Present tenses
Формы настоящего времени
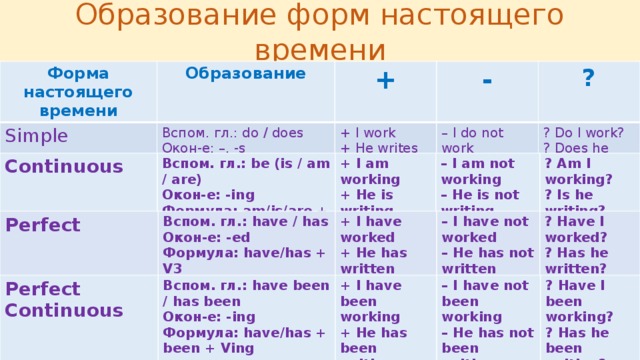
Образование форм настоящего времени
Форма настоящего времени
Образование
Simple
+
Вспом. гл.: do / does
+ I work
-
Окон-е: –, -s
+ He writes
– I do not work
Формула: V (+s)
?
? Do I work?
– He does not write
? Does he write?
Continuous
Вспом. гл.: be (is / am / are)
+ I am working
Окон-е: -ing
– I am not working
Формула: am/is/are + Ving
+ He is writing
? Am I working?
– He is not writing
? Is he writing?
Perfect
Вспом. гл.: have / has
+ I have worked
Окон-е: -ed
– I have not worked
Формула: have/has + V3
+ He has written
? Have I worked?
– He has not written
? Has he written?
Perfect Continuous
Вспом. гл.: have been / has been
+ I have been working
Окон-е: -ing
– I have not been working
Формула: have/has + been + Ving
+ He has been writing
? Have I been working?
– He has not been writing
? Has he been writing?

Применение форм настоящего времени
Форма настоящего времени
Применение
Present Simple
is used for facts and permanent states; general truths and laws of nature; habits and routines; timetables and programmes; feelings and emotions.
Present Continuous
is used for actions taking place at or around the moment of speaking; temporary situations; fixed arrangements in the near future; currently changing and developing situations; with adverbs such as always to express anger or irritation.
Present Perfect
is used for an action that happened in an unstated time in the past; an action that started in the past and continues up to the present, especially with stative verbs; a recently completed action; personal experiences or changes.
Present Perfect Continuous
is used to emphasize the duration of an action that started in the past and continues up to the present. (Present perfect continuous

Future tenses
Формы будущего времени

Образование форм будущего времени
Форма будущего времени
Образование
+
-
?
Simple
Вспом. гл.: will / shall
Формула: will/shall + V
+ I will work
– I won’t work
+ He will write
– He won’t write
? Will I work?
? Will he write?
Continuous
Вспом. гл.: will be / shall be
+ I will be working
Формула: will/shall + be + Ving
– I won’t be working
+ He will be writing
? Will I be working?
– He won’t be writing
? Will he be writing?
Perfect
Вспом. гл.: will have / shall have
+ I will have worked
Формула: will/shall + have V3
– I won’t have worked
+ He will have written
? Will I have worked?
– He won’t have written
? Will he have written?
Perfect Continuous
Вспом. гл.: will have been / shall have been
+ I will have been working
Формула: will/shall + have been + Ving
– I won’t have been working
+ He will have been writing
? Will I have been working?
– He won’t have been writing
? Will he have been writing?

Применение форм будущего времени
Форма будущего времени
Применение
Future Simple
is used for a single action in the future; an action that will take a certain period of time in the future; future course of action; recurring actions in the future; assumptions or thoughts about the future; the decision made at the moment of the conversation; promises, offers, threats, requests.
Future Continuous
is used for an action that will take place at a certain point in the future; the action, which, according to the speaker, will necessarily take place in the future; polite question about the plans of the interlocutor for the near future, especially when we need this person to do something for us;
Future Perfect
is used for a future action that will end until a certain point in the future; past the alleged action ("to be", "probably»).
Future Perfect Continuous
is used for a future long-term action that will begin before another future moment or action and will continue at that moment.

Past tenses
Формы прошедшего времени
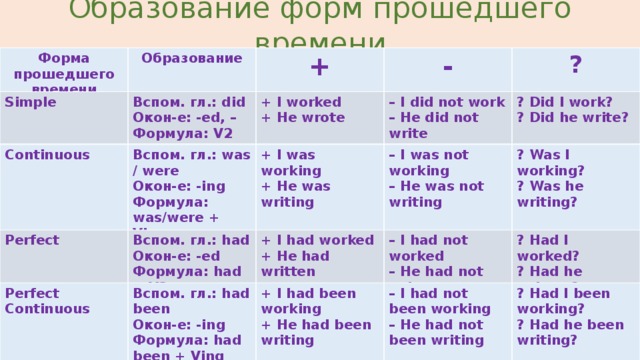
Образование форм прошедшего времени
Форма прошедшего времени
Образование
+
-
?
Simple
Вспом. гл.: did
Окон-е: -ed, –
+ I worked
– I did not work
+ He wrote
Формула: V2
– He did not write
? Did I work?
? Did he write?
Continuous
Вспом. гл.: was / were
Окон-е: -ing
+ I was working
Формула: was/were + Ving
+ He was writing
– I was not working
– He was not writing
? Was I working?
? Was he writing?
Perfect
Вспом. гл.: had
+ I had worked
Окон-е: -ed
– I had not worked
Формула: had + V3
+ He had written
? Had I worked?
– He had not written
? Had he written?
Perfect Continuous
Вспом. гл.: had been
+ I had been working
Окон-е: -ing
– I had not been working
Формула: had been + Ving
+ He had been writing
? Had I been working?
– He had not been writing
? Had he been writing?

Применение форм прошедшего времени
Форма прошедшего времени
Применение
Past Simple
is used for an action completed at a stated time in the past.
Past Continuous
is used for an action that was happening in the past and was interrupted by another action.
Past Perfect
is used for an action that happened in the past before another past action.
Past Perfect Continuous
is used to emphasise the duration of a past action that happened before another action.

Теоретическая справка
применения used to, be/get used to and/or would where possible.
"Used to" употребляется для описания действий, которые раньше происходили довольно часто, а сейчас не происходят вовсе. При переводе на русский язык часто добавляются слова "раньше", "прежде", и т.п.

Между be used to и get used to есть небольшая разница:
be used to используется для описания чего-то обычного, привычного, не кажущегося нам странным. Пример: I am used to waking up at 10 every day. – Я привык каждый день вставать в десять. (всегда вставал в это время, это для меня нормально) I am getting used to waking up at 10 every day. – Я постепенно привыкаю каждый день вставать в десять. (раньше так не делал, а теперь привыкаю и постепенно это становится нормальным) get used to / be getting used to используется для описания процесса привыкания к чему-то, что казалось странным, а теперь постепенно не кажется. get used to - это своего рода промежуточный этап на пути к be used to

Как и конструкция " used to " , глагол would может использоваться для выражения повторяющихся действий в прошлом.
В некоторых случаях would полностью аналогичен " used to " . Например: I used to go swimming twice a week. – I would go swimming twice a week. Я раньше ходил плавать два раза в неделю.

Однако в большинстве случаев, would , в отличие от " used to " , обозначает действия, происходившие время от времени, без противопоставления его настоящему моменту. При таком употреблении would используется с указателями времени, когда происходило действие. На русский язык would переводится со словами "бывало", "раньше".

Например:
When I was young, I would visit my grandmother every summer. В детстве я, бывало, навещал бабушку каждое лето.
Would не может использоваться для описания состояний, отдельных фактов или общих положений в прошлом, а только может употребляться для повторяющихся действий в прошлом.































