alienation
Immigration
Migration
Vacation
16. A species officially recognized to be in immediate danger of extinction throughout all or a significant portion of its range.
Critical Species
Threatened Species
Enlightened Species
Endangered Species
17. The ozone layer functions to
protect the Earth from asteroids
make the sky blue
filter out ultraviolet radiation
prevent global warming
18. CFC is short for
cold fired crystals
chlorofluorocarbon
carbon free chlorine
clear freon containers
19. CFCs are harmful because they
destroy ozone
cause cancer
kill plants
melt ice caps
20. Which continent has an ozone hole over it?
Antarctica
Australia
Europe
North America
Environmental Protection Quiz Keys: 1d 2a 3a 4d 5b 6b 7ª
8a 9c 10c 11a 12c 13d 14a 15c 16d 17c 18b 19a 20ª
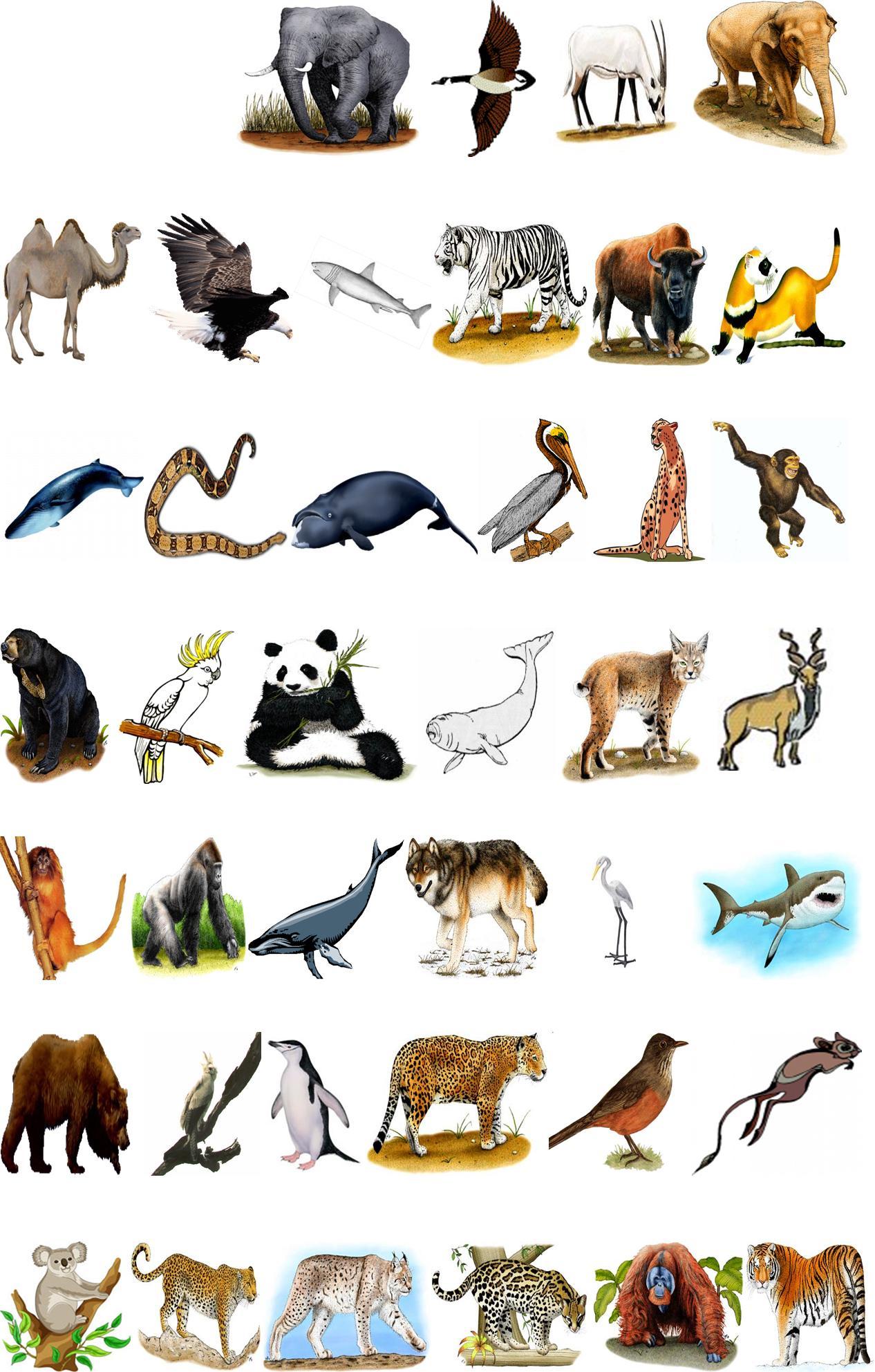




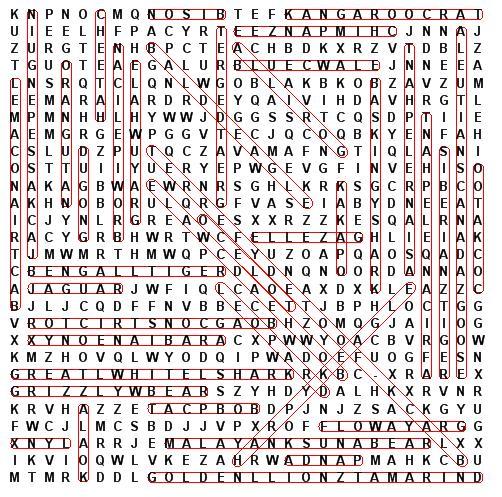
SIBERIAN TIGER
ORANGUTAN
OCELOT
LYNX
LEOPARD
KOALA
GOLDEN LION TAMARIND

Find 40 Endangered Animals. The words are hidden in the puzzle.
31. ______________
32. ______________
33. ______________
34. ______________
35. ______________
36. ______________
37. ______________
38. ______________
39. ______________
40. ______________
21. ______________
22. ______________
23. ______________
24. ______________
25. ______________
26. ______________
27. ______________
28. ______________
29. ______________
30. ______________
11. ______________
12. ______________
13. ______________
14. ______________
15. ______________
16. ______________
17. ______________
18. ______________
19. ______________
20. ______________
1. ______________
2. ______________
3. ______________
4. ______________
5. ______________
6. ______________
7. ______________
8. ______________
9. ______________
10. ______________
key:
Match the following pictures with its corresponding type of pollution.

 ( )
( )
 ( )
( )
 ( )
( )
( )
( 1 ) Soil Pollution
 ( )
( )

( )
( 2 ) Noise Pollution

( )

( )

( ) ( )
drought- temporary abnormalities determined by deficient precipitation
flood- A form of natural disaster when there is more water than the lakes, rivers, oceans, or ground can hold
exhaust fumes - gases ejected from an engine as waste products
endangered species- species whose numbers are so small that the species is at risk of extinction



















 ( )
( )












